Amaranth grain vs. Oatmeal — Health Impact and Nutrition Comparison


Summary
Amaranth grain is high in magnesium, manganese, phosphorus, zinc, potassium, and vitamin E. On the other hand, oatmeal is high in calcium, iron, choline, vitamins B1, B2, B3, and folate. Moreover, amaranth grain has more protein, net carb, dietary fiber, and fat content. While amaranth grain contains less sodium, oatmeal has fewer calories.
Table of contents
Introduction
Oatmeal is a cereal, whereas amaranth grain is a pseudocereal.
Cooked oatmeal has a porridge-like consistency and is creamy and smooth. Its hue is often light beige or off-white. When cooked, oatmeal may have a shiny surface. However, this can vary depending on the type of oats used and any additional components.
The amaranth grain is small and has a spherical form. Cooked amaranth has a chewy texture akin to caviar or tapioca pearls. Its hue is often light tan or off-white, although certain types, such as red amaranth, can have deeper tints ranging from deep red to purple.
Taste and Use
Amaranth grain is generally nutty, earthy, and somewhat sweet in flavor. Some people compare it to the flavor of whole wheat or corn. It has a unique flavor that complements a variety of cuisines and components.
Oatmeal tastes mild and somewhat sweet. It is creamy and calming. The flavor will vary based on the type of oats used and the way of cooking. Steel-cut oats have a nuttier taste and a chewier texture, whereas rolled oats are milder and softer. You can use toppings or components such as fruits, nuts, or sweeteners to enhance the flavor of oatmeal.
Varieties
Groats (whole oats), steel-cut (cut into two or three pieces), and rolled (oat flakes) oats are the most frequent oat kinds.
Amaranth is a member of the Amaranthaceae family, which includes over 70 species of annual plants(1).
Nutrition
This part of the article compares the nutritional values of cooked amaranth grain and instant oatmeal.
Macronutrients and Calories
Amaranth grain is a little denser. Amaranth grain has 75% water, whereas oatmeal has 84%. Overall, amaranth grain is high in protein, fats, and carbs. In contrast, oatmeal provides fewer calories.
Macronutrient Comparison
Calories
Compared to oatmeal, amaranth grain has more calories per hundred grams. A hundred grams of amaranth grain provides 102 calories, whereas oatmeal has 68 calories.
A cup of cooked oatmeal weighs 234 grams and has 159 calories. A cup of amaranth grain is 246 grams and provides 251 calories.
Protein
Compared to oatmeal, amaranth grain has more protein. A hundred grams of amaranth grain contains 3.8g of protein. Oatmeal has 2.37g of protein per hundred grams.
Fats
A hundred grams of amaranth grain contains 1.58g of fat. Oatmeal has 1.36g of fat per hundred grams.
Fat Type Comparison
Carbohydrates
Amaranth grain is high in total carb, net carb, and dietary fiber content. A hundred grams of amaranth grain contains 18.69g of carbs, whereas oatmeal provides 11.67g.
Amaranth grain contains 16.59g of net carbs and 2.1g of dietary fiber. Oatmeal contains 9.97g of net carbs and 1.7g of dietary fiber.
The primary carb in oatmeal and amaranth grain is starch. However, amaranth grain has more starch compared to oatmeal. A hundred grams of amaranth grain provides 16.23g of starch, whereas oatmeal has 10.37g. Furthermore, oatmeal also contains small amounts of sucrose and galactose.
Carbohydrate type comparison
Vitamins
Amaranth grains have more vitamin E. Oatmeal, on the other hand, is high in vitamins B1, B2, B3, B6, and A. Furthermore, oatmeal contains twice as much folate.
Vitamin Comparison
Minerals
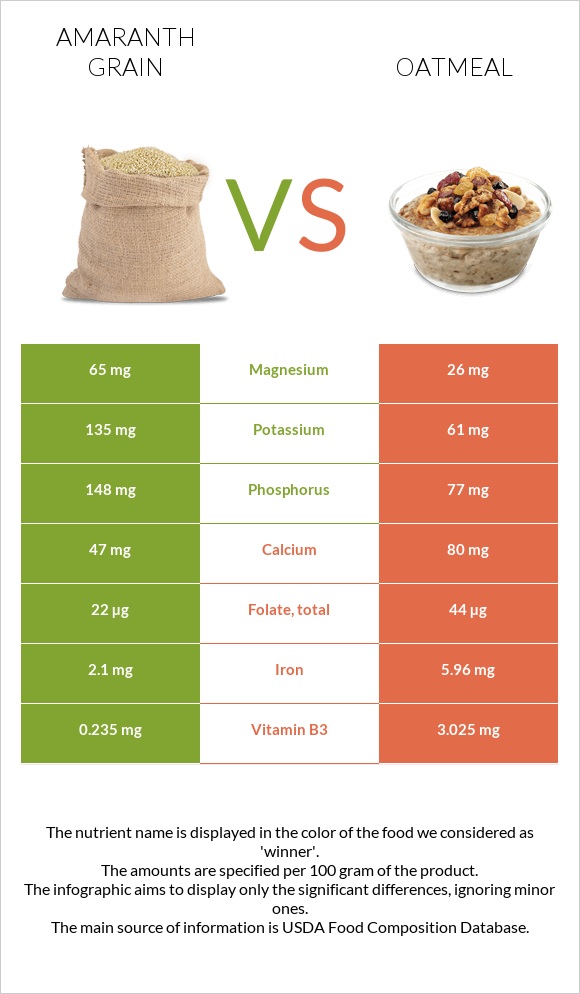
Amaranth grain contains over two times more phosphorus and potassium and 2.5 times more magnesium. Amaranth grain is also high in manganese. In contrast, oatmeal is high in calcium, iron, and choline.
Amaranth grain provides over eight times less sodium content. A hundred grams of amaranth grain contains 6mg sodium, whereas oatmeal 49mg.
Mineral Comparison
Glycemic Index
Although amaranth grain and oatmeal are high-GI foods, amaranth grain has a higher GI.
The glycemic index of amaranth grain is 97, whereas oatmeal has a glycemic index of 79.
Glycemic Load
Amaranth grain tends to have a higher glycemic load than oatmeal.
The glycemic load of amaranth grain is equal to 40. The glycemic load of oatmeal is 18.
The glycemic load of amaranth grain falls in the high category, whereas oatmeal falls in the medium category.
Acidity
The potential renal acid load (PRAL) is a way to determine the acidity of the food. The PRAL value of amaranth grain is 2.2, whereas oatmeal has the PRAL value of 1. Both are acid-forming.
Weight Loss & Diets
You may regularly use oats as an adjuvant treatment for metabolic diseases. According to the research, eating oats may decrease waist-to-hip ratio, body fat, BMI, and weight(2). Oatmeal is rich in beta-glucan, which has anti-obesity properties. Beta-glucan may also increase satiety and appetite(3).
According to the study, consumption of amaranth grain may decrease weight, body mass index (BMI), waist circumference (WC), hip circumference (HC), fat mass (FM), lean body mass (LBM), and visceral fat mass (VFM)(4).
Oatmeal and amaranth grain are plant-based and can be part of your vegan diet.
Amaranth grain and oatmeal are whole grains and can be part of the DASH diet.
As amaranth grain is a pseudocereal, it can be part of the paleo diet. In contrast, oatmeal is not paleo-friendly.
Due to their high carb content, amaranth grain and oatmeal are not keto-friendly.
Health Impact
Hepatoprotective Properties
Amaranth grain and oatmeal have hepatoprotective properties. Oatmeal consumption may lower liver profiles such as AST and ALT(2).
According to the study, the presence of flavonoids and phenolic compounds in the amaranth grain may lower levels of serum glutamate oxaloacetate transaminase (AST), serum glutamate pyruvate transaminase (ALT), serum alkaline phosphatase (SALP), and total bilirubin(5).
Anti-inflammatory Properties
Oatmeal contains some bioactive compounds, such as avenanthramides and saponins, which have anti-inflammatory properties(6).
Amaranth grain also has anti-inflammatory activities. Amaranth grain may inhibit the expression of pro-inflammatory cytokine genes(1).
Digestive Health
Oats are often not gluten-free when manufactured in a traditional manufacturing chain due to constant contamination with wheat, barley, or rye(7).
Overall, uncontaminated oats are naturally gluten-free. Oats without a gluten-free label are unsafe for celiac patients(8).
People with coeliac disease could ingest up to 100 g/d of uncontaminated oats(9).
Oat beta-glucans also can decrease colitis at the molecular and organ levels and accelerate Crohn’s disease (CD) remission(10).
Amaranth grain components, such as proteins and polysaccharides, may benefit the gut bacteria and the body's metabolism(11).
Antitumor Properties
According to the findings, Amaranthus species have an antiproliferative effect in Ehrlich’s ascites carcinoma (EAC) cells due to mitochondria-mediated apoptosis in EAC cells(12).
Oatmeal is a one-of-a-kind source of avenanthramides (AVAs), a polyphenolic alkaloid. AVA has antiproliferative, proapoptotic effects. It may also induce senescence and inhibit metastatization(13).
Anemia
Compared to amaranth grain, oatmeal contains over three times more iron. Iron deficiency is one of the most prevalent causes of anemia. Fatigue, hair loss, and restless legs are just some indications of iron deficiency(14).
Amaranth consumption may improve hemoglobin concentration and reduce the prevalence of anemia (15, 16).
Sources
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8871380/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/23371785/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/26273900/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32563253/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/18783728/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/34828872/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30029703/
- https://www.beyondceliac.org/gluten-free-diet/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/25267242/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8123447/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/36648179
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4888664/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6770293/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/28189173/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/22515252/
Infographic
Comparison summary table
 |
 |
||
| Lower in Glycemic Index |
|
||
| Lower in price |
|
||
| Rich in vitamins |
|
||
| Lower in Sugar |
|
||
| Lower in Sodium |
|
||
| Lower in Cholesterol |
|
||
| Lower in Saturated Fat |
|
||
| Rich in minerals |
|
All nutrients comparison - raw data values
| Nutrient |  |
 |
Opinion |
| Net carbs | 16.59g | 9.97g |
 |
| Protein | 3.8g | 2.37g |
 |
| Fats | 1.58g | 1.36g |
 |
| Carbs | 18.69g | 11.67g |
 |
| Calories | 102kcal | 68kcal |
 |
| Starch | 16.23g | 10.37g |
 |
| Sugar | 0.46g |
 |
|
| Fiber | 2.1g | 1.7g |
 |
| Calcium | 47mg | 80mg |
 |
| Iron | 2.1mg | 5.96mg |
 |
| Magnesium | 65mg | 26mg |
 |
| Phosphorus | 148mg | 77mg |
 |
| Potassium | 135mg | 61mg |
 |
| Sodium | 6mg | 49mg |
 |
| Zinc | 0.86mg | 0.62mg |
 |
| Copper | 0.149mg | 0.066mg |
 |
| Manganese | 0.854mg | 0.558mg |
 |
| Selenium | 5.5µg | 5µg |
 |
| Vitamin A | 433IU |
 |
|
| Vitamin A RAE | 130µg |
 |
|
| Vitamin E | 0.19mg | 0.07mg |
 |
| Vitamin B1 | 0.015mg | 0.26mg |
 |
| Vitamin B2 | 0.022mg | 0.215mg |
 |
| Vitamin B3 | 0.235mg | 3.025mg |
 |
| Vitamin B5 | 0.317mg |
 |
|
| Vitamin B6 | 0.113mg | 0.29mg |
 |
| Folate | 22µg | 44µg |
 |
| Vitamin K | 0.4µg |
 |
|
| Tryptophan | 0.04mg |
 |
|
| Threonine | 0.083mg |
 |
|
| Isoleucine | 0.105mg |
 |
|
| Leucine | 0.2mg |
 |
|
| Lysine | 0.135mg |
 |
|
| Methionine | 0.04mg |
 |
|
| Phenylalanine | 0.13mg |
 |
|
| Valine | 0.151mg |
 |
|
| Histidine | 0.057mg |
 |
|
| Trans Fat | 0.003g |
 |
|
| Saturated Fat | 0.226g |
 |
|
| Monounsaturated Fat | 0.391g |
 |
|
| Polyunsaturated fat | 0.426g |
 |
Which food is preferable for your diet?
 |
 |
|
| Low Fats diet |
|
|
| Low Carbs diet |
|
|
| Low Calories diet |
|
|
| Low Glycemic Index diet |
|
People also compare
Vitamins & Minerals Daily Need Coverage Score
Comparison summary
References
All the values for which the sources are not specified explicitly are taken from FDA’s Food Central. The exact link to the food presented on this page can be found below.
- Amaranth grain - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/170683/nutrients
- Oatmeal - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/171662/nutrients
All the Daily Values are presented for males aged 31-50, for 2000-calorie diets.





