Papaya vs. Guava — Health Impact and Nutrition Comparison


Summary
Guavas are higher in calories and fiber, while papayas are richer in calcium and vitamin A. Guavas provide nearly 4 times more vitamin C than papayas.
Table of contents
Introduction
You may have heard about guava and papaya, which are tropical fruits widely spread in non-tropical areas. This article discusses the main differences in nutritional profile and health impacts of these two fruits - guava (1) and papaya (2). You can check the daily coverages of some important nutrients they provide in the corresponding charts.
Actual differences
Papaya and guava grow at different points on the Earth: the first one is native to India, Indonesia, and Dominican Republic, while the second one is widespread in Central and South America and the Caribbean area. Papaya is larger than guava. Papaya is pear-shaped, while guava is smaller and oval in shape, often described as papaya without seeds. Papaya is green when unripe. Once it ripens, the skin changes its color to yellow or orange. Guava skin color changes from yellow to light green, and its flesh is usually white or pink. Papaya has a very soft, juicy, creamy texture: it tastes like melon and has a mildly sweet flavor. Guavas have a flowery and sweet flavor, which reminds of a mixture of strawberry, mango, and pear.
Macronutrients
Both papaya and guava are tropical fruits with many similarities, yet there are differences in how the macronutrients are distributed in each.
Calories
Papaya and guava are plant food products. Hence, these two are considered low-calorie foods. However, guava is higher in calories.
Carbs
Guava is higher in carbs compared to papaya.
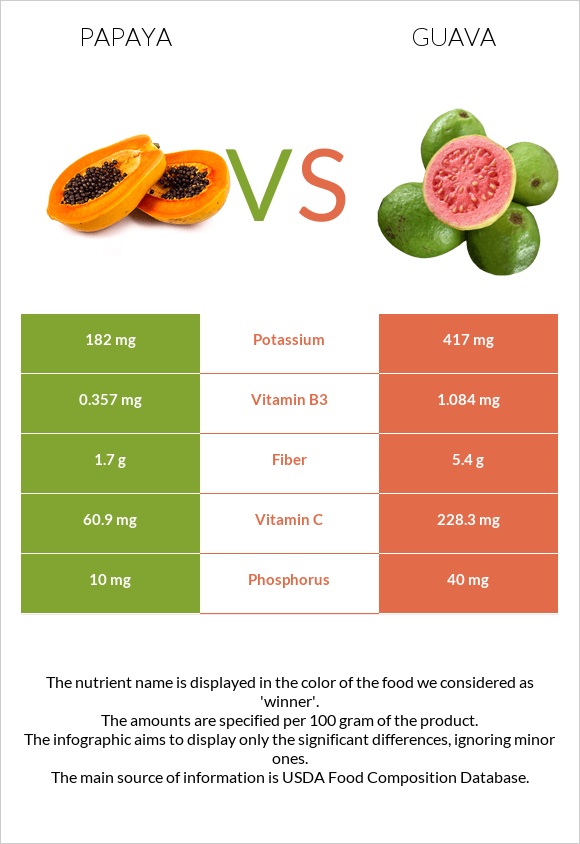
Guava provides 5.4g of dietary fiber per 100g, while the same amount of papaya contains only 1.7g.
Guava is rich in insoluble fiber.
Protein
These two fruits are supposed to contain little protein. Still, guava is higher in proteins than papaya.
Fats
Both fruits have less than 1g of fat per 100g, so we can neglect the fat amounts. Papaya and guava do not contain any amount of cholesterol.
Vitamins
Papaya and guava are rich in different vitamins.
Guavas are an excellent source of vitamin C: they are more than three times higher in vitamin C than papayas.
Papaya is richer in vitamin A.
Papaya covers 57% of the DV of vitamin A.
Vitamin Comparison
Minerals
Guava is higher in phosphorus, potassium, copper, and zinc.
Papaya is richer in calcium.
You can compare the mineral composition of these two fruits in the chart below.
Mineral Comparison
Health impact
Anticancer effects
Some test-tube and animal studies show that guava leaf extract and guava oil stop the growth of cancer cells (3) (4) (5). However, human studies are needed to confirm these results.
Papaya contains lycopene - a chemical that potentially reduces cancer risk (6). Papaya has shown a beneficial effect on breast cancer (7) and on those individuals who have been getting treatment for cancer (8).
Cardiovascular health
Lycopene and vitamin C in papayas may be helpful for preventing heart disease (9) (10).
Antioxidants and vitamins in guava leaves may be beneficial for preventing heart muscle cells from oxidative damage (11).
References
- https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/173044/nutrients
- https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/169926/nutrients
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/17571972/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/22280146/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/15979235/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/25526570/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/19468947/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/24769427/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/12566142/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/18472409/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/27296444/
Infographic
Macronutrient Comparison
Fat Type Comparison
Comparison summary table
 |
 |
||
| Lower in Sugar |
|
||
| Lower in Saturated Fat |
|
||
| Lower in price |
|
||
| Lower in Sodium |
|
||
| Lower in Glycemic Index |
|
||
| Rich in minerals |
|
||
| Rich in vitamins |
|
||
| Lower in Cholesterol | Equal | ||
All nutrients comparison - raw data values
| Nutrient |  |
 |
Opinion |
| Net carbs | 9.12g | 8.92g |
 |
| Protein | 0.47g | 2.55g |
 |
| Fats | 0.26g | 0.95g |
 |
| Carbs | 10.82g | 14.32g |
 |
| Calories | 43kcal | 68kcal |
 |
| Fructose | 3.73g |
 |
|
| Sugar | 7.82g | 8.92g |
 |
| Fiber | 1.7g | 5.4g |
 |
| Calcium | 20mg | 18mg |
 |
| Iron | 0.25mg | 0.26mg |
 |
| Magnesium | 21mg | 22mg |
 |
| Phosphorus | 10mg | 40mg |
 |
| Potassium | 182mg | 417mg |
 |
| Sodium | 8mg | 2mg |
 |
| Zinc | 0.08mg | 0.23mg |
 |
| Copper | 0.045mg | 0.23mg |
 |
| Manganese | 0.04mg | 0.15mg |
 |
| Selenium | 0.6µg | 0.6µg | |
| Vitamin A | 950IU | 624IU |
 |
| Vitamin A RAE | 47µg | 31µg |
 |
| Vitamin E | 0.3mg | 0.73mg |
 |
| Vitamin C | 60.9mg | 228.3mg |
 |
| Vitamin B1 | 0.023mg | 0.067mg |
 |
| Vitamin B2 | 0.027mg | 0.04mg |
 |
| Vitamin B3 | 0.357mg | 1.084mg |
 |
| Vitamin B5 | 0.191mg | 0.451mg |
 |
| Vitamin B6 | 0.038mg | 0.11mg |
 |
| Folate | 37µg | 49µg |
 |
| Vitamin K | 2.6µg | 2.6µg | |
| Tryptophan | 0.008mg | 0.022mg |
 |
| Threonine | 0.011mg | 0.096mg |
 |
| Isoleucine | 0.008mg | 0.093mg |
 |
| Leucine | 0.016mg | 0.171mg |
 |
| Lysine | 0.025mg | 0.072mg |
 |
| Methionine | 0.002mg | 0.016mg |
 |
| Phenylalanine | 0.009mg | 0.006mg |
 |
| Valine | 0.01mg | 0.087mg |
 |
| Histidine | 0.005mg | 0.022mg |
 |
| Saturated Fat | 0.081g | 0.272g |
 |
| Monounsaturated Fat | 0.072g | 0.087g |
 |
| Polyunsaturated fat | 0.058g | 0.401g |
 |
Which food is preferable for your diet?
 |
 |
|
| Low Fats diet |
|
|
| Low Carbs diet |
|
|
| Low Calories diet |
|
|
| Low Glycemic Index diet |
|
People also compare
Vitamins & Minerals Daily Need Coverage Score
Comparison summary
References
All the values for which the sources are not specified explicitly are taken from FDA’s Food Central. The exact link to the food presented on this page can be found below.
- Papaya - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/169926/nutrients
- Guava - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/173044/nutrients
All the Daily Values are presented for males aged 31-50, for 2000-calorie diets.