Sunflower oil vs. Canola oil — Health Impact and Nutrition Comparison


Summary
Sunflower oil is richer in polyunsaturated fats and vitamin E and has a higher smoke point. In comparison, canola oil is richer in monounsaturated fats, and vitamin K. Canola oil is lower in saturated fats. Canola oil is linked with increased risks of metabolic diseases compared to sunflower oil.
Table of contents
Introduction
Sunflower oil and canola oil are vegetable oils. Sunflower oil, as the name states, is derived from the sunflower plant seeds. In comparison, canola oil is derived from the rapeseeds of the canola plant.
They are refined oils used in everyday cooking with many applications.
Several differences exist between these two oils based on their general differences, nutritional compositions, and health impacts.
When comparing two types of oils, it is important to understand which type of information a consumer needs. It is important to know that both these oils are highly processed and refined. One of the most important aspects is the smoke point we will discuss.
General differences
Price
Canola oil is cheaper than sunflower oil, mainly because it is cheaper to produce.
Taste
Canola and sunflower oils are heavily processed and refined; due to that, they have a neutral taste.
Smoke point
One of the most important features of oils is their smoke point. It is important to know the smoke point of oils while cooking to prevent free radicals and carcinogenic compounds formation. It is important to stay within the smoke point of oils while cooking.
Canola oil has a smoke point of 204°C, whereas sunflower oil has a higher smoke point which is 232°C.
Nutritional content comparison
In this section, we will compare 100g of each oil.
Macronutrient Comparison
Calories
They have similar amounts of calories - 884 calories per 100g. These two oils are classified as foods high in calories.
Protein and carbs
They are devoid of proteins and carbs since they are refined and processed oils.
Fats
Their fat profile is important to take into consideration.
They are low in saturated fats compared to other types of oils.
They are 100% fat per weight; however, the distribution of the different types of fats matters.
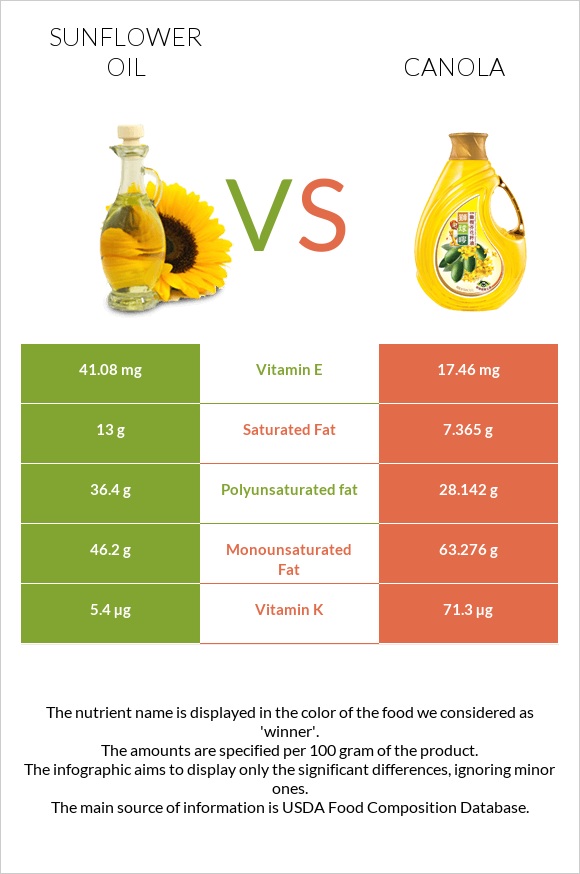
Over 85% of sunflower and canola oils’ fats are unsaturated, with sunflower oil being richer in polyunsaturated fats and canola oil being richer in monounsaturated fats. Sunflower oil is higher in saturated fatty acids.
Fat Type Comparison
Mineral
Their mineral profile is negligible.
Vitamins
The oils contain only fat-soluble vitamins E, and K. Sunflower oil is over 2 times higher in vitamin E, whereas canola oil is over 13 times higher in vitamin K.
1 tbsp of sunflower oil covers 37% of the recommended daily vitamin E intake.
Below we can visualize their vitamin diagrams.
Vitamin Comparison
Health impacts
Vitamin E
Sunflower oil is a good source of vitamin E and provides several positive health impacts (1).
Vitamin E has antioxidative, immune-supporting, and anticarcinogenic properties.
Vitamin E benefits coronary artery disease, cancer, cognitive decline, and eye disorders such as cataracts and age-related macular degeneration.
According to the NIH, excess vitamin E from food does not adversely affect health, whereas vitamin E supplements may cause bleeding, interact with statins and anticoagulants, and reduce chemotherapy effectiveness (2).
Further on, you can read about sunflower oil vs. peanut oil, which are rich in vitamin E. However, there have other differences that exist between them.
Cancer
On the one hand, canola oil may positively impact colon and breast cancer; on the other hand, it contains polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons, potentially increasing cancer risks (3, 4, 5, 6).
Raw sunflower oil may be protective against colorectal cancer, whereas heated sunflower oil may increase the risk of cancer due to the formed compounds (7, 8).
Metabolic Health
Canola oil increases the risks of obesity and metabolic diseases, including diabetes, although it does not contain any amount of carbs and has zero glycemic index (9).
In addition, canola oil, although low in saturated fats during high-temperature cooking, trans fats and other harmful chemicals are produced due to oxidation of the fats, and they are linked with increased cardiovascular disease (10).
Overall, both these oils are better than animal-based oils due to their higher amounts of unsaturated and lower saturated fats.
Taking into comparison both sunflower and canola oil, sunflower oil is richer in polyunsaturated fats, whereas canola oil is richer in monounsaturated fats. Making sunflower oil an even better option regarding metabolic diseases (11, 12).
Neurological Health
An animal study has shown that long-term canola oil consumption may negatively affect memory and synaptic integrity (normal functioning synaptic unit) (13).
Conversely, according to several animal studies, sunflower oil may beneficially affect the brain, whereas oxidized sunflower oil may be a risk factor for neurodegenerative disease (14, 15).
References
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3997530/
- https://ods.od.nih.gov/factsheets/VitaminE-HealthProfessional/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/24761850/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/23859037/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/17571951/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32162691/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/16216463/
- https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/abs/10.1080/01635588809513986
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6116055/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6116055/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/27578132/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/28635680/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5719422/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/33749789/
- https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/abs/10.1179/147683009X423391
Infographic
Mineral Comparison
Comparison summary table
 |
 |
||
| Lower in Saturated Fat |
|
||
| Lower in price |
|
||
| Lower in Sugar | Equal | ||
| Lower in Sodium | Equal | ||
| Lower in Cholesterol | Equal | ||
| Lower in Glycemic Index | Equal | ||
| Rich in minerals | Equal | ||
| Rich in vitamins | Equal | ||
All nutrients comparison - raw data values
| Nutrient |  |
 |
Opinion |
| Fats | 100g | 100g | |
| Calories | 884kcal | 884kcal | |
| Vitamin E | 41.08mg | 17.46mg |
 |
| Vitamin K | 5.4µg | 71.3µg |
 |
| Trans Fat | 0.395g |
 |
|
| Saturated Fat | 13g | 7.365g |
 |
| Monounsaturated Fat | 46.2g | 63.276g |
 |
| Polyunsaturated fat | 36.4g | 28.142g |
 |
| Omega-6 - Linoleic acid | 18.64g |
 |
|
| Omega-3 - ALA | 9.137g |
 |
Which food is preferable for your diet?
 |
 |
|
| Low Fats diet | Equal | |
| Low Carbs diet | Equal | |
| Low Calories diet | Equal | |
| Low Glycemic Index diet | Equal | |
People also compare
Vitamins & Minerals Daily Need Coverage Score
Comparison summary
References
All the values for which the sources are not specified explicitly are taken from FDA’s Food Central. The exact link to the food presented on this page can be found below.
- Sunflower oil - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/172328/nutrients
- Canola oil - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/172336/nutrients
All the Daily Values are presented for males aged 31-50, for 2000-calorie diets.




