Pumpkin seeds vs Walnuts - In-Depth Nutrition Comparison


Summary
Walnut contains more phosphorus, manganese, copper, Vitamin B6, Vitamin B1, and folate. It also has less sodium and a lower glycemic index.
On the other hand, pumpkin seed provides more zinc, fiber, magnesium, potassium, and fewer sugars and saturated fat.
Table of contents
Introduction
This article compares two widely used foods: walnut and pumpkin seeds.
What's The Actual Difference?
Walnuts belong to the genus Juglans. Walnuts are not actual botanical nuts but the edible seeds of a drupe. Pumpkin seed is the edible seed of a pumpkin or specific other squash cultivars.
They also differ in taste. Pumpkin seeds have a mild flavor, making them an excellent base for seasonings like those found in the recipes below, whereas walnuts are earthy and mild, but walnut skin might be slightly bitter.
Nutrition
At the bottom of this page, you can find nutrition infographics of pumpkin seeds and walnut.
Calories
Both are rich in calories; however, walnuts contain more calories than pumpkin seeds. It has 654 calories per 100 g, whereas pumpkin seeds have 446 calories per 100 g.
Minerals
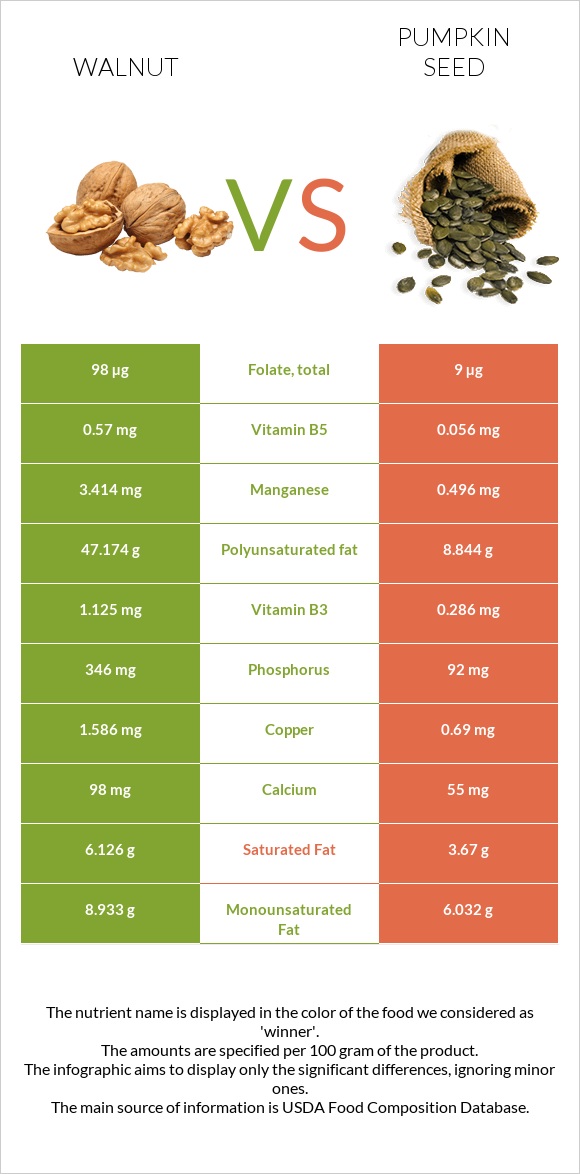
Walnut contains more calcium, copper, phosphorus, and sodium than pumpkin seeds.
On the other hand, pumpkin seeds have more iron, magnesium, potassium, and zinc than a walnut. They fall in the range of the top 10% of foods as a source of magnesium and the range of the top 7% of foods as a source of potassium.
Mineral Comparison
Vitamins
Walnut has a higher amount of vitamins than pumpkin seeds. It has 13 times more Vitamin B6, nine times more Vitamin B1, and three times more Vitamin C than pumpkin seeds.
Vitamin B5, Vitamin B3, Vitamin B2, and folate are also high in walnut.
Despite that, pumpkin seeds have more Vitamin A than walnuts.
Vitamin Comparison
Fats
Walnut contains three times more fats than pumpkin seeds. It has 65.21 of fat per 100g, while pumpkin seeds contain 19.4g of fat per 100g. In particular, pumpkin seeds have less saturated fats, but walnut has more mono- and polyunsaturated fats. Walnut falls in the range of the top 2% of foods as a source of fat.
Protein
Walnut contains more protein than pumpkin seeds. Walnut provides 18.55g, whereas pumpkin seeds have 15g of protein per 100g.
Cholesterol
Walnut and pumpkin seeds have no cholesterol.
Carbs
Pumpkin seeds have four times more carbohydrates than a walnut. They contain 53.75g of carbs per 100g, whereas pumpkin seeds provide 13.71g of carbs per 100g.
Walnut contains 6.7g of fiber and 7g of net carbs. Pumpkin seeds are also richer in fiber: 18.4g of fiber and 35.35g of net carbs. Walnut is considered low-carb food.
Glycemic Index
Walnut has a GI equal to 15, whereas the GI of pumpkin seeds is unknown: however, one study shows that adding pooled pumpkin seeds to mixed meals reduces postprandial glycemia [1].
Health Impact
Diabetes
Because of their unsaturated fat and fiber content, nuts are one of several foods that can help people with type 2 diabetes.
According to the study, consuming one tablespoon of walnut oil daily for three months resulted in an 8% decrease in fasting blood sugar in 100 people with type 2 diabetes [2].
Several studies have found that taking pumpkin juice or seed powder supplements reduced blood sugar levels in people with type 2 diabetes [3].
Cardiovascular Health
Pumpkin seeds are high in antioxidants, magnesium, zinc, and fatty acids, which may benefit your heart [4].
Animal studies have also revealed that pumpkin seed oil may lower blood pressure and cholesterol levels, which are important risk factors for heart disease [5].
According to research, eating nuts may be beneficial to those who have cardiovascular issues. Consuming walnuts has been shown in one study to help lower blood pressure in people with high blood pressure [6]. Another study found that walnuts can help lower LDL cholesterol, a significant risk factor for cardiovascular disease [7].
Cancer
Walnuts contain high levels of omega-3 fats and antioxidants, which help prevent several diseases, including cancer. Besides, walnuts are also high in 18-carbon α-linolenic acid, which may prevent or inhibit the growth of cancer cells [8].
According to a large observational study, eating pumpkin seeds was linked to a lower risk of breast cancer in postmenopausal women [9].
Other research suggests that the lignans in pumpkin seeds may play an essential role in preventing and treating breast cancer [10].
Gut Health
Eating walnuts can be beneficial to your gut microbiota and promote gut health. A daily intake of 43 grams of walnuts can increase beneficial bacteria, including those that produce butyric acid, a fatty acid that promotes gut health [11].
Brain Health
Walnuts contain amino acids and powerful antioxidants that have anti-inflammatory properties. According to several studies, including walnuts in your diet may improve cognitive function and lower your risk of developing mild cognitive impairment and Alzheimer's [12].
References
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30055778/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/28115966/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/16758316/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/15510909/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/10753555/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/21677123/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/24500935/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/25336096/
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0963996909000453
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/22591208/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29470389/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32093220/
Infographic
Macronutrient Comparison
Fat Type Comparison
Comparison summary table
 |
 |
||
| Lower in Sodium |
|
||
| Lower in Glycemic Index |
|
||
| Rich in vitamins |
|
||
| Lower in Sugar |
|
||
| Lower in Saturated Fat |
|
||
| Lower in price |
|
||
| Lower in Cholesterol | Equal | ||
| Rich in minerals | Equal | ||
All nutrients comparison - raw data values
| Nutrient |  |
 |
Opinion |
| Net carbs | 7.01g | 35.35g |
 |
| Protein | 15.23g | 18.55g |
 |
| Fats | 65.21g | 19.4g |
 |
| Carbs | 13.71g | 53.75g |
 |
| Calories | 654kcal | 446kcal |
 |
| Starch | 0.06g |
 |
|
| Fructose | 0.09g |
 |
|
| Sugar | 2.61g |
 |
|
| Fiber | 6.7g | 18.4g |
 |
| Calcium | 98mg | 55mg |
 |
| Iron | 2.91mg | 3.31mg |
 |
| Magnesium | 158mg | 262mg |
 |
| Phosphorus | 346mg | 92mg |
 |
| Potassium | 441mg | 919mg |
 |
| Sodium | 2mg | 18mg |
 |
| Zinc | 3.09mg | 10.3mg |
 |
| Copper | 1.586mg | 0.69mg |
 |
| Manganese | 3.414mg | 0.496mg |
 |
| Selenium | 4.9µg |
 |
|
| Vitamin A | 20IU | 62IU |
 |
| Vitamin A RAE | 1µg | 3µg |
 |
| Vitamin E | 0.7mg |
 |
|
| Vitamin C | 1.3mg | 0.3mg |
 |
| Vitamin B1 | 0.341mg | 0.034mg |
 |
| Vitamin B2 | 0.15mg | 0.052mg |
 |
| Vitamin B3 | 1.125mg | 0.286mg |
 |
| Vitamin B5 | 0.57mg | 0.056mg |
 |
| Vitamin B6 | 0.537mg | 0.037mg |
 |
| Folate | 98µg | 9µg |
 |
| Vitamin K | 2.7µg |
 |
|
| Tryptophan | 0.17mg | 0.326mg |
 |
| Threonine | 0.596mg | 0.683mg |
 |
| Isoleucine | 0.625mg | 0.956mg |
 |
| Leucine | 1.17mg | 1.572mg |
 |
| Lysine | 0.424mg | 1.386mg |
 |
| Methionine | 0.236mg | 0.417mg |
 |
| Phenylalanine | 0.711mg | 0.924mg |
 |
| Valine | 0.753mg | 1.491mg |
 |
| Histidine | 0.391mg | 0.515mg |
 |
| Saturated Fat | 6.126g | 3.67g |
 |
| Monounsaturated Fat | 8.933g | 6.032g |
 |
| Polyunsaturated fat | 47.174g | 8.844g |
 |
Which food is preferable for your diet?
 |
 |
|
| Low Fats diet |
|
|
| Low Carbs diet |
|
|
| Low Calories diet |
|
|
| Low Glycemic Index diet |
|
People also compare
Vitamins & Minerals Daily Need Coverage Score
Comparison summary
References
All the values for which the sources are not specified explicitly are taken from FDA’s Food Central. The exact link to the food presented on this page can be found below.
- Walnut - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/170187/nutrients
- Pumpkin seed - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/170188/nutrients
All the Daily Values are presented for males aged 31-50, for 2000-calorie diets.






