Braunschweiger vs. Turkey breast — In-Depth Nutrition Comparison
Compare
A recap on differences between Braunschweiger and Turkey breast
- Turkey breast has less Vitamin B12, Vitamin A RAE, Iron, Vitamin B2, Selenium, Vitamin B5, and Vitamin B3.
- Braunschweiger covers your daily Vitamin B12 needs 820% more than Turkey breast.
- Turkey breast contains 2110 times less Vitamin A RAE than Braunschweiger. Braunschweiger contains 4220µg of Vitamin A RAE, while Turkey breast contains 2µg.
- Turkey breast has less Sodium.
Food varieties used in this article are Braunschweiger (a liver sausage), pork and Turkey, all classes, breast, meat and skin, raw.
Infographic
Infographic link
Mineral Comparison
Mineral comparison score is based on the number of minerals by which one or the other food is richer. The "coverage" charts below show how much of the daily needs can be covered by 300 grams of the food.
Contains
more
Iron
+833.3%
Contains
more
Zinc
+79%
Contains
more
Copper
+224.3%
Contains
more
Manganese
+761.1%
Contains
more
Selenium
+158.9%
Contains
more
Calcium
+44.4%
Contains
more
Magnesium
+118.2%
Contains
more
Phosphorus
+10.7%
Contains
more
Potassium
+38.2%
Contains
less
Sodium
-94%
Contains
more
Iron
+833.3%
Contains
more
Zinc
+79%
Contains
more
Copper
+224.3%
Contains
more
Manganese
+761.1%
Contains
more
Selenium
+158.9%
Contains
more
Calcium
+44.4%
Contains
more
Magnesium
+118.2%
Contains
more
Phosphorus
+10.7%
Contains
more
Potassium
+38.2%
Contains
less
Sodium
-94%
Vitamin Comparison
Vitamin comparison score is based on the number of vitamins by which one or the other food is richer. The "coverage" charts below show how much of the daily needs can be covered by 300 grams of the food.
:
Contains
more
Vitamin A
+234083.3%
Contains
more
Vitamin B1
+329.3%
Contains
more
Vitamin B2
+1226.1%
Contains
more
Vitamin B3
+60.9%
Contains
more
Vitamin B5
+444.3%
Contains
more
Folate
+528.6%
Contains
more
Vitamin B12
+4683.3%
Contains
more
Vitamin B6
+45.5%
Contains
more
Vitamin A
+234083.3%
Contains
more
Vitamin B1
+329.3%
Contains
more
Vitamin B2
+1226.1%
Contains
more
Vitamin B3
+60.9%
Contains
more
Vitamin B5
+444.3%
Contains
more
Folate
+528.6%
Contains
more
Vitamin B12
+4683.3%
Contains
more
Vitamin B6
+45.5%
Macronutrient Comparison
Macronutrient breakdown side-by-side comparison
Contains
more
Fats
+306%
Contains
more
Carbs
+∞%
Contains
more
Other
+217.3%
Contains
more
Protein
+51%
Contains
more
Water
+38.4%
Protein:
14.5 g
Fats:
28.5 g
Carbs:
3.1 g
Water:
50.6 g
Other:
3.3 g
Protein:
21.89 g
Fats:
7.02 g
Carbs:
0 g
Water:
70.05 g
Other:
1.04 g
Contains
more
Fats
+306%
Contains
more
Carbs
+∞%
Contains
more
Other
+217.3%
Contains
more
Protein
+51%
Contains
more
Water
+38.4%
Fat Type Comparison
Fat type breakdown side-by-side comparison
Contains
more
Monounsaturated Fat
+378.6%
Contains
more
Polyunsaturated fat
+92.3%
Contains
less
Saturated Fat
-79.5%
Saturated Fat:
9.307 g
Monounsaturated Fat:
12.731 g
Polyunsaturated fat:
3.193 g
Saturated Fat:
1.91 g
Monounsaturated Fat:
2.66 g
Polyunsaturated fat:
1.66 g
Contains
more
Monounsaturated Fat
+378.6%
Contains
more
Polyunsaturated fat
+92.3%
Contains
less
Saturated Fat
-79.5%
Comparison summary table
Pay attention to the rightmost column. It displays the amounts side by side, giving a clearer understanding of the difference.
 |
 |
||
| Lower in Sugar |
|
||
| Lower in Sodium |
|
||
| Lower in Cholesterol |
|
||
| Lower in Saturated Fat |
|
||
| Lower in Glycemic Index |
|
||
| Rich in vitamins |
|
||
| Lower in price | Equal | ||
| Rich in minerals | Equal | ||
All nutrients comparison - raw data values
| Nutrient |  |
 |
Opinion |
| Net carbs | 3.1g | 0g |
 |
| Protein | 14.5g | 21.89g |
 |
| Fats | 28.5g | 7.02g |
 |
| Carbs | 3.1g | 0g |
 |
| Calories | 327kcal | 157kcal |
 |
| Calcium | 9mg | 13mg |
 |
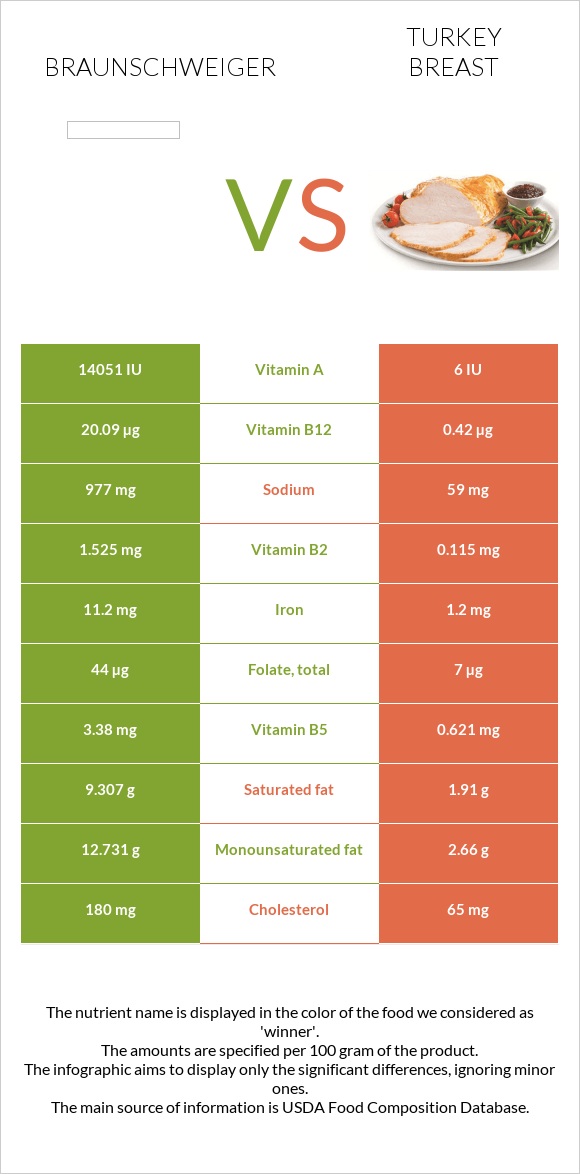
| Iron | 11.2mg | 1.2mg |
 |
| Magnesium | 11mg | 24mg |
 |
| Phosphorus | 168mg | 186mg |
 |
| Potassium | 199mg | 275mg |
 |
| Sodium | 977mg | 59mg |
 |
| Zinc | 2.81mg | 1.57mg |
 |
| Copper | 0.24mg | 0.074mg |
 |
| Manganese | 0.155mg | 0.018mg |
 |
| Selenium | 58µg | 22.4µg |
 |
| Vitamin A | 14051IU | 6IU |
 |
| Vitamin A RAE | 4220µg | 2µg |
 |
| Vitamin E | 0.35mg |
 |
|
| Vitamin D | 48IU |
 |
|
| Vitamin D | 1.2µg |
 |
|
| Vitamin B1 | 0.249mg | 0.058mg |
 |
| Vitamin B2 | 1.525mg | 0.115mg |
 |
| Vitamin B3 | 8.368mg | 5.2mg |
 |
| Vitamin B5 | 3.38mg | 0.621mg |
 |
| Vitamin B6 | 0.33mg | 0.48mg |
 |
| Folate | 44µg | 7µg |
 |
| Vitamin B12 | 20.09µg | 0.42µg |
 |
| Vitamin K | 1.6µg |
 |
|
| Tryptophan | 0.145mg | 0.242mg |
 |
| Threonine | 0.534mg | 0.957mg |
 |
| Isoleucine | 0.484mg | 1.099mg |
 |
| Leucine | 1.032mg | 1.704mg |
 |
| Lysine | 0.909mg | 1.996mg |
 |
| Methionine | 0.311mg | 0.616mg |
 |
| Phenylalanine | 0.553mg | 0.857mg |
 |
| Valine | 0.616mg | 1.141mg |
 |
| Histidine | 0.32mg | 0.66mg |
 |
| Cholesterol | 180mg | 65mg |
 |
| Saturated Fat | 9.307g | 1.91g |
 |
| Omega-3 - DHA | 0g | 0.01g |
 |
| Omega-3 - DPA | 0g | 0.01g |
 |
| Monounsaturated Fat | 12.731g | 2.66g |
 |
| Polyunsaturated fat | 3.193g | 1.66g |
 |
Which food is preferable for your diet?
is better in case of low diet
 |
 |
|
| Low Fats diet |
|
|
| Low Carbs diet |
|
|
| Low Calories diet |
|
|
| Low Glycemic Index diet |
|
People also compare
Vitamins & Minerals Daily Need Coverage Score
The summary scores indicate the extent to which this food can fulfill your daily vitamin and mineral requirements if you consume 3 servings, consisting of 100 grams of each (an approximation of 3 serving sizes).
Vitamins Daily Need Coverage Score
357%
29%
Minerals Daily Need Coverage Score
114%
37%
Comparison summary
Which food is lower in Sugar?
Turkey breast is lower in Sugar (difference - 0g)
Which food contains less Sodium?
Turkey breast contains less Sodium (difference - 918mg)
Which food is lower in Cholesterol?
Turkey breast is lower in Cholesterol (difference - 115mg)
Which food is lower in Saturated Fat?
Turkey breast is lower in Saturated Fat (difference - 7.397g)
Which food is lower in glycemic index?
Braunschweiger is lower in glycemic index (difference - 0)
Which food is richer in vitamins?
Braunschweiger is relatively richer in vitamins
Which food is cheaper?
?
The foods are relatively equal in price ($)
Which food is richer in minerals?
?
It cannot be stated which food is richer in vitamins. See the charts below for detailed information. See the charts below for detailed information. See the charts below for detailed information.





