Chicken breast vs. Ground chicken — Which One Is Healthier?


Summary
Chicken breast is higher in choline, phosphorus, magnesium, selenium, calcium, manganese, protein, carbs, and vitamins A, E, K, B3, B6, and folate. On the other hand, ground chicken has more potassium, zinc, copper, fats, and vitamins B1, B2, B5, and B12. In addition, chicken breast has less cholesterol, calories, and saturated fats, whereas ground chicken has less sodium content.
Table of contents
Introduction
The chicken breast is a lean meat obtained from the chicken's pectoral muscle. Ground chicken is made from chicken components such as thigh meat, breast meat, or a mixture of the two.
One complete chicken has two parts, or chicken breasts, which are usually divided and sold as separate breasts.
First, you should select the chicken portions and take off any bones. Next, use a food processor or meat grinder to grind the meat.
While chicken breast and ground chicken are derived from the same source, their variances in texture, fat content, and preparation methods distinguish them as distinct in their own right, catering to various culinary demands and tastes.
Appearance, Taste, and Use
Chicken breast has a firm and smooth feel, but ground chicken has a grainy and loose texture. Chicken breast has a mild, subtle flavor, whereas ground chicken is juicier and more flavorful. The color of chicken breast is pale, whereas ground chicken is pale pink.
Chicken breast and ground chicken can be used in many different ways when cooking. How you cook them and your seasonings can significantly affect their taste.
You can use chicken breast in a cooked, grilled, or roasted. In contrast, you can use ground chicken in various dishes such as meatballs, burgers, casseroles, and stir-fries. Ground chicken is ideal for blending with other ingredients, shaping into patties, or integrating into sauces.
Cooking Time
The cooking time for ground chicken and chicken breast can change depending on some factors.
Depending on their thickness, boneless, skinless chicken breasts are usually best cooked for 20 to 30 minutes at 375°F (190°C). Thinner cuts will cook more quickly, while thicker ones can take longer.
Depending on the recipe and the size of the pieces, ground chicken is usually cooked for 15 to 20 minutes in an oven or skillet when used in dishes like meatballs, burgers, or casseroles.
Nutrition
In this part of the article, we will compare the nutritional values of chicken breast and ground chicken, concentrating on differences.
Macronutrients and Calories
Chicken breast and ground chicken have similar nutritional densities, the breast being a little denser. Breast contains 60% water, whereas ground chicken contains 65% water.
Macronutrient Comparison
Calories
Chicken breast and ground chicken have similar calorie counts, with ground chicken containing only two more calories in a 100g serving. The breast has 187 calories, whereas ground chicken provides 189 calories. Serving sizes for breast and ground chicken are 0.5 breast (bone and skin removed) and 3oz (crumbled). One serving of breast has 161 kcal and weighs 86g. The weight of one serving of ground chicken is 85g, which provides 161 kcal.
Protein
Chicken breast and ground chicken are good sources of protein.
The breast has a higher protein content than ground chicken. In a 100g serving, chicken breast has 33.44 grams of protein, whereas ground chicken contains 23.28g.
Fats
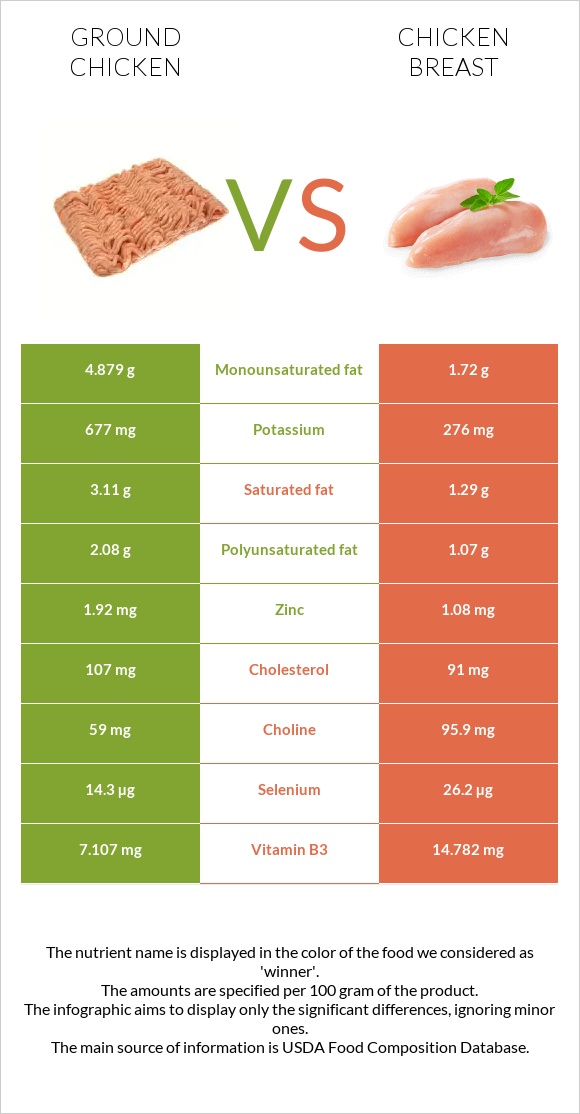
A hundred grams of ground chicken provides 10.92 grams of fat, whereas the breast has 4.71 grams. Ground chicken has over 2.8 times more monounsaturated fat and 1.9 times more polyunsaturated fat.
In comparison, chicken breast provides over 2.5 times less saturated fat. In a 100g serving, chicken breast and ground chicken have 1.29g and 3.11g of saturated fat, respectively. Chicken breast has 1.72g of monounsaturated fat, whereas ground chicken contains 4.879g. Ground chicken has 0.087g of trans fat.
Fat Type Comparison
Omega-3 Fatty Acids
Both contain small amounts of omega-3 fatty acids. Chicken breast has 0.06g of omega-3, whereas ground chicken provides 0.1g. Ground chicken has more omega-3 DHA and ALA, whereas breast is higher in EPA and DPA.
Carbohydrates
Ground chicken does not contain carbohydrates, while chicken breast has only 0.51g.
Cholesterol
Ground chicken has more cholesterol compared to chicken breast. A hundred grams of the breast provides 91mg, whereas ground chicken has 107mg.
Vitamins
Chicken breast contains two times more vitamin B3 and folate. In a 100g serving, chicken breast and ground chicken have 14.8g and 7g of vitamin B3 (niacin), respectively. Chicken breast is higher in vitamins B6, K, and E, whereas ground chicken has more vitamins B1, B2, B5, and B12. In addition, chicken breast has 23IU of vitamin A, while ground chicken does not contain it.
Vitamin Comparison
Minerals
Chicken breast has over two times more selenium, calcium, and 1.5 times more choline. Chicken breast is high in phosphorus, sodium, magnesium, iron, and manganese.
On the other hand, ground chicken has 2.5 times more potassium. A hundred grams of ground chicken has 677mg of potassium, whereas the breast has 276mg. Moreover, ground chicken contains slightly more zinc and copper.
Mineral Comparison
Glycemic Index
Foods with no carbs naturally do not promote glucose absorption and, as a result, do not have a glycemic index. The glycemic index of chicken breast and ground chicken is 0.
Acidity
The PRAL value shows the ability of the food to break down into bases or acids inside the body. Chicken breast has a PRAL level of 18.7. The PRAL level of ground chicken is 5. That shows that the breast is significantly more acid-producing than ground chicken.
Health Impact
Muscle Building
Chicken breast is a low-fat, high-protein food with little carbs. It contains high-quality protein, notably leucine, which is known for stimulating muscle protein synthesis (1, 2).
The lean composition of chicken breast makes it suitable for people who want to increase lean muscle mass while limiting their fat consumption. Because of its high protein content and few additional additives, it is a favorite of many bodybuilders, athletes, and fitness fanatics. Like chicken breast, ground chicken provides the necessary amino acids and can help muscle growth and repair. Choosing lean slices of ground chicken is crucial to prevent excessive fat content if the objective is to develop lean muscle mass.
Chicken breast and ground chicken can be part of a well-balanced muscle-building diet. However, when combining these meals into a muscle-building nutrition plan, it is critical to consider the total macronutrient balance, individual dietary preferences, and specific fitness goals.
Foodborne Infections
Campylobacter, Salmonella, and Clostridium perfringens bacteria can be found in raw and undercooked chicken (3, 4).
Ground meat is more likely to have harmful germs compared to breast because it is made from mixed meats. Chicken breasts usually only have bacteria on the surface, while bacteria in ground meat are prevalent.
Moreover, ground meat is touched more often than whole pieces of meat, so there's a better chance for bacteria to spread from hands to kitchen surfaces and other foods (5).
Cancer
Eating poultry may lower the risk of lung cancer and esophageal cancer (6).
According to the meta-analysis, eating poultry may be somewhat linked to a lower risk of colorectal cancer (7).
Ground chicken can include white, dark meats, and some chicken skin. According to the USDA, ground poultry can only comprise muscle meat and skin with associated fat in their typical proportions, with no extra ingredients such as giblets (8). According to the study, chicken consumption with the skin on may increase the risk of prostate cancer (9, 10).
Cardiovascular Health
Studies suggest that chicken breast and boneless chicken leg meat may inhibit ACE (angiotensin-converting enzyme), which is similar to the effect of antihypertensive medications such as Captopril, Lisinopril, Perindopril, and others. Incorporating these tasty and nutritious meats into your diet may provide a natural way to improve cardiovascular health (11,12,13).
Choosing lean white meat may reduce the risk of cardiometabolic disease. Studies suggest that this particular dietary choice may have potentially beneficial effects on your health (14).
It should be noted that chicken meat is an exceptional source of nutrition and should be a part of your healthy diet. Its low cholesterol, high protein, and PUFA (polyunsaturated fatty acid) content make it a valuable and beneficial food that can improve overall health (15).
Sources
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/10418071/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/34684538/
- https://www.cdc.gov/foodsafety/chicken.
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0362028X22129406
- https://www.foodsafetynews.com/2022/07/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/24395380/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/24788671/
- https://ask.usda.gov/s/article/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/21930800/
- https://osher.ucsf.edu/patient-care/
- https://pubs.acs.org/doi/abs/10.1021/jf020604h
- https://pubs.acs.org/doi/abs/10.1021/jf0508201
- https://pubs.acs.org/doi/abs/10.1021/jf100977z
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/36558372/
- https://link.springer.com/article/10.1186/1476-511X-13-42
Infographic
Comparison summary table
 |
 |
||
| Lower in Sodium |
|
||
| Lower in Cholesterol |
|
||
| Lower in Saturated Fat |
|
||
| Rich in minerals |
|
||
| Lower in Sugar | Equal | ||
| Lower in Glycemic Index | Equal | ||
| Lower in price | Equal | ||
| Rich in vitamins | Equal | ||
All nutrients comparison - raw data values
| Nutrient |  |
 |
Opinion |
| Net carbs | 0g | 0.51g |
 |
| Protein | 23.28g | 33.44g |
 |
| Fats | 10.92g | 4.71g |
 |
| Carbs | 0g | 0.51g |
 |
| Calories | 189kcal | 187kcal |
 |
| Calcium | 8mg | 16mg |
 |
| Iron | 0.93mg | 1.14mg |
 |
| Magnesium | 28mg | 31mg |
 |
| Phosphorus | 234mg | 246mg |
 |
| Potassium | 677mg | 276mg |
 |
| Sodium | 75mg | 79mg |
 |
| Zinc | 1.92mg | 1.08mg |
 |
| Copper | 0.062mg | 0.054mg |
 |
| Manganese | 0.016mg | 0.021mg |
 |
| Selenium | 14.3µg | 26.2µg |
 |
| Vitamin A | 0IU | 23IU |
 |
| Vitamin A RAE | 0µg | 7µg |
 |
| Vitamin E | 0.39mg | 0.42mg |
 |
| Vitamin D | 5IU |
 |
|
| Vitamin D | 0.1µg |
 |
|
| Vitamin B1 | 0.121mg | 0.079mg |
 |
| Vitamin B2 | 0.302mg | 0.125mg |
 |
| Vitamin B3 | 7.107mg | 14.782mg |
 |
| Vitamin B5 | 1.327mg | 1.04mg |
 |
| Vitamin B6 | 0.538mg | 0.64mg |
 |
| Folate | 2µg | 4µg |
 |
| Vitamin B12 | 0.51µg | 0.37µg |
 |
| Vitamin K | 2.1µg | 2.4µg |
 |
| Tryptophan | 0.196mg | 0.39mg |
 |
| Threonine | 0.97mg | 1.412mg |
 |
| Isoleucine | 1.06mg | 1.765mg |
 |
| Leucine | 1.816mg | 2.509mg |
 |
| Lysine | 2.014mg | 2.836mg |
 |
| Methionine | 0.596mg | 0.925mg |
 |
| Phenylalanine | 0.912mg | 1.328mg |
 |
| Valine | 1.102mg | 1.659mg |
 |
| Histidine | 0.706mg | 1.037mg |
 |
| Cholesterol | 107mg | 91mg |
 |
| Trans Fat | 0.087g |
 |
|
| Saturated Fat | 3.11g | 1.29g |
 |
| Omega-3 - DHA | 0.031g | 0.03g |
 |
| Omega-3 - EPA | 0.008g | 0.01g |
 |
| Omega-3 - DPA | 0.016g | 0.02g |
 |
| Monounsaturated Fat | 4.879g | 1.72g |
 |
| Polyunsaturated fat | 2.08g | 1.07g |
 |
| Omega-6 - Eicosadienoic acid | 0.015g |
 |
|
| Omega-6 - Linoleic acid | 1.787g |
 |
|
| Omega-6 - Gamma-linoleic acid | 0.02g |
 |
|
| Omega-3 - ALA | 0.081g |
 |
Which food is preferable for your diet?
 |
 |
|
| Low Fats diet |
|
|
| Low Carbs diet |
|
|
| Low Calories diet |
|
|
| Low Glycemic Index diet | Equal | |
People also compare
Vitamins & Minerals Daily Need Coverage Score
Comparison summary
References
All the values for which the sources are not specified explicitly are taken from FDA’s Food Central. The exact link to the food presented on this page can be found below.
- Ground chicken - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/171117/nutrients
- Chicken breast - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/171078/nutrients
All the Daily Values are presented for males aged 31-50, for 2000-calorie diets.