Persimmon and Diabetes - Is It Good For Diabetics
Introduction
We will talk about how persimmon can help control blood sugar levels and its beneficial effects on diabetes. Persimmons' carbohydrates and glycemic index can differ depending on the variety and growing conditions; however, in this article, these numbers are for an average native raw persimmon.
Glycemic Index and Carbohydrates
The total amount of carbs you eat directly impacts your blood glucose levels, so it can be useful for people with diabetes to track what they consume.
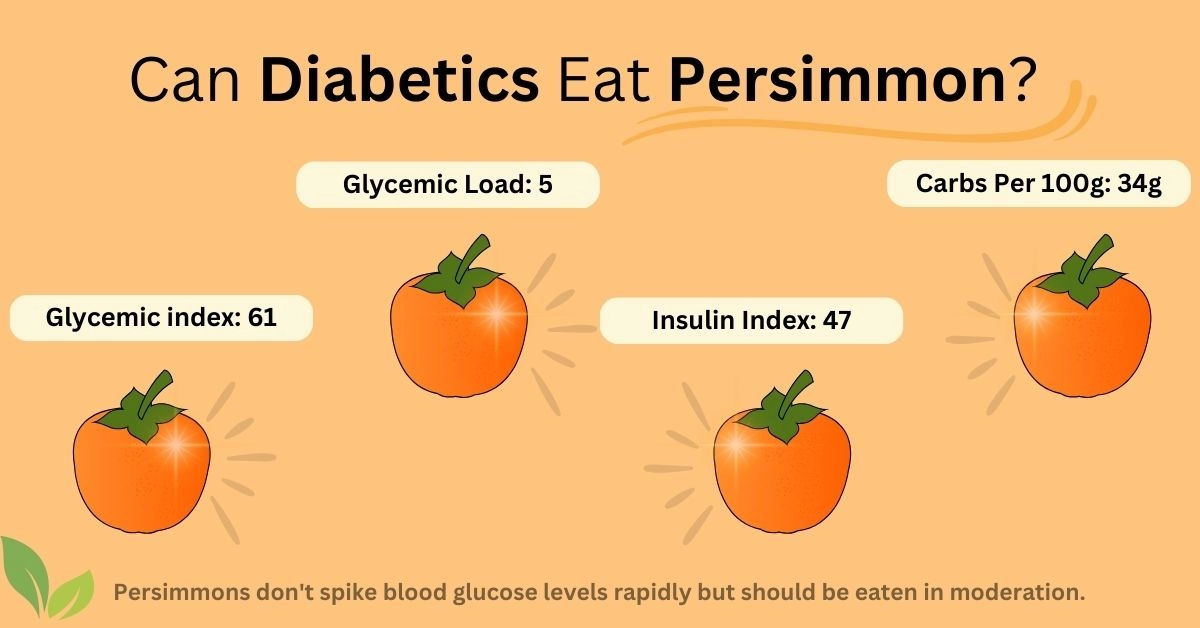
One medium-sized persimmon (about 25g) contains 9g of carbohydrates, while a 100g serving of persimmon provides 33.5g. You can find detailed information on persimmon nutrition here.
However, Japanese persimmons are lower in carbohydrates - 18.6g per 100g serving. The carbohydrate content in this fruit consists of 19% dietary fiber and 81% net carbs (1).
Persimmons fall in the top 25% of foods in our database as a source of carbohydrates.
Persimmon has been researched to have a glycemic index equal to 61, which is considered a moderate GI (2). This shows that despite the high carbohydrate content, persimmons do not raise blood glucose levels too quickly. However, they should still be consumed in moderation.
Also, you can visit our Glycemic index chart page to find GI values of 350+ pages.
Type-2 Diabetes
One study of 117 people with diabetes shows that increased consumption of foods high in soluble dietary fiber, such as persimmons, can help lower cholesterol, reduce blood sugar levels, and keep your digestive system healthy (3).
However, track the amount of persimmon you eat, as too much consumption can negatively affect blood glucose levels.
Persimmon contains a high amount of vitamin C; it falls in the range of the top 11% of foods as a source of vitamin C.
Another study involving 31 people (26 men and five women) with type 2 diabetes with the intake of 500 mg of vitamin C shows the beneficial effect of vitamin C on blood sugar levels (4). For 98% of participants, post-meal blood sugar levels were significantly lower following four months of vitamin C supplementation.
Persimmons are high in a natural antioxidant called ellagic acid. According to research, ellagic acid is a promising treatment for chronic diseases, particularly ulcerative colitis, Crohn's disease, Alzheimer's disease, and diabetes. Ellagic acid appears to have anti-diabetic activity via its action on pancreatic cells, stimulating insulin secretion and decreasing glucose intolerance (5).
Persimmon syrup has also been researched to have positive effects on diabetic patients as it can lower blood glucose levels (6)
References
- https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/169941/nutrients
- https://academic.oup.com/ajcn/article/83/5/1161/4649595
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4950069/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30394006/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/27671829/
- https://www.researchgate.net/publication/264027834
