Ground beef vs. Beef sirloin — Health Impact and Nutrition Comparison


Summary
Beef sirloin is lower in calories and fats. Sirloin is richer in proteins, phosphorus, potassium, and vitamins B3 and B6. In comparison, ground beef is richer in iron and vitamin B12. Fatty ground beef increases the risks of cardiovascular disease. Ground beef is cheaper.
Table of contents
Introduction
This article is a comparison between beef sirloin and ground beef. Both of them are derived from different parts of the meat.
Sirloin is a steak cut derived from the beef's rear back. In comparison, ground beef can be made from most cuts of beef.
In this article, we will compare cooked forms of both. The sirloin is a trimmed 0' fat cut, and the ground beef is 70/30 ground.
We will compare them based on some of their general differences, nutritional content, and health impacts.
General differences
Well, one of the main differences is the texture. Ground beef is ground meat, and sirloin is a full-cut beef steak.
This aspect is essential, considering how we can use these cuts. We can prepare different dishes for ground beef, such as lasagna, bolognese pasta, burrito, tacos, burger patty, and many other dishes. In comparison, sirloin, since it's a steak cut, we can do barbeque and steak and cut them into cubes in soups.
Price
Ground beef is more often prepared by different types of cuts available in the beef, so relatively it's a cheaper cut compared to sirloin.
Taste
Since it's 70/30, ground beef has a fattier taste than sirloin. The taste also depends on herbs, spices, and other aromatics often used while preparing these meats.
Nutritional content comparison
This section will compare 100g of each in cooked forms.
Calories
Ground beef is higher in calories compared to sirloin. This is primarily due to the higher fat profile of ground beef.
Sirloin contains 177 calories, and ground beef contains 241 calories.
Carbs and glycemic index
They have negligible carbs, and their glycemic index is 0.
Protein
Sirloin is richer in protein compared to ground beef. Sirloin contains 30g of protein, whereas ground beef contains 24g.
Fats
The difference in their fat profile is very significant. Ground beef contains 15g of fats, and sirloin contains 5g. In addition, ground beef contains higher amounts of saturated fats and dietary cholesterol.
Fat Type Comparison
Minerals
Their mineral profile is similar to a certain extent. The difference is between phosphorus and potassium, higher in sirloin, and iron, higher in ground beef.
Below we can visualize their mineral content.
Mineral Comparison
Vitamins
Sirloin is richer in vitamins B3 and B6. In comparison, ground beef is richer in vitamin B12.
Most of these vitamins are near their daily recommended values, and the vitamin B12 amount in ground beef is 3x the RDV.
Vitamin Comparison
Health impacts
Both are derivatives of beef meat, so they have common health impacts. However, due to their nutritional profiles, some differences exist between them.
If you are looking for a substitute for ground meat, you can read this article comparing ground turkey and ground beef.
Gastrointestinal infections
Since ground beef gets exposed to many leftovers in the grinder/mincer and gets mixed, we can have the presence of Ecoli, which can cause gastrointestinal infections. In severe cases, this Ecoli can cause HUS hemolytic uremic syndrome.
It is always recommended not to eat burgers or ground meat in uncooked (medium or rare) forms. Cook thoroughly to prevent any gastrointestinal infections. (1)
Since the inside is not exposed to the outer environment, Sirloin can be eaten medium.
Anemia
Ground beef is richer in vitamin B12, and consumption of vitamin B12 is linked with decreased risks of megaloblastic anemia. In addition, it is richer in iron, decreasing the risks of iron deficiency anemia. (2)(3)
Noting that sirloin is also rich in vitamin B12 and iron.
Overall red meat consumption is associated with decreased risks of iron deficiency and megaloblastic anemias.
It is vital to add red meat to your diet in moderate amounts.
Cardiovascular health
Ground beef is higher in saturated fats, which are associated with increased cardiovascular disease risks. (4)
If you are further interested in the negative impacts of red meat, you can read this article.
References
Infographic
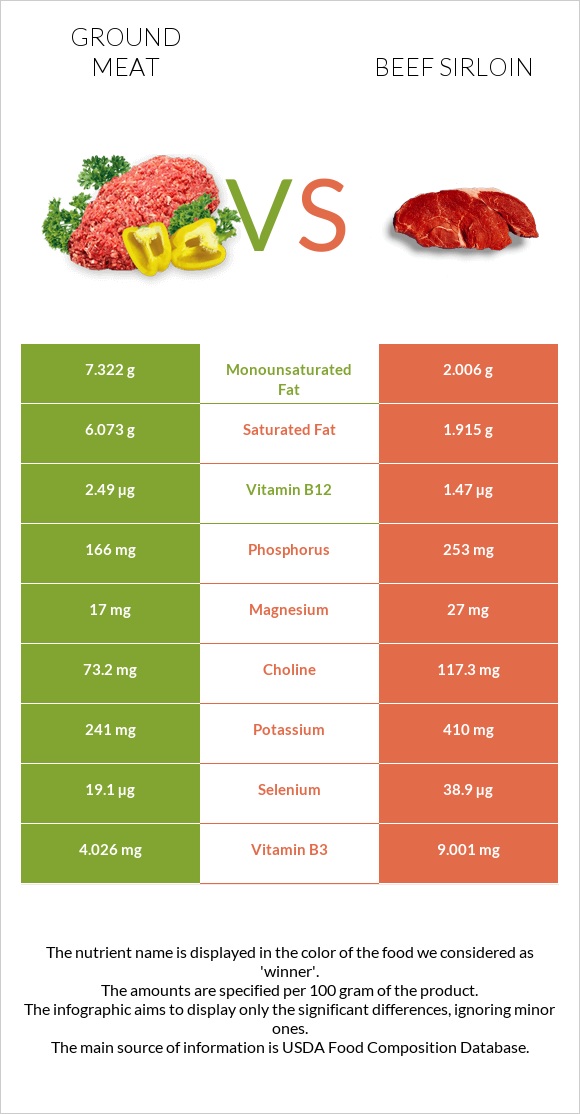
Macronutrient Comparison
Comparison summary table
 |
 |
||
| Lower in Sodium |
|
||
| Lower in Cholesterol |
|
||
| Lower in Saturated Fat |
|
||
| Lower in price |
|
||
| Lower in Sugar | Equal | ||
| Lower in Glycemic Index | Equal | ||
| Rich in minerals | Equal | ||
| Rich in vitamins | Equal | ||
All nutrients comparison - raw data values
| Nutrient |  |
 |
Opinion |
| Protein | 23.87g | 30.8g |
 |
| Fats | 15.37g | 5.03g |
 |
| Calories | 241kcal | 177kcal |
 |
| Calcium | 33mg | 22mg |
 |
| Iron | 2.27mg | 1.92mg |
 |
| Magnesium | 17mg | 27mg |
 |
| Phosphorus | 166mg | 253mg |
 |
| Potassium | 241mg | 410mg |
 |
| Sodium | 73mg | 66mg |
 |
| Zinc | 5.84mg | 5.7mg |
 |
| Copper | 0.079mg | 0.085mg |
 |
| Manganese | 0.009mg | 0.011mg |
 |
| Selenium | 19.1µg | 38.9µg |
 |
| Vitamin A | 9IU | 0IU |
 |
| Vitamin A RAE | 3µg | 0µg |
 |
| Vitamin E | 0.12mg | 0.39mg |
 |
| Vitamin D | 2IU |
 |
|
| Vitamin B1 | 0.051mg | 0.088mg |
 |
| Vitamin B2 | 0.171mg | 0.163mg |
 |
| Vitamin B3 | 4.026mg | 9.001mg |
 |
| Vitamin B5 | 0.512mg | 0.607mg |
 |
| Vitamin B6 | 0.311mg | 0.681mg |
 |
| Folate | 7µg | 10µg |
 |
| Vitamin B12 | 2.49µg | 1.47µg |
 |
| Vitamin K | 2.9µg | 1.4µg |
 |
| Tryptophan | 0.121mg | 0.202mg |
 |
| Threonine | 0.923mg | 1.23mg |
 |
| Isoleucine | 1.055mg | 1.401mg |
 |
| Leucine | 1.861mg | 2.45mg |
 |
| Lysine | 1.976mg | 2.603mg |
 |
| Methionine | 0.614mg | 0.802mg |
 |
| Phenylalanine | 0.931mg | 1.217mg |
 |
| Valine | 1.172mg | 1.528mg |
 |
| Histidine | 0.775mg | 0.983mg |
 |
| Cholesterol | 88mg | 81mg |
 |
| Trans Fat | 1.173g |
 |
|
| Saturated Fat | 6.073g | 1.915g |
 |
| Monounsaturated Fat | 7.322g | 2.006g |
 |
| Polyunsaturated fat | 0.408g | 0.185g |
 |
| Omega-6 - Gamma-linoleic acid | 0.008g |
 |
Which food is preferable for your diet?
 |
 |
|
| Low Fats diet |
|
|
| Low Carbs diet | Equal | |
| Low Calories diet |
|
|
| Low Glycemic Index diet | Equal | |
People also compare
Vitamins & Minerals Daily Need Coverage Score
Comparison summary
References
All the values for which the sources are not specified explicitly are taken from FDA’s Food Central. The exact link to the food presented on this page can be found below.
- Ground beef - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/169474/nutrients
- Beef sirloin - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/168636/nutrients
All the Daily Values are presented for males aged 31-50, for 2000-calorie diets.





