Kumquat vs. Lemon — Health Impact and Nutrition Comparison


Summary
Kumquat contains more minerals, more Vitamin A, Vitamin B2, Vitamin B3, and a lower GI. On the other hand, lemon has more Vitamin C, Vitamin B6, less sodium, and sugars.
Table of contents
Introduction
Kumquats and lemons are prevalent fruits and are used worldwide. We will discuss their similarities and differences, focusing on nutrition and health impact.
What's The Actual Difference?
Both lemon and kumquat have distinctly citrus flavors. However, kumquat is slightly sweeter, and lemon is more bitter or sour.
On the outside, lemons and kumquat are easy to differentiate; lemons look yellow and oval, and kumquat appears in shades of orange and round forms. Kumquat is smaller than lemons; it is about the size of an olive.
Varieties
Lemons are members of the Citrus genus. Lemons originated in South Asia, but they are now a popular citrus fruit used worldwide. Lisbon lemons and Eureka lemons are the most popular lemon varieties. Kumquats, also known as cumquats, are a genus of small fruit-bearing trees in the Rutaceae family and Citrus genus. Kumquat means "golden orange" in Chinese. A kumquat isn't much bigger than a grape, but this bite-sized fruit packs a punch of sweet-tart citrus flavor. Nagami Kumquats are the most popular variety in the USA.
Uses
Both kumquat and lemon also can be eaten raw or used in different ways: in marmalade, liqueur, and cocktails, as a garnish, and also as a flavor for different dishes.
Lemon leaves are used to make a tee and prepare meats and seafood. Kumquat also can be baked into bread.
Nutrition
Both kumquats and lemons have rich nutrition content. You can find the visual infographics at the bottom of this page.
Calories
Kumquat has two times more calories than lemons. It contains 71 calories per 100g, while lemons contain only 29 calories per 100g.
Vitamins
Kumquat is richer in Vitamin A, Vitamin B2, Vitamin B3, and Folate.
Vitamin A is 12 times higher in kumquat than in lemon.
On the other hand, lemon has higher Vitamin C and Vitamin B6. Lemon falls in the range of the top 12% of foods as a source of Vitamin C. The amounts of Vitamin B5, Vitamin B1, and Vitamin E are equal in these fruits. Both fruits have no Vitamin D, Vitamin K, and Vitamin B12.
Vitamin Comparison
Minerals
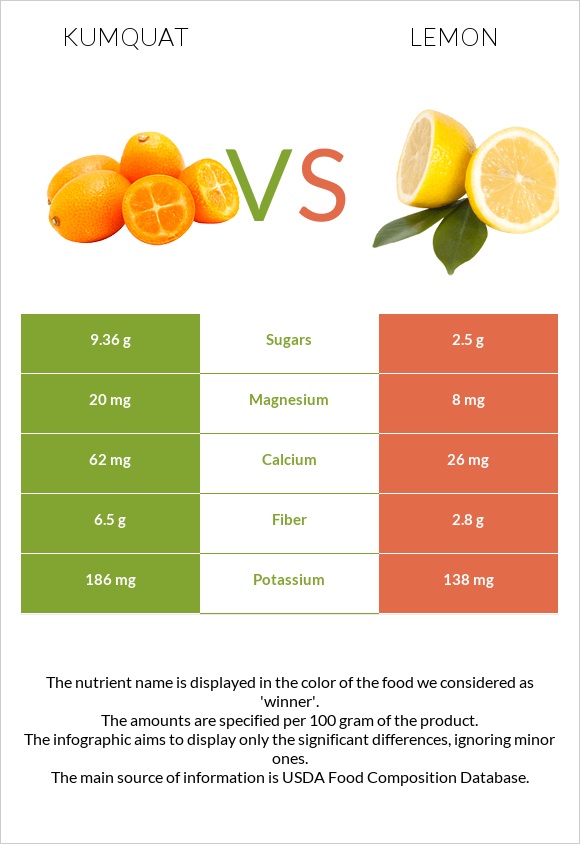
In comparison, kumquat has a relatively higher amount of minerals—more copper, potassium, magnesium, calcium, zinc, iron, and phosphorus.
Kumquat falls in the range of the top 30% of foods as a source of calcium.
On the other hand, lemon has less sodium than a kumquat.
Mineral Comparison
Glycemic Index
The GI of lemon has not yet been measured. The glycemic index of kumquats is 0.
Fats
Both carrots and apples have fats less than 1g. Kumquat contains 0.86g of fat, and lemon has 0.3g of fat.
Carbs
Kumquat contains almost two times more carbs than lemon. It has 16g per 100g, whereas lemon has 9.32g per 100g. The central part of kumquat carbs is net carbs: 9.4 g. However, kumquat also has more fiber: 6.5g per 100g. It falls in the range of the top 15% of foods as a source of fiber.
Cholesterol
Both fruits have no cholesterol.
Health Impact
Cardiovascular Health
Citrus fruits are high in flavonoids and linked to lower cardiovascular mortality and morbidity. Lemons and kumquats are high in flavonoids, Vitamin C, and fiber, linked to a lower risk of cardiovascular disease. One study [1] shows that eating 24 grams of citrus fiber per day for a month reduced total blood cholesterol levels.
According to studies [2], citrus fruits contain phytochemicals with potent antioxidant and hypolipidemic properties. These compounds may help to lower blood pressure and fight against oxidative stress.
Diabetes
Research shows that lemon juice can slow the digestion of carbohydrates to sugar. This effect is caused by the acidity of lemon juice, which slows starch digestion.
According to the findings, adding a drink to diabetics' meals can help level out blood sugar spikes.
In one study [3], patients were given a three-day lemon diet. The study concluded that this treatment alleviates specific symptoms, such as glucose levels associated with diabetes.
One animal study [4] shows that kumquat extract may reduce fasting blood sugar, total cholesterol, LDL (bad) cholesterol, and triglycerides. However, more research is needed.
Immune System
Many studies have shown that Vitamin C helps with common cold recovery. Furthermore, a lack of Vitamin C can harm your immune system, especially if you are elderly [5]. Both lemons and kumquat are high in Vitamin C and contain enough Vitamin A and minerals to strengthen your immune system. Animal and test-tube studies [6] indicate that kumquat plant compounds may aid in the activation of immune cells known as natural killer cells. In addition, Vitamin C can help boost immunity in people who engage in strenuous physical activity. More research is needed.
Side Effects
Allergy
People who are allergic to citrus may also be allergic to raw lemons and kumquat. People allergic to citrus fruit peels are frequently allergic to limonene, a chemical found in citrus fruit peels. These people may be able to drink fresh juice despite having contact dermatitis from simply touching the outside of citrus fruit. Intense tingling and itching of the lips, tongue, and throat are common symptoms [7].
Heartburn
Due to their acidic nature, lemons can cause heartburn and worsen the symptoms of gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD). This is especially likely if raw lemons are consumed on an empty stomach. However, regarding watered lemon juice, the results primarily depend on the consumer. Some people may experience heartburn, whereas others may feel relief from it [8, 9].
References
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0271531705801757
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/17344514/
- https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jamainternalmedicine/article-abstract/654086
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/24705395/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/17636648/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/25849817/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/23308273/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/35047433/
- A Comparative Analysis of Antimicrobial and Antioxidant Activity between Green Tea, Green Coffee, Pine Apple and Lemon Juice
Infographic
Macronutrient Comparison
Fat Type Comparison
Comparison summary table
 |
 |
||
| Lower in Sugar |
|
||
| Lower in Sodium |
|
||
| Lower in Saturated Fat |
|
||
| Lower in Glycemic Index |
|
||
| Lower in price |
|
||
| Rich in minerals |
|
||
| Lower in Cholesterol | Equal | ||
| Rich in vitamins | Equal | ||
All nutrients comparison - raw data values
| Nutrient |  |
 |
Opinion |
| Net carbs | 9.4g | 6.52g |
 |
| Protein | 1.88g | 1.1g |
 |
| Fats | 0.86g | 0.3g |
 |
| Carbs | 15.9g | 9.32g |
 |
| Calories | 71kcal | 29kcal |
 |
| Sugar | 9.36g | 2.5g |
 |
| Fiber | 6.5g | 2.8g |
 |
| Calcium | 62mg | 26mg |
 |
| Iron | 0.86mg | 0.6mg |
 |
| Magnesium | 20mg | 8mg |
 |
| Phosphorus | 19mg | 16mg |
 |
| Potassium | 186mg | 138mg |
 |
| Sodium | 10mg | 2mg |
 |
| Zinc | 0.17mg | 0.06mg |
 |
| Copper | 0.095mg | 0.037mg |
 |
| Manganese | 0.135mg | 0.03mg |
 |
| Selenium | 0µg | 0.4µg |
 |
| Vitamin A | 290IU | 22IU |
 |
| Vitamin A RAE | 15µg | 1µg |
 |
| Vitamin E | 0.15mg | 0.15mg | |
| Vitamin C | 43.9mg | 53mg |
 |
| Vitamin B1 | 0.037mg | 0.04mg |
 |
| Vitamin B2 | 0.09mg | 0.02mg |
 |
| Vitamin B3 | 0.429mg | 0.1mg |
 |
| Vitamin B5 | 0.208mg | 0.19mg |
 |
| Vitamin B6 | 0.036mg | 0.08mg |
 |
| Folate | 17µg | 11µg |
 |
| Saturated Fat | 0.103g | 0.039g |
 |
| Monounsaturated Fat | 0.154g | 0.011g |
 |
| Polyunsaturated fat | 0.171g | 0.089g |
 |
Which food is preferable for your diet?
 |
 |
|
| Low Fats diet |
|
|
| Low Carbs diet |
|
|
| Low Calories diet |
|
|
| Low Glycemic Index diet |
|
People also compare
Vitamins & Minerals Daily Need Coverage Score
Comparison summary
References
All the values for which the sources are not specified explicitly are taken from FDA’s Food Central. The exact link to the food presented on this page can be found below.
- Kumquat - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/168154/nutrients
- Lemon - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/167746/nutrients
All the Daily Values are presented for males aged 31-50, for 2000-calorie diets.





