Guava vs. Passion fruit — Health Impact and Nutrition Comparison


Summary
Passion fruit is rich in fibers, iron, magnesium, phosphorus, vitamins B2, B3, and A. Guava is rich in folate, vitamins E, B1, B5, and B6, copper, and magnesium. Guava is lower in carbs and glycemic index. They provide pos
itive effects on overall health.
Table of contents
- Introduction
- What are the actual differences?
- Nutritional data comparison
- Glycemic index
- Calories
- Macronutrients
- Carbs and fibers
- Protein
- Fats
- Vitamin C
- Vitamins
- Minerals
- Antioxidants
- Weight loss and diets
- Health impacts
- Cardiovascular health
- Diabetes
- Obesity
- Metabolic syndrome
- Drug interactions
- Immunity
- Women’s Health
- Kidney and liver
- Sleep
- References
Introduction
Passion fruit is a vine tree fruit native to the South American continent, mostly Brazil, Paraguay, and Argentina. It is mostly grown and cultivated in tropical and subtropical regions. Brazil produces the most passion fruit, filling nearly 60% of the world market supply. Botanically, it belongs to the family of berries.
Guava is a tropical fruit that is grown in tropical and subtropical climates. Guava is indigenous to Central and Northern South America, and it was found in Peru in about 800 BC. India has the most significant guava cultivation, accounting for 45 percent of the market; the other two nations that provide most of the market are China and Thailand.
Guavas are botanically defined as berries, which is an intriguing fact about them.
In this article, we will discuss the difference between passion fruit and guava according to their main differences, nutritional content, diets and weight loss, and health impacts.
What are the actual differences?
Other than their nutritional content difference, health impacts, and weight loss applications, we have certain differences that are also important to mention.
Varieties
There are different types of passion fruits; for example, the most common one is the purple passion fruit. The shell of the passion fruit is purple, and the inside is dark yellow. Another type is the yellow passion fruit which is sweeter than the purple passion fruit. Last but not least, sweet granadilla, which has a yellow shell but inside is darker than that of the yellow passion fruit, is the sweetest.
On the other hand, there are also different types of guava: red Malaysian guava and red Indian guava, which are suitable for eating. Mexican cream guava and lemon guava are suitable for desserts and frosting. There is also a very peculiar guava which is called strawberry guava due to its peculiar strawberry flavor. Other types also exist; however, these are the most commonly found in markets.
Shelf life
Passion fruit has a longer shelf life which can last up to 1 month in unrefrigerated conditions, mostly due to its hard shell. On the other hand, guava has a shorter shelf life, and this is due to its softer shell as compared to that of passion fruit.
Price
Passion fruit is more expensive than guava. This is mostly due to its delicacy and sensitivity in agriculture. The vine is very sensitive to the change of almost all variables. If any variable changes, the passion fruit yield might become very sour.
Taste and flavor
There is a vast difference between guava and passion fruit when it comes to flavor and taste.
On the one hand, passion fruit has a solid shell that has to be cut, and on the inside, there is the pulp which has a jelly-like consistency that is filled with small seeds. The inside is all edible.
Passion fruit has a distinct smell that is not common with any other fruit.
Guava, on the other hand, has a soft cover that can be eaten. Inside it is solid with seeds that can also be eaten. All the parts of the guava can be eaten. Guava has a specific flavor and aroma.
Culinary world
Passion fruit can be eaten raw, turned into juices that are usually mixed with other juices. It is also turned into a puree usually used in alcoholic cocktails, giving a sweet and aromatic taste to cocktails.
Guava may also be turned into drinks, and one popular guava-based juice consumed in Mexico is aqua Fresca. Guava may also be eaten raw in the same way as passion fruit. Guava pectin is used in marmalades and jellies in several Asian nations.
Nutritional data comparison
Glycemic index
Guava has a lower glycemic index compared to passion fruit. However, both have a glycemic index lower than 20, classifying them as low glycemic index foods.
Calories
Guava is lower in calories compared to passion fruit.
Macronutrients
Guava is higher in water, as indicated in the chart shown below. Passion fruit is comparably richer in carbs. You can read more detailed information in the corresponding sections.
Macronutrient Comparison
Carbs and fibers
Passion fruit contains higher amounts of carbs as compared to guava. However, it is important to note that passion fruit is richer in fiber, and the carb amount also contains the fibers.
Protein
They both have similar amounts of proteins, and it is not very remarkable.
Fats
Guava and passion fruit have negligible amounts of fats.
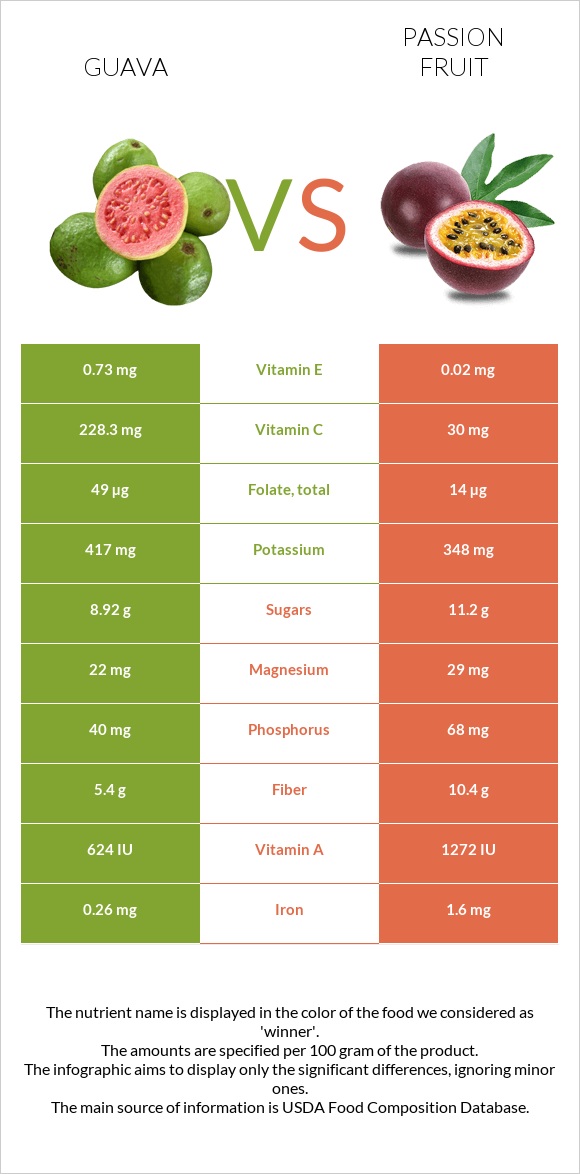
Vitamin C
Vitamin C is a very important vitamin component of these fruits.
Guava is very rich in vitamin C as compared to passion fruit. 300g of passion fruit can satisfy 100% of the recommended daily value, whereas, in the case of guava, it satisfies 760% of the recommended daily value.
Vitamin C has significant health impacts as it is a very important antioxidant. These will be discussed in further paragraphs.
Vitamins
Passion fruit is richer in vitamins A, B2, and B3. Guava is rich in folate, vitamins E, B1, B5, and B6. It is also important to note vitamin C, which was discussed in the paragraph above, noting that guava is richer in vitamin C.
Vitamin Comparison
Minerals
Passion fruit is richer in iron, magnesium, and phosphorus. On the other hand, guava is richer in potassium and copper.
Mineral Comparison
Antioxidants
Both fruits contain antioxidants, and passion fruit contains vitamin C, vitamin A, and polyphenols. Guava is rich in vitamin C, which is a very important antioxidant, and it also contains polyphenols.
Weight loss and diets
Vegan
Passion fruit and guava are recommended to be consumed in the vegan diet. They both provide rich and versatile macronutrient and micronutrient profiles.
Keto
Passion fruit and guava are not part of the keto diet as they contain a higher amount of carbs than is allowed during the keto diet.
Weight loss
Passion fruit and guavas are excellent additions to weight-loss regimens. They offer a variety of tastes and aromas and various health advantages, and they are both rich in macro and micronutrients. However, when it comes to price and availability, they are more expensive than the average fruits.
Health impacts
Cardiovascular health
Passion fruit has been linked with decreased risks of developing cardiovascular diseases as it has cardioprotective properties. Mostly cardiovascular diseases arise after metabolic syndrome (1).
Guava intake is associated with lower cholesterol and triglyceride levels and an increase in HDL levels, which have cardioprotective properties. As a result, guava has been related to a lower risk of cardiovascular disease and atherosclerosis (2).
Diabetes
Guava consumption is linked to lower fasting blood glucose levels. As a result of having control over blood glucose and insulin, the risk of acquiring type 2 diabetes is reduced (3).
Consuming the rind of the passion fruit peel has beneficial effects on diabetic patients. The peel of yellow passion fruit consumption is linked with decreased risks of developing insulin resistance in type 2 diabetic individuals (4).
Obesity
Guava intake can lessen blood glucose and cholesterol levels, lowering the risk of developing high BMI levels and obesity (5).
Passion fruit consumption is related to decreased risk of obesity, which will be discussed further in the metabolic syndrome section.
Metabolic syndrome
Passion fruit contains piceatannol, which has overall reduced risks of insulin sensitivity, glucose and lipid level decrease, and overall protective effects. Piceatannol is linked with decreased risks of metabolic syndrome and obesity, as was mentioned before (6).
Guava and mostly guava leaves are important in reducing metabolic syndrome risks in individuals. As mentioned above, guava reduces risks of cardiovascular disorders, including hypertension, decreases risks of diabetes and obesity, and overall decreases risks of developing metabolic syndrome. In addition to that, guava leaf extract has a direct relation with decreased risks of metabolic syndrome (7).
Drug interactions
Passion fruit flowers might interact with central nervous system depressants and sedatives and amplify their effect and oversedate (8).
No drug interactions have been observed with guava.
Immunity
Vitamin C is an antioxidant and immune booster that helps prevent oxidative stress disorders due to its antioxidative effects. In addition to that, it boosts the immune system to fight off any infections (9).
Women’s Health
Guava extracts have reduced pain levels in women who have stomach cramps throughout their menstrual periods. These, however, occur during the intake of guava extracts rather than the guava fruit itself (10).
Kidney and liver
Patients with uncontrolled diabetes may develop nephropathy. Guava extracts have been proven to lower the risk of diabetic nephropathy (11).
The passion fruit extract has been shown to have hepatoprotective and nephroprotective properties (12).
Sleep
Passion fruit flower has a sedative and calming effect that acts on the central nervous system by flavonoids (13).
References
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31608249/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/1332463/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/6660217/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/23088514/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5071920/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5691758/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2831039/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/19441067/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29099763/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/17112693/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/22581156/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30894908/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7251050/
Infographic
Fat Type Comparison
Comparison summary table
 |
 |
||
| Lower in Saturated Fat |
|
||
| Lower in Glycemic Index |
|
||
| Lower in Sugar |
|
||
| Lower in Sodium |
|
||
| Lower in price |
|
||
| Rich in vitamins |
|
||
| Lower in Cholesterol | Equal | ||
| Rich in minerals | Equal | ||
All nutrients comparison - raw data values
| Nutrient |  |
 |
Opinion |
| Net carbs | 8.92g | 12.98g |
 |
| Protein | 2.55g | 2.2g |
 |
| Fats | 0.95g | 0.7g |
 |
| Carbs | 14.32g | 23.38g |
 |
| Calories | 68kcal | 97kcal |
 |
| Sugar | 8.92g | 11.2g |
 |
| Fiber | 5.4g | 10.4g |
 |
| Calcium | 18mg | 12mg |
 |
| Iron | 0.26mg | 1.6mg |
 |
| Magnesium | 22mg | 29mg |
 |
| Phosphorus | 40mg | 68mg |
 |
| Potassium | 417mg | 348mg |
 |
| Sodium | 2mg | 28mg |
 |
| Zinc | 0.23mg | 0.1mg |
 |
| Copper | 0.23mg | 0.086mg |
 |
| Manganese | 0.15mg |
 |
|
| Selenium | 0.6µg | 0.6µg | |
| Vitamin A | 624IU | 1272IU |
 |
| Vitamin A RAE | 31µg | 64µg |
 |
| Vitamin E | 0.73mg | 0.02mg |
 |
| Vitamin C | 228.3mg | 30mg |
 |
| Vitamin B1 | 0.067mg | 0mg |
 |
| Vitamin B2 | 0.04mg | 0.13mg |
 |
| Vitamin B3 | 1.084mg | 1.5mg |
 |
| Vitamin B5 | 0.451mg |
 |
|
| Vitamin B6 | 0.11mg | 0.1mg |
 |
| Folate | 49µg | 14µg |
 |
| Vitamin K | 2.6µg | 0.7µg |
 |
| Tryptophan | 0.022mg |
 |
|
| Threonine | 0.096mg |
 |
|
| Isoleucine | 0.093mg |
 |
|
| Leucine | 0.171mg |
 |
|
| Lysine | 0.072mg |
 |
|
| Methionine | 0.016mg |
 |
|
| Phenylalanine | 0.006mg |
 |
|
| Valine | 0.087mg |
 |
|
| Histidine | 0.022mg |
 |
|
| Saturated Fat | 0.272g | 0.059g |
 |
| Monounsaturated Fat | 0.087g | 0.086g |
 |
| Polyunsaturated fat | 0.401g | 0.411g |
 |
Which food is preferable for your diet?
 |
 |
|
| Low Fats diet |
|
|
| Low Carbs diet |
|
|
| Low Calories diet |
|
|
| Low Glycemic Index diet |
|
People also compare
Vitamins & Minerals Daily Need Coverage Score
Comparison summary
References
All the values for which the sources are not specified explicitly are taken from FDA’s Food Central. The exact link to the food presented on this page can be found below.
- Guava - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/173044/nutrients
- Passion fruit - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/169108/nutrients
All the Daily Values are presented for males aged 31-50, for 2000-calorie diets.



