Curry and Diabetes - Is It Good For Diabetics

Introduction
Curry powder is a spice blend primarily of ginger, garlic, and turmeric. Some blends may include garlic and cinnamon. We are going to find out how curry acts on blood glucose levels.
Glycemic Index and Carbohydrates
The glycemic index value of curry powder equals 5, which is considered low GI.
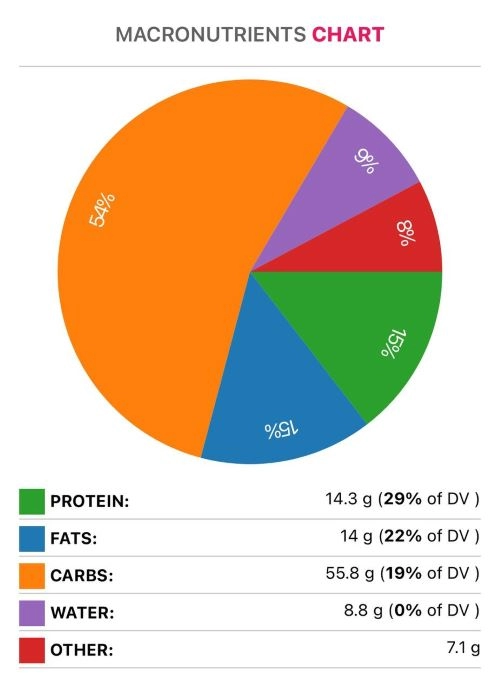
However, curry powder has a moderate amount of carbohydrates: 55.83g per 100g, of which 53g are fiber, and only 2.6g are net carbs.
However, since curry powder is usually consumed in very low amounts (0.5g or 0.25 tablespoon), it has only 0.3g of carbs per serving.
Since curry powder has a tiny amount of carbs, a high amount of fiber, and a low GI, its consumption will not raise blood sugar levels.
To find more glycemic index values for over 350 foods, visit our Glycemic index chart page.
Type-2 Diabetes
Research shows that curry powder has beneficial effects on blood glucose levels.
One study (1) indicates curry powder may help stabilize blood sugar levels and make diabetes more manageable.
It benefits blood glucose levels due to its anti-inflammatory and antioxidant effects, which work against oxidative stress.
Another study (2) showed that curry supplementation in alloxan-induced diabetic rats has significantly reduced blood glucose and increased total hemoglobin and glycosylated hemoglobin. It also prevented decreased body weight and reduced total cholesterol levels.
According to extensive research (3), turmeric (an essential component of curry powder) may reduce developing obesity, a significant risk factor for type 2 diabetes, atherosclerosis, cancer, and other chronic diseases. Turmeric exhibits activity against obesity through antioxidant and anti-inflammatory mechanisms; it also may improve insulin sensitivity.
