Lettuce vs. Kale raw — Health Impact and Nutrition Comparison


Summary
Kale is three times richer in fiber, and it is overall richer in vitamins C, B2, B6, K, A, and E. In addition, Kale is richer in calcium, manganese, iron, potassium, phosphorus, magnesium, and copper
Introduction
Both being members of different plant families, lettuce and kale tend to have many differences. The two vegetables are packed with minerals and vitamins. However, kale and lettuce differ in nutrient content. This article discusses the general and nutritional differences and the health impacts of raw lettuce(1) and raw kale(2).
Taste and appearance
Kale belongs to the family Brassica, also known as crucifers. It has a thicker stem and green color. They usually taste strong and earthy but are not spicy, unlike many greens. Kale is native to Europe.
Lettuce comes from the Mediterranean area. It belongs to the Asteraceae family. Lettuce leaves are longer and juicier than kale ones. They are commonly green, but you can find purple varieties as well. This vegetable has a sweeter taste, but the stem can be bitter.
Nutrition
Vitamins
Both kale and lettuce are rich in vitamins. However, kale has a richer vitamin profile.
Kale is richer in vitamins C, B2, B6, K, A, and E.
For more detailed information, check the vitamin comparison chart shown below.
Vitamin Comparison
Contains
more
Vitamin B5Vitamin B5
+47.3%
Contains
more
Vitamin CVitamin C
+1204.3%
Contains
more
Vitamin AVitamin A
+35.1%
Contains
more
Vitamin EVitamin E
+600%
Contains
more
Vitamin B1Vitamin B1
+57.1%
Contains
more
Vitamin B2Vitamin B2
+62.5%
Contains
more
Vitamin B3Vitamin B3
+166.7%
Contains
more
Vitamin B6Vitamin B6
+201.1%
Contains
more
Vitamin KVitamin K
+458%
Contains
more
FolateFolate
+271.1%
Minerals
Similar to their vitamin comparison, kale has a richer mineral profile aswell.
Kale is higher in calcium, manganese, iron, potassium, phosphorus, magnesium, and copper than lettuce.
Kale is more than three times richer in phosphorus and more than two times higher in potassium than lettuce.
Mineral Comparison
Contains
less
SodiumSodium
-26.3%
Contains
more
MagnesiumMagnesium
+261.5%
Contains
more
CalciumCalcium
+316.7%
Contains
more
PotassiumPotassium
+153.1%
Contains
more
IronIron
+70.9%
Contains
more
CopperCopper
+5069%
Contains
more
ZincZinc
+211.1%
Contains
more
PhosphorusPhosphorus
+217.2%
Contains
more
ManganeseManganese
+163.6%
Contains
more
SeleniumSelenium
+50%
Macronutrients
Proteins
Vegetables are generally not considered protein sources, but they contain some amounts of proteins. Kale provides more protein than lettuce. It contains 4.28g per 100g of vegetables, compared to 1.36g of lettuce.
Carbs
Kale has more carbs than lettuce. Kale has 8.75g of carbohydrates per 100g, while lettuce has 2.87g. Furthermore, lettuce has fewer sugars than kale.
Fiber
Kale provides nearly three times more fiber than lettuce. Kale is usually higher in insoluble fiber, while lettuce contains more soluble fiber.
Net carbs
Net carbs are the carbohydrates in food used to synthesize energy. Subtract the amount of fiber from the total carbs in the food to get the net carb amount.
Kale provides 8.75 grams of carbs with 3.6 grams of fiber. On the other hand, lettuce provides 2.87 grams of carbohydrates and 1.3 grams of fiber per serving. Kale has 5.15 grams of net carbs, whereas lettuce has 1.57 grams. Hence, lettuce has a lower net carb content.
Fats
Lipids are not found in kale or lettuce in considerable quantities. Lettuce has 0.2 grams of fat per 100 grams of vegetable, whereas kale has 0.93 grams. The two vegetables are equal in cholesterol content: they do not contain a significant amount.
Calories
Kale has 49 calories per 100g of vegetable, compared to 15 for lettuce.
Health impact
Cardiovascular health
Lettuce is associated with improved cardiovascular health due to its phytochemicals which are linked with decreased risks of myocardial infarction activity (3).
Kale contains phytochemicals that are associated with positive impacts on cardiovascular health (10).
Liver protective effects and Antioxidants
Phenolic compounds in lettuce are associated with decreased risks of oxidative damage in liver cells (4).
Kale contains quercetin which is an antioxidant aswell (8)(9)
Anticancer
Biofortified lettuce with iodine has been shown to induce apoptosis in cancer cells, thus having anti-carcinogenic activities (5).
kaempferol in kale has anticarcinogenic activity and anti-inflammatory activity (11).
Antidiabetic
lettuce phytochemicals have shown to have activity towards glucosidase and glucose receptors in the gastrointestinal tract, and overall they reduce carbohydrate breakdown and absorption. Overall, having a positive impact on type 2 diabetes and insulin resistance (6)(7).
Kale provides relatively large amounts of quercetin and kaempferol (9). These chemicals have anti-inflammatory, anti-cancer, and heart-protective effects.
REFERENCES
- https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/169249/nutrients
- https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/168421/nutrients
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/15297097/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/33879443/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/35480668/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/18503731/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC9219965/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5214562/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/19253943/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29557674/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31248102/
Infographic
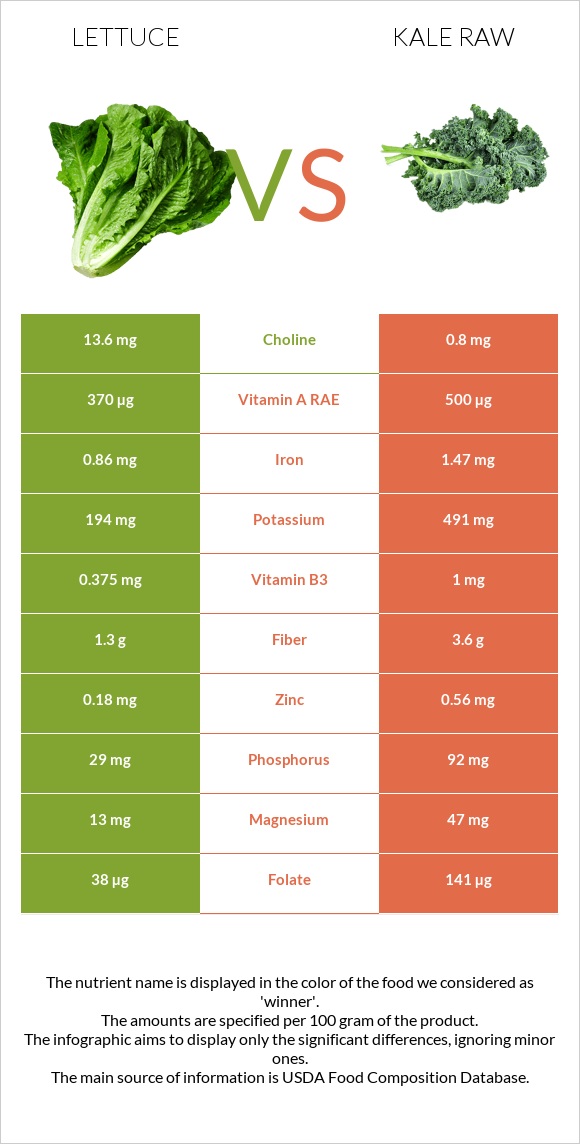
All nutrients comparison - raw data values
| Nutrient |  |
 |
DV% diff. |
| Vitamin K | 126.3µg | 704.8µg | 482% |
| Copper | 0.029mg | 1.499mg | 163% |
| Vitamin C | 9.2mg | 120mg | 123% |
| Folate | 38µg | 141µg | 26% |
| Manganese | 0.25mg | 0.659mg | 18% |
| Vitamin A | 370µg | 500µg | 14% |
| Vitamin B6 | 0.09mg | 0.271mg | 14% |
| Calcium | 36mg | 150mg | 11% |
| Potassium | 194mg | 491mg | 9% |
| Fiber | 1.3g | 3.6g | 9% |
| Phosphorus | 29mg | 92mg | 9% |
| Vitamin E | 0.22mg | 1.54mg | 9% |
| Magnesium | 13mg | 47mg | 8% |
| Iron | 0.86mg | 1.47mg | 8% |
| Protein | 1.36g | 4.28g | 6% |
| Vitamin B2 | 0.08mg | 0.13mg | 4% |
| Vitamin B3 | 0.375mg | 1mg | 4% |
| Zinc | 0.18mg | 0.56mg | 3% |
| Vitamin B1 | 0.07mg | 0.11mg | 3% |
| Calories | 15kcal | 49kcal | 2% |
| Carbs | 2.87g | 8.75g | 2% |
| Choline | 13.6mg | 0.8mg | 2% |
| Polyunsaturated fat | 0.082g | 0.338g | 2% |
| Fats | 0.15g | 0.93g | 1% |
| Selenium | 0.6µg | 0.9µg | 1% |
| Vitamin B5 | 0.134mg | 0.091mg | 1% |
| Fructose | 0.43g | 1% | |
| Net carbs | 1.57g | 5.15g | N/A |
| Sugar | 0.78g | 2.26g | N/A |
| Sodium | 28mg | 38mg | 0% |
| Saturated fat | 0.02g | 0.091g | 0% |
| Monounsaturated fat | 0.006g | 0.052g | 0% |
| Tryptophan | 0.009mg | 0% | |
| Threonine | 0.059mg | 0% | |
| Isoleucine | 0.084mg | 0% | |
| Leucine | 0.079mg | 0% | |
| Lysine | 0.084mg | 0% | |
| Methionine | 0.016mg | 0% | |
| Phenylalanine | 0.055mg | 0% | |
| Valine | 0.07mg | 0% | |
| Histidine | 0.022mg | 0% |
Macronutrient Comparison
| Contains more WaterWater | +13% |
| Contains more ProteinProtein | +214.7% |
| Contains more FatsFats | +520% |
| Contains more CarbsCarbs | +204.9% |
| Contains more OtherOther | +212.5% |
Fat Type Comparison
| Contains less Sat. FatSaturated fat | -78% |
| Contains more Mono. FatMonounsaturated fat | +766.7% |
| Contains more Poly. FatPolyunsaturated fat | +312.2% |
References
All the values for which the sources are not specified explicitly are taken from FDA’s Food Central. The exact link to the food presented on this page can be found below.
- Lettuce - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/169249/nutrients
- Kale raw - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/168421/nutrients
All the Daily Values are presented for males aged 31-50, for 2000-calorie diets.
