Banana Glycemic Index (GI) - Is It High or Low?
Different studies show different values for bananas’ Glycemic Index (GI). Let’s discuss the most trustworthy ones.
According to Harvard Medical School's GI data, bananas have a low glycemic index of 51 ± 3 (1).
One study found that factors such as size, texture, viscosity (internal friction or ‘thickness’), and ripeness of a food affect its GI. For instance, although both ripe and unripe bananas have a low GI (less than 55), an unripe banana may have a GI of 30, while a ripe banana has a GI of 51 (2).
The International Table of Glycemic Index Values publishes over ten different GI values for bananas, ranging from 30 to 75, with the mean values listed underneath the data. The table also shows that some values fall in the low, medium, or even high GI category. These inconsistencies are caused by methodological factors, varieties, different test methods of different laboratories, etc. (3).
Banana glycemic index may also vary depending on its starch and amylopectin content. A study comparing three different banana plants shows that the species with the lowest GI contains the lowest amounts of starch and amylopectin (5). Banana glycemic index (GI)
Another study compared different varieties of bananas (4). This study shows significantly higher GI values for bananas overall, with the highest being the Njalipoovan banana. None had a low GI value.
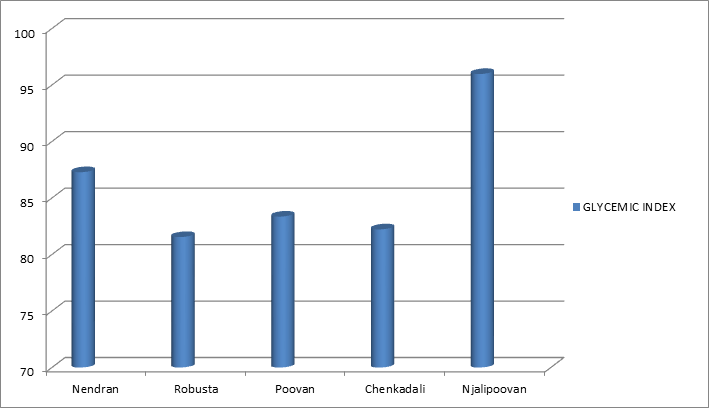
Thus, summing up all the data, we chose 48 for the banana’s average glycemic index value.
You can also see the glycemic indexes for 350+ foods on our glycemic index chart page.



