Piceatannol — Supplements, Structure, Health Benefits, & More
Summary
Piceatannol, a naturally occurring polyphenolic compound found in plants like Japanese knotweed and grapes, offers various biological activities, including anti-inflammatory, anticancer, and antioxidant properties. Structurally similar to resveratrol, piceatannol's effectiveness is attributed to its ability to alter cellular signaling pathways.
Although piceatannol is stable in solid form, it can degrade when exposed to light and air and has low bioavailability due to rapid metabolism in the liver.
Piceatannol’s benefits include antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects, weight management, diabetes support, cardiovascular health, skin health, and anticancer properties.
Supplementation options include capsules, tablets, and topical applications, with doses typically ranging from 10 to 50 mg per day, though precise recommendations are still lacking. Foods rich in piceatannol include grapes, passion fruit seeds, blueberries, and rhubarb.
Table of contents
- Introduction
- Structure and Properties
- Metabolism
- Piceatannol Supplements and Recommended Intakes
- Foods Rich in Piceatannol
- Health Benefits of Piceatannol
- Antioxidant and Anti-inflammatory effects
- Piceatannol and Weight Management
- Piceatannol and Diabetes
- Cardiovascular Health
- Piceatannol and Skin Health
- Piceatannol Anticancer Effects
- Health Downsides
- References
Introduction
Piceatannol, which shares structural similarities with resveratrol, demonstrates many biological activities, such as anti-inflammatory, anticancer, and antioxidant properties. Its capacity to alter cellular signaling pathways has captured the interest of researchers, making it a viable option for the management and prevention of a number of chronic diseases.
This article will explore the structure, properties, health impact, and supplementation of piceatannol.
Structure and Properties
Piceatannol is a natural compound with the molecular formula C14H12O4 and a 244.24 g/mol molecular weight. Structurally, it belongs to a group of compounds called stilbenes and features two aromatic rings connected by a double-bonded ethene bridge. What makes piceatannol special is the presence of four hydroxyl groups (OH) on the rings located at specific positions (1). These hydroxyl groups play a crucial role in its powerful antioxidant properties by donating hydrogen atoms to neutralize harmful free radicals.
The double bond in the ethene bridge gives the molecule a rigid and flat structure, which helps it interact effectively with various biological targets.
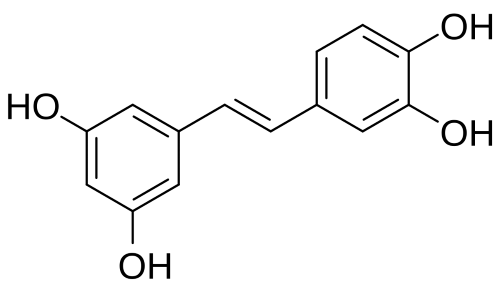
Piceatannol exhibits high stability in its solid form but can be sensitive to light and air, leading to degradation over time. It is slightly soluble in water but more soluble in organic solvents such as ethanol and dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) (2). Multiple hydroxyl groups also enable piceatannol to engage in hydrogen bonding.
Metabolism
Piceatannol undergoes extensive metabolism in the body, primarily through the action of liver enzymes. Upon ingestion, it is absorbed in the intestines and then subjected to phase I and phase II metabolic processes. During phase I metabolism, piceatannol may undergo oxidation, reduction, or hydrolysis, which is mainly facilitated by cytochrome P450 enzymes. This phase exposes functional groups that make the compound more water-soluble. In phase II metabolism, piceatannol undergoes conjugation reactions, such as glucuronidation, sulfation, and methylation, enhancing its solubility and promoting its excretion (3).
The liver plays a crucial role in these processes, ensuring that piceatannol and its metabolites are efficiently excreted via the kidneys in urine. However, the bioavailability of piceatannol is relatively low due to rapid metabolism and elimination, which can limit its therapeutic potential.
Piceatannol Supplements and Recommended Intakes
Piceatannol is available in various supplement forms, including capsules and tablets, which are appropriate for daily consumption. For those who prefer adding supplements to their food or drinks, piceatannol can also be found in powdered and liquid forms. Additionally, due to its antioxidant properties, piceatannol is included in skincare products like creams and serums for topical application.
Due to limited clinical research, the recommended intake and dosage of piceatannol are not well-established. However, doses in supplements typically range from 10 mg to 50 mg per day (4).
It is important to note that the appropriate dosage can vary depending on factors like individual health conditions, age, and the specific formulation of the supplement.
Foods Rich in Piceatannol
Piceatannol is found naturally in several foods, particularly those rich in resveratrol. Grapes, especially red and purple varieties, are a primary source of piceatannol, with the compound concentrated in their skins (5). Passion fruit, particularly its seeds, is another notable source (6). Blueberries also contain piceatannol, adding to the variety of ways you can incorporate this polyphenol into your diet (7) (8). Additionally, red wine, derived from grape skins, and raw peanuts offer smaller amounts of piceatannol (9).
Health Benefits of Piceatannol
Piceatannol is known for its strong antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties. Emerging research suggests that it may protect against chronic diseases such as cardiovascular conditions, obesity, and certain types of cancer.
Additionally, its effects on improving skin health and supporting metabolic function make it a promising compound in nutritional science and wellness.
In the following sections, we will discuss the health benefits of piceatannol in detail.
Antioxidant and Anti-inflammatory effects
Piceatannol exerts its antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects through multiple mechanisms that help protect the body from cellular damage. As an antioxidant, piceatannol neutralizes free radicals, annulling these unstable molecules before they harm cells and DNA. It also enhances the activity of endogenous antioxidant enzymes, such as superoxide dismutase (SOD) and glutathione peroxidase, which are crucial in defending against oxidative stress (10). Additionally, piceatannol inhibits lipid peroxidation, preventing the oxidative degradation of lipids that can lead to cell damage (11). On the anti-inflammatory side, piceatannol modulates inflammatory pathways by inhibiting the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines and enzymes, such as COX-2, and downregulating NF-κB, a key regulator of inflammation (12).
Piceatannol is known for inhibiting Syk (spleen tyrosine kinase), a key enzyme involved in immune response, inflammation, and cell signaling (13). By binding to the active site of Syk, piceatannol prevents its activation. It disrupts downstream signaling pathways that lead to the activation of immune cells and the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines. This inhibition of Syk reduces NF-κB activation and other transcription factors that drive inflammation, making piceatannol a potent anti-inflammatory agent. Additionally, by modulating Syk activity, piceatannol can influence the immune response, potentially reducing excessive inflammation and autoimmune reactions.
Piceatannol and Weight Management
Piceatannol may support weight management through various mechanisms that impact fat metabolism and energy balance. It inhibits adipogenesis, the formation of new fat cells, by interfering with key signaling pathways and transcription factors like PPARγ, which are essential for fat cell development (14).
Piceatannol enhances lipolysis, the breakdown of stored fats, by increasing the activity of enzymes involved in this process (15). It also improves insulin sensitivity, helping to regulate blood sugar levels and reduce fat accumulation.
Furthermore, piceatannol has been shown to increase energy expenditure by activating pathways that promote the browning of white fat, which converts energy-storing white fat into energy-burning brown fat.
Piceatannol and Diabetes
One key way piceatannol helps during diabetes is by enhancing insulin sensitivity (16). This allows cells to respond more effectively to insulin, thereby improving glucose uptake and lowering blood sugar levels (17). Additionally, piceatannol inhibits the enzyme α-glucosidase, which slows down the digestion and absorption of carbohydrates, leading to a more gradual rise in blood sugar after meals (18).
Cardiovascular Health
By scavenging free radicals and enhancing the activity of antioxidant enzymes, piceatannol helps reduce oxidative stress, a key factor in developing atherosclerosis and other cardiovascular diseases (19). Its anti-inflammatory effects further support heart health by inhibiting the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines and reducing vascular inflammation, which can lead to plaque formation in arteries. Piceatannol also promotes vasodilation by enhancing nitric oxide production, a molecule that relaxes blood vessels and improves blood flow (20). Additionally, piceatannol has been shown to inhibit platelet aggregation, reducing the risk of blood clots that can lead to heart attacks and strokes (21).
Piceatannol and Skin Health
Piceatannol significantly benefits skin health, primarily due to its potent antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and anti-aging properties.
As an antioxidant, piceatannol helps against skin aging, protecting skin cells from damage caused by environmental factors like UV radiation and pollution. Its anti-inflammatory properties further support skin health by reducing redness, swelling, and irritation, making it beneficial for conditions such as acne, eczema, and psoriasis (22).
Piceatannol also enhances skin elasticity and reduces the appearance of fine lines and wrinkles (23). It achieves this by stimulating collagen production, a key protein maintaining skin firmness and structure. Additionally, piceatannol has been found to inhibit the activity of enzymes like elastase, which breaks down elastin, another protein that keeps skin supple and smooth (24).
Piceatannol Anticancer Effects
Piceatannol has shown potential as an anti-cancer agent due to its ability to inhibit cancer cell growth and induce apoptosis, or programmed cell death, in various cancer types (25). Its antioxidant properties help protect cells from DNA damage caused by free radicals, which can lead to cancer development. Piceatannol interferes with multiple signaling pathways crucial for cancer cell proliferation, such as the PI3K/Akt and MAPK pathways. By disrupting these pathways, piceatannol can slow down tumor growth and prevent the spread of cancer cells (metastasis) (26). Furthermore, piceatannol has been found to inhibit angiogenesis, the process by which tumors form new blood vessels to sustain their growth (27).
Research suggests that piceatannol may effectively combat breast cancer by inhibiting cell proliferation and inducing apoptosis in breast cancer cells (26). In prostate cancer, piceatannol can suppress tumor growth and reduce metastasis by disrupting key signaling pathways involved in cancer progression (27).
Studies indicate that piceatannol may be beneficial in treating colon cancer by inducing cell cycle arrest and enhancing the effectiveness of other chemotherapeutic agents (28). Its effects on leukemia cells, particularly by triggering apoptosis and inhibiting cell growth, further highlight its potential as an anti-cancer agent (29).
Health Downsides
Cytotoxicity
Piceatannol's cytotoxicity primarily targets cancer cells, but it is crucial to consider its effects on healthy cells as well. While piceatannol shows potential in selectively inducing apoptosis in cancer cells and inhibiting their proliferation, its impact on healthy cells can vary. Research indicates that piceatannol can affect normal cells, including those in the liver, kidneys, and gastrointestinal tract, particularly at higher doses. However, at typical supplemental doses, piceatannol is generally considered to have a favorable safety profile and is less likely to cause significant cytotoxicity in healthy cells (30). Nonetheless, careful monitoring is advised, especially for individuals with existing health conditions or those on other medications, to ensure that the benefits outweigh any potential risks to healthy cells.
Drug Interactions
Piceatannol may interact with various medications, potentially affecting their efficacy or increasing the risk of adverse effects. Notably, piceatannol's effects on blood clotting could interact with anticoagulants or antiplatelet drugs, such as warfarin or aspirin, potentially enhancing their blood-thinning effects and increasing the risk of bleeding.
Piceatannol’s impact on insulin sensitivity and blood glucose regulation may influence the effectiveness of diabetes medications, requiring careful monitoring of blood sugar levels. Furthermore, piceatannol can affect liver enzymes involved in drug metabolism, potentially altering the pharmacokinetics of certain medications and leading to unpredictable effects (31).
References
- https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/Piceatannol
- https://www.apexbt.com/piceatannol.html
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31837280/
- https://www.researchgate.net/publication/320481241_The_Effect_of_Piceatannol_from_Passion_Fruit_Passiflora_edulis_Seeds_on_Metabolic_Health_in_Humans
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/B9780443154577000253
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/23649341/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/15264904/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2912479/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/17316017/
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1878535224003411
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7473378/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/25374129/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/12044809/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7918058/
- https://www.mdpi.com/2072-6643/15/6/1374
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29057795/
- https://www.mdpi.com/2075-1729/14/5/589
- https://pubs.rsc.org/en/content/articlelanding/2020/ra/c9ra09028b
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S1383574211000974
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0006291X12023455
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/10489881/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/36264002/
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2405580824001109
- https://academicjournals.org/journal/JMPR/article-full-text-pdf/57A1AC615314.pdf
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8509003/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3812238/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32824997/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/35616191/
- https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Piceatannol-Exhibits-Cytotoxic-Effects-in-Leukemia-Cancer-Cells_fig1_327380184
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7998146/
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0887233320304409

