Arugula vs. Spinach — Health Impact and Nutrition Comparison


Summary
Arugula and spinach are not radically different, having similar calories, macronutrient content, and glycemic index; however, spinach contains four times more vitamins A and K, as well as two times more folate and vitamin C. Spinach is also relatively higher in iron, potassium, copper, manganese, and magnesium. This makes spinach a better choice in terms of nutrition.
While arugula and spinach both have numerous beneficial effects on health, spinach has been studied more extensively in the area of health.
Introduction
We all know that leafy vegetables are good for our health but are some greens better than others? This article will compare two greens – arugula and spinach – to see what nutrients they provide us with and how they impact our bodies.
Classification
Arugula has many names, including salad rocket, garden rocket, eruca, rucola, colewort, and, scientifically, Eruca vesicaria, Eruca sativa, or Brassica eruca. It belongs to the Eruca genus and the Brassicaceae family. Arugula shares this family with broccoli, cauliflower, cabbage, Brussels sprouts, and many more vegetables.
Spinach or Spinacia oleracea belongs to the Spinacia genus and the Amaranthaceae family. This family also includes vegetables, such as garden beets and chard, as well as pseudocereal quinoa.
Appearance
Arugula and spinach are easy to differentiate from each other by appearance.
Spinach has smaller, rounded triangular leaves, while arugula leaves are pinnate-shaped with lobes on each side.
Arugula leaves also tend to be darker in color when compared to spinach.
Taste and Use
Arugula is famous for its peppery and slightly bitter taste. Spinach, however, has a much milder flavor, becoming more robust as it is cooked.
Arugula is believed to have originated from the Mediterranean region: Morocco, Portugal, Lebanon, and Syria. It’s either eaten raw as a side dish in Turkey, Egypt, Brazil, and Cyprus or is used as an ingredient in various dishes. For example, it is often added to pizza in Italy. Spinach, on the other hand, comes from ancient Persia. It is used in raw, fresh form in burgers and salads, often to replace lettuce.
Varieties
Based on the cultivar, the nutritional and physical properties of these greens can change.
The three main types of spinach are savoy, semi-savoy, and smooth-leafed spinach. Savoy spinach is also known as curly-leaf spinach. This variety usually has crispier leaves and is easier to cook with. The most popular varieties of savoy spinach are Regiment and Bloomsdale.
Semi-savoy spinach, as the name suggests, is somewhere in between savoy and smooth spinach. It has crispier leaves when compared to smooth-leafed spinach but is easier to clean than savoy spinach. The two common types of semi-savoy spinach are Tyee and Catalana.
And finally, the most popular varieties of smooth-leafed spinach are Space and Red Cardinal spinach.
Arugula also has a wide variety of cultivars with differing appearances, tastes, and nutritional values. The two primary commercially available groups of arugula are wild and common arugula. Wild arugula tends to have a more pungent taste.
Some of the widely known common varieties of arugula are Astro, Sylvetta, and Apollo.
Nutrition
The nutritional values are presented for raw arugula and spinach.
Macronutrients and Calories
The recommended serving size for both arugula and spinach is one cup, which is equivalent to 30 grams of spinach and 20 grams of arugula.
Although the serving sizes are only 20-30 grams, the nutritional content comparison below is made for 100 grams of serving to highlight the differences better.
As can be easily seen in the visual nutrition comparison below, these foods have very similar nutritional contents. The macronutrient structure is nearly the same. Both arugula and spinach consist of 91% water, spinach being only a little denser.
Macronutrient Comparison
Contains
more
FatsFats
+69.2%
Contains
more
ProteinProtein
+10.9%
Contains
more
OtherOther
+22.9%
Calories
Arugula and spinach are very similar in calorie content, both being very low in calories.
A 100g serving of arugula contains 25 calories, only two more calories when compared to spinach.
Protein and Fats
Leafy vegetables are not particularly rich in most macronutrients. However, spinach contains a little more protein when compared to arugula.
The protein quality in both of these vegetables is high, as they contain some levels of all essential amino acids.
Arugula and spinach are very low in fats. Nevertheless, arugula has a slightly higher content of fats. The fat-type breakdown below also indicates that the predominant fats found in these greens are polyunsaturated fatty acids.
Naturally, arugula and spinach contain no cholesterol.
Fat Type Comparison
Contains
more
Mono. FatMonounsaturated fat
+390%
Contains
more
Poly. FatPolyunsaturated fat
+93.3%
Contains
less
Sat. FatSaturated fat
-26.7%
Carbohydrates
Arugula and spinach contain nearly the same amount of carbohydrates. However, arugula is higher in sugar, while spinach contains more dietary fiber.
The little sugar content of spinach is made up of sucrose, glucose, fructose, and galactose.
Vitamins
There are relatively notable differences in vitamin content.
Spinach is the winner in the vitamin category, as it contains significantly higher levels of almost all vitamins.
Although both arugula and spinach are great sources of vitamins A, C, K, and folate, spinach contains 4 times more vitamin K and vitamin A, as well as around 2 times more folate and vitamin C.
Some other vitamins found in higher amounts in spinach, when compared to arugula but in low quantities when put in the context of daily need, include vitamin B6, vitamin E, and vitamin B2.
Spinach and arugula are both completely absent in vitamin B12 and vitamin D.
Vitamin Comparison
Contains
more
Vitamin B5Vitamin B5
+572.3%
Contains
more
Vitamin CVitamin C
+87.3%
Contains
more
Vitamin AVitamin A
+294.1%
Contains
more
Vitamin EVitamin E
+372.1%
Contains
more
Vitamin B1Vitamin B1
+77.3%
Contains
more
Vitamin B2Vitamin B2
+119.8%
Contains
more
Vitamin B3Vitamin B3
+137.4%
Contains
more
Vitamin B6Vitamin B6
+167.1%
Contains
more
Vitamin KVitamin K
+344.7%
Contains
more
FolateFolate
+100%
Minerals
Most minerals appear in approximately the same amounts. It’s important to mention that both arugula and spinach are relatively rich in iron, magnesium, potassium, copper, calcium, and manganese.
That being said, spinach is relatively higher in iron, potassium, magnesium, copper, and manganese.
Arugula, on the other hand, is slightly higher in calcium.
Although both are also low in sodium, arugula is slightly lower when compared to spinach.
Mineral Comparison
Contains
more
CalciumCalcium
+61.6%
Contains
less
SodiumSodium
-65.8%
Contains
more
MagnesiumMagnesium
+68.1%
Contains
more
PotassiumPotassium
+51.2%
Contains
more
IronIron
+85.6%
Contains
more
CopperCopper
+71.1%
Contains
more
ZincZinc
+12.8%
Contains
more
ManganeseManganese
+179.4%
Contains
more
SeleniumSelenium
+233.3%
Nitrates
Leafy green vegetables are rich in natural compounds called dietary nitrates, which are partially responsible for various beneficial effects of these greens, such as improving vascular functions (1, 2).
Arugula is over four times richer in dietary nitrates when compared to spinach (2).
The nitrate content can be found in different amounts depending on the seasonal period. Studies have shown the nitrate content of leafy green vegetables to be higher in autumn (3),
Glycemic Index
An exact number has not yet been calculated for the glycemic index of arugula and spinach. However, dark green leafy vegetables are considered to have a low glycemic index due to their low sugar content (4).
One study has shown spinach consumption to lower the glycemic response of the meal. At the same time, another study found that spinach only improves insulin sensitivity but has no effect on blood glucose levels (5, 6).
Acidity
The pH value of the arugula is estimated to be around 6.9, making the acidity of the arugula neutral (7).
Spinach, however, has a slightly more acidic pH value that can fall anywhere from 5.38 to 7.18, depending on the cooking method (8).
An alternative way of looking at the acidity of foods is the potential renal acid load or the PRAL value. This value demonstrates how much acid or base the given food produces inside the organism.
The PRAL value of arugula and spinach are -7.9 and -11.8, respectively. This shows us that spinach is more base-producing when compared to arugula.
Weight Loss & Diets
Green leafy vegetables famously fit well into weight-loss diets.
Arugula and spinach are no exceptions, being low-calorie foods. A 100-gram serving of these vegetables provides 25 calories or less. Green leafy vegetables are also a good source of dietary fiber and micronutrients.
Of the two vegetables, spinach is the preferred choice during low-calorie, low-fat, and low-carb diets. However, both arugula and spinach are low in calories, fats, and carbohydrates.
Green leafy vegetables, especially spinach, are rich in a compound called thylakoid. Thylakoid has been found to reduce hunger and cravings for palatable foods and increase satiety in overweight women (9). This means that eating spinach or arugula before a meal can help reduce overeating.
Health Impact
Health Benefits
In addition to the nutrients stated above, these leafy vegetables are also rich in antioxidants and phytonutrients, such as carotenoids, phenolic acids, and flavonoids. Due to these and other compounds, arugula and spinach have certain favorable impacts on health.
Both foods are very healthy and nutritious. However, spinach appears to be part of more scientific studies.
Cardiovascular Health
An inverse association has been found between the intake of green leafy vegetables, such as arugula spinach, and cardiovascular disease and mortality (10).
Green leafy vegetable consumption may decrease the risk of atherosclerotic vascular disease, coronary heart disease, and stroke (11).
Dietary nitrate may also contribute to the management of high blood pressure (12). Overall, dietary nitrate has been studied to reduce morbidity and mortality (2).
It should be noted that one effective approach to lower hypertension is to follow the Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension (DASH) diet. This diet emphasizes the consumption of fruits, vegetables, leafy greens (such as arugula and spinach), low-fat dairy, whole grains, nuts, and legumes. At the same time, it limits the intake of sodium, added sugar, and processed meat.
Diabetes
As mentioned above, both spinach and arugula are low glycemic index foods containing few sugars.
An extract of arugula leaves exhibited antidiabetic effects on cells that were responsive to insulin, which may prove helpful in the treatment of type 2 diabetes (13).
Spinach consumption can help control metabolic syndrome due to its high level of antioxidants (14).
Cancer
A compound found in arugula, called erucin, has been found to have the potential to prevent cancer by inhibiting the division of tumor cells (15).
Spinach has been researched to help protect against colorectal, breast, bladder, lung, and prostate cancers (16, 17).
Downsides and Risks
Vitamin K and Drugs
Green leafy vegetables, especially spinach, are rich in vitamin K. There has been some concern that due to this fact, these vegetables may interact negatively with certain blood thinners, such as warfarin, which work by inhibiting the blood clotting function of vitamin K. However, available evidence does not support the advice to modify dietary habits when starting therapy with vitamin K antagonists (18).
Sources
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0891584914004407
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6116056/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5412236/
- Dark Green Leafy Vegetables
- HYPOGLYCEMIC EFFECT OF SPINACH AND FENUGREEK LEAVES IN TYPE 2 DIABETICS
- https://www.researchgate.net/publication/270676832
- http://www.nphsystem.guide/vegetable_values.htm
- https://www.webpal.org/SAFE/aaarecovery/2_food_storage/Processing/lacf-phs.htm
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S019566631500197X
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5837313/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5986475/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4525132/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6130626/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5534315/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4065051/
- https://www.aicr.org/cancer-prevention/food-facts/spinach/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3209415/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4998867/
Infographic
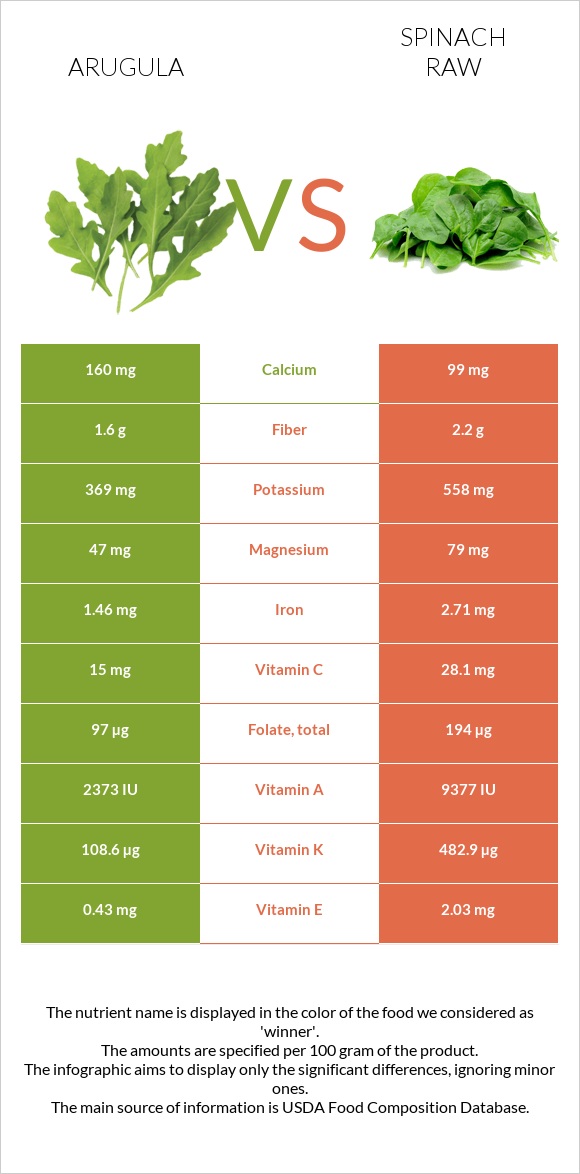
All nutrients comparison - raw data values
| Nutrient |  |
 |
DV% diff. |
| Vitamin K | 108.6µg | 482.9µg | 312% |
| Vitamin A | 119µg | 469µg | 39% |
| Manganese | 0.321mg | 0.897mg | 25% |
| Folate | 97µg | 194µg | 24% |
| Iron | 1.46mg | 2.71mg | 16% |
| Vitamin C | 15mg | 28.1mg | 15% |
| Vitamin E | 0.43mg | 2.03mg | 11% |
| Vitamin B6 | 0.073mg | 0.195mg | 9% |
| Magnesium | 47mg | 79mg | 8% |
| Vitamin B2 | 0.086mg | 0.189mg | 8% |
| Vitamin B5 | 0.437mg | 0.065mg | 7% |
| Calcium | 160mg | 99mg | 6% |
| Potassium | 369mg | 558mg | 6% |
| Copper | 0.076mg | 0.13mg | 6% |
| Vitamin B1 | 0.044mg | 0.078mg | 3% |
| Vitamin B3 | 0.305mg | 0.724mg | 3% |
| Fiber | 1.6g | 2.2g | 2% |
| Sodium | 27mg | 79mg | 2% |
| Protein | 2.58g | 2.86g | 1% |
| Zinc | 0.47mg | 0.53mg | 1% |
| Selenium | 0.3µg | 1µg | 1% |
| Choline | 15.3mg | 19.3mg | 1% |
| Polyunsaturated fat | 0.319g | 0.165g | 1% |
| Calories | 25kcal | 23kcal | 0% |
| Fats | 0.66g | 0.39g | 0% |
| Net carbs | 2.05g | 1.43g | N/A |
| Carbs | 3.65g | 3.63g | 0% |
| Sugar | 2.05g | 0.42g | N/A |
| Phosphorus | 52mg | 49mg | 0% |
| Saturated fat | 0.086g | 0.063g | 0% |
| Monounsaturated fat | 0.049g | 0.01g | 0% |
| Tryptophan | 0.039mg | 0% | |
| Threonine | 0.122mg | 0% | |
| Isoleucine | 0.147mg | 0% | |
| Leucine | 0.223mg | 0% | |
| Lysine | 0.174mg | 0% | |
| Methionine | 0.053mg | 0% | |
| Phenylalanine | 0.129mg | 0% | |
| Valine | 0.161mg | 0% | |
| Histidine | 0.064mg | 0% | |
| Fructose | 0.15g | 0% |
References
All the values for which the sources are not specified explicitly are taken from FDA’s Food Central. The exact link to the food presented on this page can be found below.
- Arugula - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/169387/nutrients
- Spinach raw - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/168462/nutrients
All the Daily Values are presented for males aged 31-50, for 2000-calorie diets.
