Barley vs. Amaranth — Health Impact and Nutrition Comparison


Summary
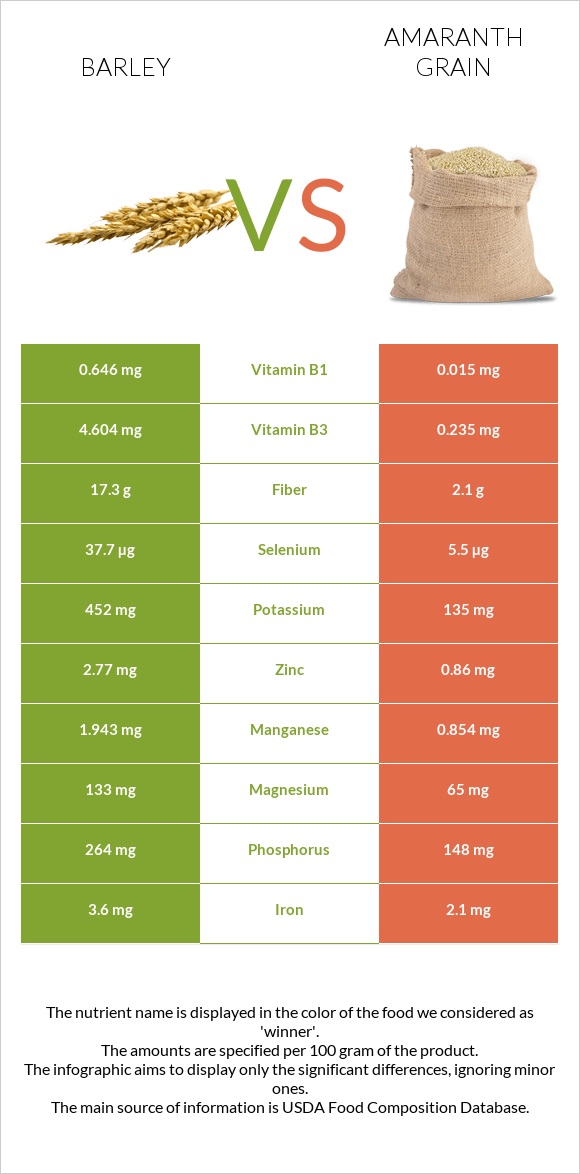
Amaranth grain has more magnesium, phosphorus, manganese, iron, potassium, calcium, copper, zinc, folate, and vitamin E. In contrast, barley provides more selenium, choline, and vitamins B1, B2, B3, B5, and K. Moreover, barley has more net carbs, fiber, and calories, whereas amaranth grain provides more protein, fats, sodium, and oxalates.
Introduction
Amaranth comes from Mexico and Central America. It was a staple food for the Aztecs and was also grown by the Incas in South America.
Barley is among the earliest cultivated grains globally, with historical evidence of its cultivation dating back to ancient civilizations in the Middle East.
Nutrition
In this section, we will compare the nutritional values of cooked barley and cooked amaranth grain, concentrating on differences.
Macronutrients and Calories
Barley is denser compared to amaranth grain. Barley contains 69% water, whereas amaranth grain contains 75% water. Barley provides more calories and carbs, while amaranth has more protein and fats.
Macronutrient Comparison
Contains
more
CarbsCarbs
+51%
Contains
more
ProteinProtein
+68.1%
Contains
more
FatsFats
+259.1%
Contains
more
OtherOther
+175%
Calories
Compared to amaranth grain, barley provides more calories per hundred grams. A 100g amaranth grain has 102 calories, whereas barley has 123 calories. The serving size for amaranth grain and barley is 1 cup. One serving of amaranth grain has 251 kcal (246g), whereas one serving of barley provides 193 kcal (157g).
Protein
Amaranth grain and barley are not good sources of protein. A hundred grams of barley provides 2.26g of protein, whereas amaranth grain has 3.8g.
Gluten
Amaranth grain is gluten-free, whereas barley contains gluten (1, 2).
Fats
Amaranth grain has more fat than barley. In a 100g serving, amaranth grain and barley have 1.58g and 0.44g of fat, respectively.
Carbohydrates
Barley is high in total, net carbs, and dietary fiber content.
100g of amaranth grain contains 18.69g of carbohydrates, of which 2.1g are dietary fiber and 16.59g are net carbs.
100g of barley contains 28.2g of carbohydrates, of which 3.8g are dietary fiber and 24.4g are net carbs.
Vitamins
Amaranth grain provides more folate and vitamin E. On the other hand, barley contains more vitamin B1 and vitamin B3. Moreover, barley has small amounts of vitamin K. Both lack vitamin C and vitamin D.
Vitamin Comparison
Contains
more
Vitamin B1Vitamin B1
+453.3%
Contains
more
Vitamin B2Vitamin B2
+181.8%
Contains
more
Vitamin B3Vitamin B3
+777.9%
Contains
more
Vitamin B5Vitamin B5
+∞%
Contains
more
Vitamin KVitamin K
+∞%
Contains
more
Vitamin EVitamin E
+1800%
Contains
more
FolateFolate
+37.5%
Minerals
Barley has over 1.5 times more selenium, whereas amaranth grain has five times more calcium and over three times more manganese, magnesium, and phosphorus. Amaranth grain also has more potassium, iron, copper, and zinc. On the other hand, barley has two times less sodium.
Mineral Comparison
Contains
less
SodiumSodium
-50%
Contains
more
SeleniumSelenium
+56.4%
Contains
more
MagnesiumMagnesium
+195.5%
Contains
more
CalciumCalcium
+327.3%
Contains
more
PotassiumPotassium
+45.2%
Contains
more
IronIron
+57.9%
Contains
more
CopperCopper
+41.9%
Contains
more
PhosphorusPhosphorus
+174.1%
Contains
more
ManganeseManganese
+229.7%
Oxalate content
Amaranth grain provides over 56 times more oxalates. A hundred grams of amaranth grain contains 1510mg of oxalates, whereas the oxalate content of barley is only 27mg.
Glycemic Index
Overall, amaranth grain has a higher glycemic index. Amaranth grain has a glycemic index of 97. The glycemic index of barley is 28. The GI for amaranth grain falls in the high category, whereas barley is a low-GI food.
Glycemic Load
The average glycemic load of barley is 14, whereas the glycemic load of amaranth grain is 40. Barley falls in the medium category, whereas amaranth grain falls in the high category.
Acidity
The potential renal acid load (PRAL) is a way to measure the acidity of the food. The PRAL value of barley is 0.4, whereas amaranth grain has the PRAL value of 2.2. Both are acid-forming, the amaranth grain being more acid-forming.
Weight Loss & Diets
Vegan/ Vegetarian: Vegan diets exclude all animal products, including meat, dairy, eggs, and honey. Amaranth grain and barley are plant-based foods, making them entirely suitable for a vegan diet. Vegetarians do not eat meat and may consume dairy products and eggs. Both are suitable for vegetarian diets.
Mediterranean: Barley and amaranth grain can be part of this diet.
Keto: The keto diet includes low-carb, high-fat, and high-protein foods.
Due to their high carb content, amaranth grain and barley are not keto-friendly.
Paleo: The paleo diet focuses on consuming natural, unadulterated foods and avoiding manufactured foods. Amaranth grain and barley are not paleo-friendly.
Gluten-free: Barley contains gluten and is not suitable for individuals following a gluten-free diet. On the other hand, amaranth grain is a good option in a gluten-free diet, and you can use it as a substitute for gluten-containing grains like barley, wheat, and rye.
Health Benefits
Antioxidant Properties
Whole grains like amaranth and barley are good sources of phytochemicals and have antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activities (3, 4, 5).
Diabetes
Amaranth grain has anti-diabetic properties. It may lower blood sugar levels (3).
Amaranth grain may improve calcium homeostasis, increase calcium content in the diet, improve calcium signaling in blood, kidney, and liver tissues, and enhance tissue protection against oxidative stress. In this way, amaranth grain may potentially aid in the control of Type 2 diabetes (6).
Additionally, aqueous extract from steamed red amaranth leaves has shown potential against diabetic retinopathy (3).
Prolonged consumption of the hydroalcoholic extract from barley seeds may offer advantages in managing and controlling diabetes mellitus. This effect is through the euglycemic agents such as biguanides (7).
Another study suggested that a mixture of barley and rice may reduce postprandial blood sugar levels in individuals with Type 2 diabetes (8).
Digestive Health
Barley contains nutrients like beta-glucan, which may aid gut health.
Eating barley leads to alterations in the gut microbiota. The study revealed a positive correlation between the consumption of barley and increased levels of Bifidobacterium and Butyricicoccus in the gut (5, 9).
Pseudocereals such as amaranth grain, quinoa, and buckwheat could benefit the gut microbiota. They may positively impact the body's metabolism (10).
Cancer
According to the study, amaranth grain has antiproliferative and anticancer properties. It may inhibit cancer cell growth and cause apoptosis (3, 4).
Barley consumption may induce apoptosis. According to the study, barley extract may reduce prostate and breast cancer cell proliferation (11).
Barley extract also may reduce the growth of colon cancer cells while leaving colon epithelial cells unaffected (12).
Downsides and Risks
Gluten-Related Disorders
Barley contains gluten, which can cause reactions in people with celiac disease or gluten sensitivity. People with gluten-related disorders ( celiac disease, non-celiac gluten sensitivity, gluten sensitivity) should use gluten-free grains and flour and avoid gluten-containing grains such as wheat, barley, and rye. Amaranth grain, quinoa, millet, and buckwheat are gluten-free grains and can be alternatives for people with celiac diseases or gluten sensitivity (1, 2, 13, 14).
Classification
Barley (Hordeum vulgare) belongs to the family Poaceae and the Hordeum genus. On the other hand, amaranth grain is classified as a dicot plant and belongs to the family Amaranthaceae and the Amaranthus genus.
Appearance
Barley grains are small, oval-shaped, and have an outer hull. Unlike it, amaranth grains are tiny, spherical, bead-like, and do not have an outer hull. Amaranth grains are much smaller than barley grains.
Barley is generally golden, tan, or pale beige. Depending on the variety, amaranth grain can vary in color from light cream to dark reddish-brown.
Barley grains have a firm texture and are typically smooth. In contrast, amaranth grains are silky and slightly glossy.
Taste and Use
Barley has a nutty flavor with a slightly sweet undertone, whereas amaranth grain has a slightly nutty taste with a hint of sweetness.
When cooked, barley has a chewy texture that adds a nice bite to dishes. When cooked, amaranth grain has a soft and slightly sticky texture.
Barley's flavor is versatile and may adapt well to savory and sweet dishes. It has a comforting and wholesome taste that complements soups, stews, salads, and baked goods.
Amaranth grain has a rich and robust flavor that pairs well with different ingredients. Amaranth's flavor is more distinct than barley, with a peppery undertone that sets it apart. It can be used in savory and sweet dishes, adding a unique taste and texture.
Barley flour can create a lighter and softer texture in baked goods than amaranth flour. In contrast, amaranth grain gives a denser and chewier texture. Barley flour contains gluten, which gives baked goods structure and elasticity. It is unsuitable for individuals with gluten intolerances, whereas you can use amaranth flour in gluten-free baking for cakes, muffins, pancakes, and other baked goods. Barley flour is used in baked goods like bread, muffins, and cookies, providing a unique flavor profile and texture.
Sources
- https://www.beyondceliac.org/gluten-free-diet/is-it-gluten-free/amaranth/
- https://www.beyondceliac.org/gluten-free-diet/is-it-gluten-free/barley/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8871380/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4888664/
- https://academic.oup.com/nutritionreviews/article/
- https://www.hindawi.com/journals/ecam/2018/4098942/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4311281/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/35463852/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/35287729/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/36648179/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/28584641/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30922050/
- https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/35186332/
Infographic
All nutrients comparison - raw data values
| Nutrient |  |
 |
DV% diff. |
| Manganese | 0.259mg | 0.854mg | 26% |
| Phosphorus | 54mg | 148mg | 13% |
| Vitamin B3 | 2.063mg | 0.235mg | 11% |
| Magnesium | 22mg | 65mg | 10% |
| Iron | 1.33mg | 2.1mg | 10% |
| Fiber | 3.8g | 2.1g | 7% |
| Starch | 16.23g | 7% | |
| Selenium | 8.6µg | 5.5µg | 6% |
| Vitamin B1 | 0.083mg | 0.015mg | 6% |
| Copper | 0.105mg | 0.149mg | 5% |
| Calcium | 11mg | 47mg | 4% |
| Protein | 2.26g | 3.8g | 3% |
| Carbs | 28.22g | 18.69g | 3% |
| Vitamin B2 | 0.062mg | 0.022mg | 3% |
| Vitamin B5 | 0.135mg | 3% | |
| Fats | 0.44g | 1.58g | 2% |
| Folate | 16µg | 22µg | 2% |
| Choline | 13.4mg | 2% | |
| Calories | 123kcal | 102kcal | 1% |
| Potassium | 93mg | 135mg | 1% |
| Vitamin E | 0.01mg | 0.19mg | 1% |
| Vitamin K | 0.8µg | 1% | |
| Polyunsaturated fat | 0.214g | 1% | |
| Net carbs | 24.42g | 16.59g | N/A |
| Sugar | 0.28g | N/A | |
| Zinc | 0.82mg | 0.86mg | 0% |
| Sodium | 3mg | 6mg | 0% |
| Vitamin B6 | 0.115mg | 0.113mg | 0% |
| Saturated fat | 0.093g | 0% | |
| Monounsaturated fat | 0.057g | 0% | |
| Tryptophan | 0.038mg | 0% | |
| Threonine | 0.077mg | 0% | |
| Isoleucine | 0.083mg | 0% | |
| Leucine | 0.154mg | 0% | |
| Lysine | 0.084mg | 0% | |
| Methionine | 0.043mg | 0% | |
| Phenylalanine | 0.127mg | 0% | |
| Valine | 0.111mg | 0% | |
| Histidine | 0.051mg | 0% |
People also compare
References
All the values for which the sources are not specified explicitly are taken from FDA’s Food Central. The exact link to the food presented on this page can be found below.
- Barley - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/170285/nutrients
- Amaranth - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/170683/nutrients
All the Daily Values are presented for males aged 31-50, for 2000-calorie diets.




