Sweet potato vs Yam - Health impact and Nutrition Comparison


Summary
Yams and sweet potatoes are entirely different vegetables. In nutritional comparison, yam is richer in fiber and has a lower insulin index, sodium, and sugar content than sweet potatoes.
However, yams are also higher in calories and net carbs, while sweet potatoes are significantly richer in vitamins and minerals.
Sweet potatoes contain 150 times more vitamin A, and 4 times more vitamin B2. They are also a better source of calcium, zinc, magnesium, iron, and phosphorus.
While both of them have anti-diabetic, antioxidant, and antiproliferative effects, sweet potatoes can also contribute to good eyesight, while yams can be useful for women’s hormonal health.
Introduction
Most people have at least once seen a tuberous root vegetable named yam in United States supermarkets, but oftentimes it is actually a type of sweet potato. Furthermore, there’s a chance you’ve never tasted or even seen real yam unless you bought it in specialized ethnic or international markets.
So, as you can already guess from what has been said, sweet potatoes and yams are completely different vegetables. However, they have some similarities, and their names are sometimes used interchangeably. Let’s deal with this confusion.
What Is The Main Difference?
Both sweet potato and yam are tuber vegetables.
Sweet potatoes are tapered and prolonged vegetables covered with smooth skin, the color of which varies from beige, yellow, orange, or red to purple or brown. The flesh also varies depending on the type, from purple and orange to white. The flavor of the flesh is sweet, and the texture is moist and juicy. Sweet potatoes originated in South and Central America.
On the other hand, yams are bigger. The skin is rough and bark-like, while the flesh is white, yellow, purple or pink, starchy, dry, and less sweet. Yams originated in Asia and Africa; nowadays, they are common in the Caribbean and Central America.
There are a few reasons for the sweet potato and yam confusion. It first started in the 30s of the 20th Century, when Louisiana farmers had marketed their sweet potatoes as “yam” to differentiate them from the other types of sweet potatoes growing in other states.
According to another version, enslaved Africans in the US had called the local sweet potatoes “nyami,” which became yam, owing to the resemblance with the true yams they had known in Africa.
Taste and Usage
Well, most of you may ask whether yams and sweet potatoes taste the same. Sweet potato tastes sweeter and creamier, while yam has a starchier flavor and texture that is more similar to a white potato.
However, both sweet potatoes and yams are used in many different recipes and dishes, such as sweet potato pie, sweet potato casserole, sweet potato fries, yam balls, yam porridge, and so on.
Nutritional Comparison
It seems essential to emphasize that sweet potatoes and yams are also different in terms of nutrition.
The information below is presented for 100g servings of sweet potato and yam, baked without salt.
The average serving size per person is one cup of cubed vegetables, which weighs 136g for yams and 200g for sweet potatoes.
Macronutrients and Calories
From the viewpoint of macronutrient compositions, these vegetables are similar; however, yam is a little denser in nutrients, consisting of 70% water and 30% nutrients. Sweet potatoes are made up of 76% water and 24% nutrients.
Macronutrient Comparison
Contains
more
ProteinProtein
+34.9%
Contains
more
OtherOther
+77.6%
Contains
more
CarbsCarbs
+32.7%
Calories
Yam is slightly higher in calories, providing 116 calories per 100g serving, whereas sweet potatoes contain 90 calories.
Carbohydrates
Yams are also richer in carbohydrates by about 7g per every 100g serving, this is mostly due to net carbs. However, yams are higher in dietary fiber as well.
A 100g serving of yams contains 27.5g of carbs, while the same serving of sweet potatoes provides 20.7g of carbohydrates.
Sweet potatoes and yams have high contents of starch; however, yam is much higher in it, while sweet potatoes are richer in simple sugars, such as sucrose, maltose, fructose, and glucose.
Both sweet potatoes and yams are excellent sources of dietary fiber.
Protein
While these vegetables are not exceptionally rich in protein, sweet potatoes contain slightly higher levels, with 2g of protein per 100g serving, compared to 1.5g of protein found in yam.
Fats
Sweet potatoes and yam contain insignificant amounts of fats and no cholesterol.
Vitamins
Sweet potatoes are the ultimate winner in the vitamin category. They contain 150 times more vitamin A, 4 times more vitamin B2, and over 2 times more vitamins B3, B5, and E. Sweet potatoes are also richer in vitamins B1, B6, and C.
On the other hand, yams contain around 3 times more folate or vitamin B9.
Vitamin Comparison
Contains
more
Vitamin CVitamin C
+62%
Contains
more
Vitamin AVitamin A
+15916.7%
Contains
more
Vitamin EVitamin E
+108.8%
Contains
more
Vitamin B1Vitamin B1
+12.6%
Contains
more
Vitamin B2Vitamin B2
+278.6%
Contains
more
Vitamin B3Vitamin B3
+169.4%
Contains
more
Vitamin B5Vitamin B5
+184.2%
Contains
more
Vitamin B6Vitamin B6
+25.4%
Contains
more
FolateFolate
+166.7%
Minerals
Sweet potatoes are also somewhat richer in minerals, being a better source of calcium, zinc, magnesium, iron, and phosphorus.
Nevertheless, yams are richer in potassium and almost 2 times lower in sodium.
Mineral Comparison
Contains
more
MagnesiumMagnesium
+50%
Contains
more
CalciumCalcium
+171.4%
Contains
more
IronIron
+32.7%
Contains
more
ZincZinc
+60%
Contains
more
ManganeseManganese
+34%
Contains
more
PotassiumPotassium
+41.1%
Contains
less
SodiumSodium
-77.8%
Contains
more
SeleniumSelenium
+250%
Glycemic Index
The glycemic index of boiled butternut pumpkin falls in the range of 51±6. Pumpkin from Jamaica, cubed, skinned, and cooked, has a glycemic index of 66±4, whereas a pumpkin from South Africa that has been boiled in salt water has a glycemic index of 75±9. The combined results of all three studies bring the pumpkin glycemic index to 64 (1).
Based on 21 different studies, the average glycemic index of yam has been calculated to be 68 (1).
Thus, sweet potato and yam have similar glycemic index values.
Insulin Index
The insulin index of foods presents how much the given food can raise blood insulin levels after intake.
The insulin index of orange sweet potatoes has been researched to be 96, whereas yams have an insulin index of 64 (2, 3).
While the glycemic index of yams and sweet potatoes is similar, yams have a lower insulin index value.
Health Impact
Yam is higher in fiber and resistant starches, contributing to our digestive health. Fiber prevents constipation, feeds our healthy gut bacteria, and reduces the risk of colorectal cancer and inflammation. Besides, fiber helps with weight loss since it turns into a gel, filling up the stomach and keeping us full for a long time.
On the other hand, sweet potatoes help gain weight since they are a good source of complex starches, vitamins, minerals, and proteins and are easy to digest.
It is worth mentioning that yams have specific compounds called saponins, such as dioscorin, diosgenin, and dioscin. One study has discovered immunomodulatory, blood pressure-lowering, and antioxidant activities of dioscorins extracted from different types of yams (7). Diocsorins can also protect airway epithelial cells from allergen destruction. According to research, diosgenin in yam contributes to improving the status of sex hormones, antioxidants, and lipids, reducing the risk of cardiovascular diseases and breast cancer in postmenopausal women (8, 9).
Eye Health
Sweet potato is higher in vitamin A and carotenoids(especially beta-carotene), which ensure the light-detecting function of the eyes. A vitamin A deficiency may lead to xerophthalmia – pathologically dry eyes that can, in turn, lead to night blindness. Purple sweet potatoes are also beneficial to our eyesight due to special antioxidants, anthocyanins, which protect the eyes (12).
Cancer
In vitro and in vivo studies on mice claim that anthocyanins extracted from purple sweet potatoes have slowed the growth of stomach, bladder, colon, colorectal, and breast cancer cells (4, 5, 6). These antioxidants have expressed significant anti-proliferative and anti-metastatic effects, preventing different types of cancer. Besides, studies on mice show that anthocyanins extracted from purple sweet potatoes can improve learning and memory by contributing to brain function improvement (10, 11).
Diabetes
It is worthy to note that both sweet potato and yam possess anti-diabetic effects. Studies demonstrate that white-skinned sweet potatoes and yams improve glucose and lipid metabolism by decreasing insulin resistance (13, 14, 15).
According to this study, sweet potato consumption may also lower glycosylated hemoglobin A1c levels and increase insulin sensitivity (16).
References
- https://academic.oup.com/ajcn/article/114/5/1625/6320814
- https://ses.library.usyd.edu.au/handle/2123/11945
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2957607/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/23784800
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/29749527
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4609785/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3943009/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/11428178
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16093400
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/14609130
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/19863544
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/10706405
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/17645559
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/19629697
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4632431/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6486146/
Infographic
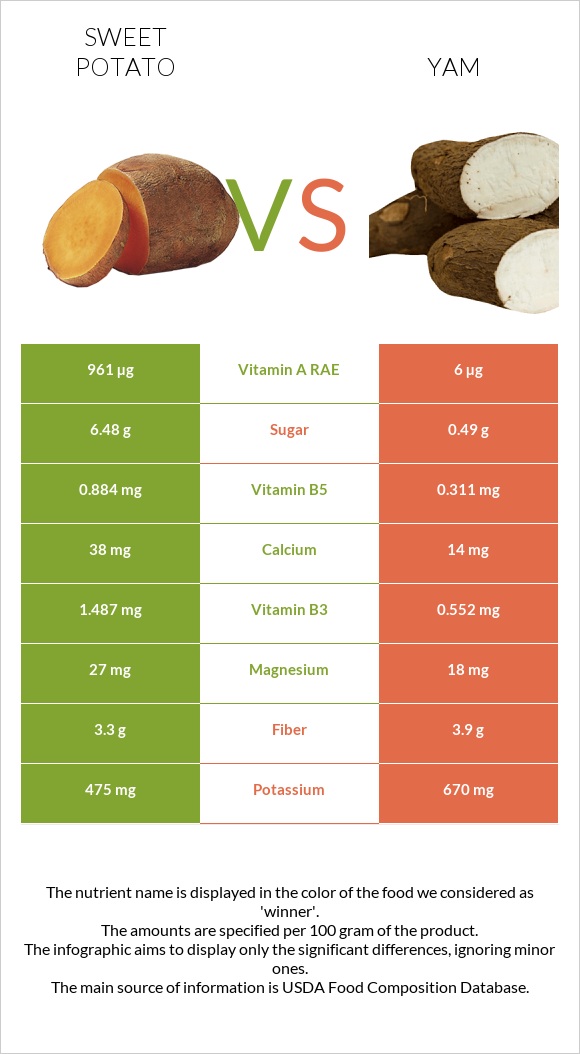
All nutrients comparison - raw data values
| Nutrient |  |
 |
DV% diff. |
| Vitamin A | 961µg | 6µg | 106% |
| Vitamin B5 | 0.884mg | 0.311mg | 11% |
| Vitamin C | 19.6mg | 12.1mg | 8% |
| Potassium | 475mg | 670mg | 6% |
| Vitamin B2 | 0.106mg | 0.028mg | 6% |
| Vitamin B3 | 1.487mg | 0.552mg | 6% |
| Manganese | 0.497mg | 0.371mg | 5% |
| Vitamin B6 | 0.286mg | 0.228mg | 4% |
| Starch | 7.05g | 3% | |
| Folate | 6µg | 16µg | 3% |
| Carbs | 20.71g | 27.48g | 2% |
| Magnesium | 27mg | 18mg | 2% |
| Calcium | 38mg | 14mg | 2% |
| Iron | 0.69mg | 0.52mg | 2% |
| Fiber | 3.3g | 3.9g | 2% |
| Vitamin E | 0.71mg | 0.34mg | 2% |
| Calories | 90kcal | 116kcal | 1% |
| Protein | 2.01g | 1.49g | 1% |
| Copper | 0.161mg | 0.152mg | 1% |
| Zinc | 0.32mg | 0.2mg | 1% |
| Phosphorus | 54mg | 49mg | 1% |
| Sodium | 36mg | 8mg | 1% |
| Selenium | 0.2µg | 0.7µg | 1% |
| Vitamin B1 | 0.107mg | 0.095mg | 1% |
| Choline | 13.1mg | 16.2mg | 1% |
| Fructose | 0.5g | 1% | |
| Fats | 0.15g | 0.14g | 0% |
| Net carbs | 17.41g | 23.58g | N/A |
| Sugar | 6.48g | 0.49g | N/A |
| Vitamin K | 2.3µg | 2.3µg | 0% |
| Saturated fat | 0.052g | 0.029g | 0% |
| Monounsaturated fat | 0.002g | 0.005g | 0% |
| Polyunsaturated fat | 0.092g | 0.06g | 0% |
| Tryptophan | 0.04mg | 0.012mg | 0% |
| Threonine | 0.107mg | 0.052mg | 0% |
| Isoleucine | 0.07mg | 0.05mg | 0% |
| Leucine | 0.118mg | 0.094mg | 0% |
| Lysine | 0.084mg | 0.058mg | 0% |
| Methionine | 0.037mg | 0.02mg | 0% |
| Phenylalanine | 0.114mg | 0.069mg | 0% |
| Valine | 0.11mg | 0.06mg | 0% |
| Histidine | 0.039mg | 0.033mg | 0% |
Fat Type Comparison
| Contains more Poly. FatPolyunsaturated fat | +53.3% |
| Contains less Sat. FatSaturated fat | -44.2% |
| Contains more Mono. FatMonounsaturated fat | +150% |
People also compare
References
All the values for which the sources are not specified explicitly are taken from FDA’s Food Central. The exact link to the food presented on this page can be found below.
- Sweet potato - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/168483/nutrients
- Yam - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/170072/nutrients
All the Daily Values are presented for males aged 31-50, for 2000-calorie diets.






