Turnips vs. Potato — Health Impact and Nutrition Comparison


Summary
In summary, potatoes contain more minerals and vitamins. Turnips, on the other hand, provide more vitamin C and calcium. Potatoes contain four times more carbs. Furthermore, potatoes are high in fat and protein content. Turnips and potatoes are high-GI foods and do not contain cholesterol.
Moreover, potatoes are high in calories and contain less sodium.
Introduction
Potatoes and turnips are white rood vegetables. The kinds utilized in this article are turnips, cooked, boiling, drained, without salt, and potatoes, baked, flesh, and skin, without salt. We will compare their nutritional values and health effects.
Classification
Turnips (Brassica rapa) belong to the genus Brassica and the mustard family (Brassicaceae).
Potato (Solanum tuberosum) belongs to the Solanum genus and nightshade family (Solanaceae).
Appearance
Potatoes are starchy subterranean tubers that vary in form and size. They are often round, oval, and long. Potatoes' skin tone can be pale brown to deep red or even purple. Inside potatoes have creamy white color.
Turnips are root vegetables. They have smooth, waxy skin and a spherical or slightly flattened form. Turnips vary in color, although they are often white or cream-colored, with purple or pink tones at the top.
Turnips have a crisp texture. Baked potatoes have a smooth and moist character. Mashed potatoes have a smooth and creamy texture.
Taste
Turnips have a distinctive taste. They are described as gently peppery or somewhat bitter in flavor. The flavor of turnips varies according to their size and maturity. Younger turnips have a softer taste with a sweet undertone, but larger and more mature turnips have a robust and distinct flavor.
Potatoes have a moderate, earthy, and somewhat sweet flavor in general. However, various potato types might have slight taste and texture changes. The cooking process can also affect the flavor of potatoes. Boiled or steamed potatoes have a more delicate and light flavor, but roasted potatoes are golden and crispy on the outside and have a rich, nuttier flavor.
Nutrition
Macronutrients and Calories
Potatoes are high in all macronutrients. Potatoes contain over 3.5 times more protein, 1.5 times more fat, six times more net carbs, and four times more calories.
Macronutrient Comparison
Contains
more
WaterWater
+25%
Contains
more
ProteinProtein
+252.1%
Contains
more
FatsFats
+62.5%
Contains
more
CarbsCarbs
+318%
Contains
more
OtherOther
+141.8%
Calories
Potatoes provide over four times more calories. A hundred grams of turnips contain 22 calories. A hundred grams of potatoes provide 93 calories.
Protein
Both contain all amino acids. Potatoes provide more protein. A hundred grams of turnips contain only 0.71g of protein, whereas potatoes provide 2.5g.
Fats
Turnips and potatoes contain less than 0.5g of fat per 100 grams. Turnips provide only 0.08g of fats, whereas potatoes provide 0.13g. Moreover, potatoes contain more polyunsaturated fats, whereas turnips provide more monounsaturated and less saturated fats.
Fat Type Comparison
Contains
less
Sat. FatSaturated fat
-76.5%
Contains
more
Mono. FatMonounsaturated fat
+66.7%
Contains
more
Poly. FatPolyunsaturated fat
+35.7%
Carbohydrates
Potatoes are the winner in carbs content. Potatoes contain over four times more carbs and six times more net carbs.
100g of turnips contains 5.06g of carbohydrates, of which 2g are dietary fiber and 3.06g are net carbs.
100g of potatoes contains 21.15g of carbohydrates, of which 2.2g are dietary fiber and 18.95g are net carbs.
The main carbohydrate found in potatoes is starch. Potato provides 17.27g of starch, whereas turnips do not contain it.
Turnips and potatoes are cholesterol-free.
Vitamins
Compared to turnips, potatoes are high in vitamins B3, B5, B6, B1, and K. Potatoes contain two times more vitamins B2 and E and three times more folate. On the other hand, turnips provide more vitamin C. Potatoes also provide 10IU of vitamin A, whereas turnips do not.
Vitamin Comparison
Contains
more
Vitamin CVitamin C
+20.8%
Contains
more
Vitamin AVitamin A
+∞%
Contains
more
Vitamin EVitamin E
+100%
Contains
more
Vitamin B1Vitamin B1
+137%
Contains
more
Vitamin B2Vitamin B2
+108.7%
Contains
more
Vitamin B3Vitamin B3
+371.6%
Contains
more
Vitamin B5Vitamin B5
+164.8%
Contains
more
Vitamin B6Vitamin B6
+364.2%
Contains
more
Vitamin KVitamin K
+1900%
Contains
more
FolateFolate
+211.1%
Minerals
In comparison to turnips, potatoes are almost high in all minerals. Turnips are over two times high in calcium. Turnips provide 33mg of calcium, whereas potatoes contain 15mg.
Potatoes, on the other hand, provide more potassium, magnesium, phosphorus, and choline. Potatoes also contain less sodium. Sodium content in turnips is 16mg, whereas potatoes provide 10mg.
Mineral Comparison
Contains
more
CalciumCalcium
+120%
Contains
more
MagnesiumMagnesium
+211.1%
Contains
more
PotassiumPotassium
+202.3%
Contains
more
IronIron
+500%
Contains
more
CopperCopper
+5800%
Contains
more
ZincZinc
+200%
Contains
more
PhosphorusPhosphorus
+169.2%
Contains
less
SodiumSodium
-37.5%
Contains
more
ManganeseManganese
+208.5%
Contains
more
SeleniumSelenium
+100%
Glycemic Index
Turnips and potatoes are high-GI foods. The glycemic index of cooked turnips is 85(1). The glycemic index of potatoes is 86.
Acidity
The pH level of turnips is 5.5-6.8(2). Potatoes, on the other hand, have a ph level of 5.4-5.9(3). The potential renal acid load (PRAL) is another method for determining the acidity of foods. Turnips have a PRAL value of -3.1. The PRAL value of potatoes is -8.3. Both are alkaline.
Weight Loss & Diets
Turnips and potatoes are plant-based foods and do not contain any animal products, so they are vegan. Also, they are vegetarian foods.
Due to their low-carb, low-fat, and high-fiber content, turnips are keto-friendly. On the other hand, potatoes are high in carbs and do not allow in the keto diet.
Turnips are also allowed in the paleo diet, whereas potatoes are not paleo-friendly.
Turnips and potatoes are allowed in the DASH diet.
You can use vegetables such as potatoes and turnips during the Mediterranean diet.
As turnips are non-starchy, low-carb, and high-protein, they are allowed in the Dukan diet. On the other hand, potatoes are not allowed in the Dukan diet.
Health Impact
Antidiabetic Activity
According to the study, ethanol extracts of turnip root may improve glucose transportation and insulin resistance. Ethanol extract may reduce the levels of blood glycosylated hemoglobin, plasma insulin, and C-peptide (4).
According to the study, a high intake of potatoes (baked, mashed, French fries, boiled) is associated with a higher risk of type 2 diabetes (T2D) (5).
Antimicrobial Activity
Turnips contain methanol extract, which has an antimicrobial effect. Turnips may inhibit the growth of some Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria (Escherichia coli, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Salmonella Paratyphi, and Sarcina lutea). Turnip roots also have anti-H. pylori effect(4).
Potatoes, on the other hand, have antimicrobial, antifungal, and antiviral effects. Potato protease inhibitors I and II inhibit the growth of Phytophthora infestans, Rhizoctonia solani, Botrytis cinerea, and Fusarium fungus. Some potato proteins may inhibit pathogens such as Staphylococcus aureus, Listeria monocytogenes, or Candida albicans(6).
Antioxidant Activity
Phenolic and organic acids contained in turnips have antioxidant activity(4).
Carotenoids, flavonoids, and phenolics found in potatoes have antioxidant activity. They are powerful singlet oxygen (O2) quenchers and scavengers of other reactive oxygen species(ROS)(7).
Anticancer Activity
Turnips have anticancer activity due to the high content of glucosinolates (isothiocyanate). According to the study, isothiocyanate inhibited the growth of the human prostate cancer cell(4).
According to the findings, eating more than three potatoes daily was linked to a higher risk of colorectal cancer(CRC)(8).
Sources
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3650508/
- file:///C:/Users/Admin/Downloads/ILGM-SPECIES_TurnipsForForage.pdf
- https://www.clemson.edu/extension/food/food2market/documents/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8360391/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/26681722/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31144014/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8122721/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/28323437/
Infographic
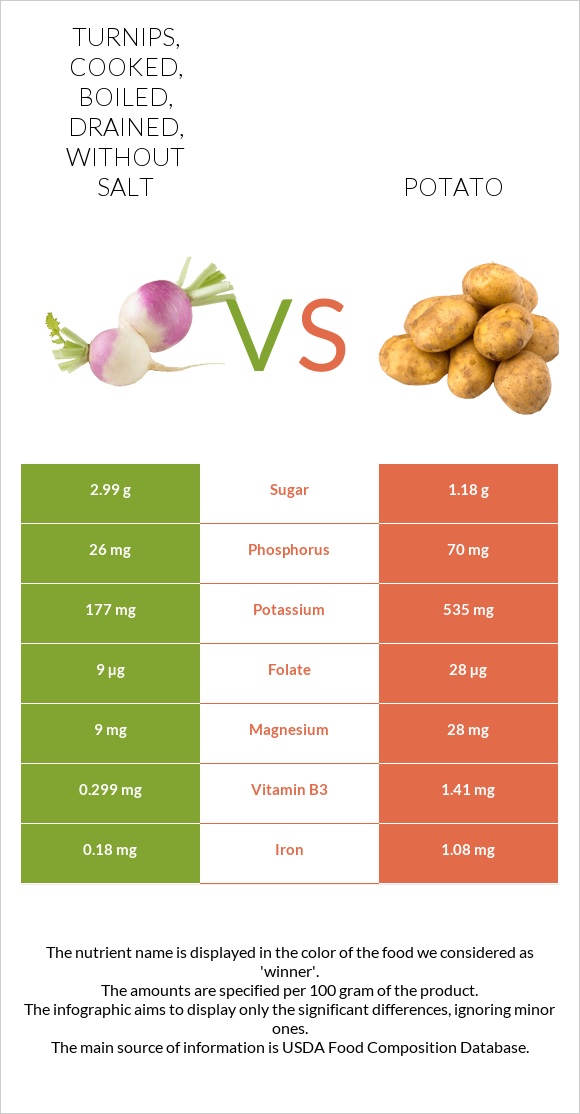
All nutrients comparison - raw data values
| Nutrient |  |
 |
DV% diff. |
| Vitamin B6 | 0.067mg | 0.311mg | 19% |
| Copper | 0.002mg | 0.118mg | 13% |
| Potassium | 177mg | 535mg | 11% |
| Iron | 0.18mg | 1.08mg | 11% |
| Starch | 17.27g | 7% | |
| Vitamin B3 | 0.299mg | 1.41mg | 7% |
| Phosphorus | 26mg | 70mg | 6% |
| Manganese | 0.071mg | 0.219mg | 6% |
| Carbs | 5.06g | 21.15g | 5% |
| Magnesium | 9mg | 28mg | 5% |
| Vitamin B5 | 0.142mg | 0.376mg | 5% |
| Folate | 9µg | 28µg | 5% |
| Calories | 22kcal | 93kcal | 4% |
| Protein | 0.71g | 2.5g | 4% |
| Vitamin B1 | 0.027mg | 0.064mg | 3% |
| Vitamin C | 11.6mg | 9.6mg | 2% |
| Calcium | 33mg | 15mg | 2% |
| Zinc | 0.12mg | 0.36mg | 2% |
| Vitamin B2 | 0.023mg | 0.048mg | 2% |
| Vitamin K | 0.1µg | 2µg | 2% |
| Fiber | 2g | 2.2g | 1% |
| Choline | 8.7mg | 14.8mg | 1% |
| Fats | 0.08g | 0.13g | 0% |
| Net carbs | 3.06g | 18.95g | N/A |
| Sugar | 2.99g | 1.18g | N/A |
| Sodium | 16mg | 10mg | 0% |
| Vitamin A | 0µg | 1µg | 0% |
| Vitamin E | 0.02mg | 0.04mg | 0% |
| Selenium | 0.2µg | 0.4µg | 0% |
| Saturated fat | 0.008g | 0.034g | 0% |
| Monounsaturated fat | 0.005g | 0.003g | 0% |
| Polyunsaturated fat | 0.042g | 0.057g | 0% |
| Tryptophan | 0.007mg | 0.025mg | 0% |
| Threonine | 0.02mg | 0.081mg | 0% |
| Isoleucine | 0.029mg | 0.08mg | 0% |
| Leucine | 0.026mg | 0.119mg | 0% |
| Lysine | 0.028mg | 0.13mg | 0% |
| Methionine | 0.009mg | 0.038mg | 0% |
| Phenylalanine | 0.014mg | 0.099mg | 0% |
| Valine | 0.023mg | 0.125mg | 0% |
| Histidine | 0.011mg | 0.042mg | 0% |
| Fructose | 0.34g | 0% |
References
All the values for which the sources are not specified explicitly are taken from FDA’s Food Central. The exact link to the food presented on this page can be found below.
- Turnips, cooked, boiled, drained, without salt - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/170058/nutrients
- Potato - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/170093/nutrients
All the Daily Values are presented for males aged 31-50, for 2000-calorie diets.
