Basil vs. Oregano — Health Impact and Nutrition Comparison


Summary
Oregano contains more vitamins, minerals, and protein than basil. Oregano contains 30 times more Vitamin E and 12 times more iron than basil. On the other hand, basil is lower in sugars, calories, and sodium and has higher Vitamin C and Vitamin A levels.
Introduction
In this article, you can find a detailed description of the differences between basil and oregano. Both are natural sources of micronutrients, certain minerals, and vitamins. The article will be focused on their nutrition and impact on health.
Varieties
Basil belongs to the family of Lamiaceae; there are more than 40 known varieties of basil. The most common and used ones are Sweet Basil, Lemon Basil, and Holy Basil. In general, plants can reach heights of 30-50 cm. Oregano belongs to the Mint family. It is a flowering plant and is native to Western and Southwestern Eurasia.
The most common oregano types are Syrian Oregano, Greek Oregano, and Common Oregano [1] [2].
Uses
Oregano is a culinary herb used for flavor; it is more flavorful when dried than fresh. The taste is aromatic and slightly bitter.
Oregano has popularity in Italian and American cuisine, used with meat, fish, and vegetables.
Basil is minty and peppery, and it is usually used fresh.
The dried basil may lose most of its flavor. It is used mainly in pesto and tomato sauce marinara. In some medical practices, basil is known for its therapeutic properties [1] [2].
Nutrition
Basil and oregano have a comprehensive nutritional profile. Our page contains various charts and infographics that visualize their nutrition. Please scroll down the page to check them out.
Micronutrients
Overall, oregano is richer in micronutrients than basil. It contains more carbs, protein, fiber, and fats.
On the other hand, basil has fewer sugars.
Both contain no cholesterol [3].
Calories
In general, oregano contains more calories than basil. The level of calories in oregano is 11 times higher in oregano. Each oregano has about 265 calories per 100 g, whereas each basil has 23 calories per 100 g.
Minerals
Oregano is relatively richer in Potassium, Iron, Calcium, Zinc, and Copper. The amounts of Magnesium and Copper are two times higher in oregano. On the other hand, basil has a lower level of sodium [4].
Mineral Comparison
Contains
less
SodiumSodium
-84%
Contains
more
MagnesiumMagnesium
+321.9%
Contains
more
CalciumCalcium
+802.3%
Contains
more
PotassiumPotassium
+327.1%
Contains
more
IronIron
+1060.9%
Contains
more
CopperCopper
+64.4%
Contains
more
ZincZinc
+232.1%
Contains
more
PhosphorusPhosphorus
+164.3%
Contains
more
ManganeseManganese
+334.7%
Contains
more
SeleniumSelenium
+1400%
Vitamins
The vitamin content of oregano is relatively higher. Oregano contains 30 times more Vitamin E, four times more Vitamin B1, five times more Vitamin B2 than basil. Vitamin K, Vitamin B3, and Vitamin B5, and Folate are also higher in oregano. On the other hand, basil contains more Vitamin C and Vitamin A. The amount of this Vitamin C is six times higher in basil than in oregano. Both contain no Vitamin B12 and Vitamin B9, and Vitamin D [5] [6].Vitamin Comparison
Contains
more
Vitamin CVitamin C
+682.6%
Contains
more
Vitamin AVitamin A
+210.6%
Contains
more
Vitamin EVitamin E
+2182.5%
Contains
more
Vitamin B1Vitamin B1
+420.6%
Contains
more
Vitamin B2Vitamin B2
+594.7%
Contains
more
Vitamin B3Vitamin B3
+414.4%
Contains
more
Vitamin B5Vitamin B5
+340.7%
Contains
more
Vitamin B6Vitamin B6
+573.5%
Contains
more
Vitamin KVitamin K
+49.9%
Contains
more
FolateFolate
+248.5%
Potassium
Potassium is an essential mineral, which may help normalize water balance and blood pressure in the body. Overall, oregano contains more potassium than basil. Oregano has 1260 mg potassium per 100 g, while basil has 295mg per 100g [4].
Glycemic Index
The glycemic index is the ranking of carbohydrates in the food that may promote better blood sugar management. The estimated glycemic index of oregano is 14 times lower; it is about 5, whereas the glycemic index of basil is about 70.
Health Benefits
Cancer
Basil contains antioxidants, such as lutein, beta-carotene, and beta-cryptoxanthin. These antioxidants have many health benefits; in particular, they may help reduce the risk of several types of cancer, including lung cancer, liver cancer, oral cancer, and skin cancer [7].
Oregano is also high in antioxidants, such as carvacrol and thymol, which may help fight damage from free radicals in the human body and help to stop the growth of cancer cells [8].
Cardiovascular Health
Oregano extract has been found to be potentially beneficial in lowering blood pressure by activating endothelial nitric oxide synthase. Additionally, it can bind to peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors (PPARs), which are also targeted by drugs such as Dapagliflozin and Fibrates that are used to treat various metabolic syndrome complications. This makes oregano extract a potential candidate for reducing cardiovascular risk [9].
A recent study has shown that a raw basil extract may reduce systolic, diastolic, and mean blood pressure in a dose-dependent manner. The median effective dose is 30 mg/kg. This antihypertensive effect is due to eugenol, which blocks calcium channels (like Amlodipine and Nicardipine). Additionally, in comparison with Captopril, basil reduced systolic and diastolic blood pressure by about 20 and 15 mm Hg, respectively, while captopril reduced them by 35 and 22 mm Hg [10, 11].
It's worth noting that consuming basil may help lower LDL (“bad” cholesterol) levels in the blood and prevent the development of atherosclerosis [12].
Diabetes
One study found that an extract from basil helped reduce high blood sugar levels. In particular, extract from sweet basil may help treat the long-term effects of high blood sugar [13].
According to one in vitro study, the extract from basil leaves helps manage the inhibition of a-glucosidase and pancreatic a-amylase enzymes. As a result, it may help to treat type 2 diabetes [14].
Anti-inflammation
Researches suggest that oregano may reduce inflammation. This herb contains essential oil and carvacrol, which according to a mouse study, reduced inflammation in those mice with colitis. However, human studies are needed.
Basil also contains essential oils, such as eugenol, linalool, and citronellol, that can help fight inflammation. Moreover, research shows that basil's essential oil may help treat various diseases that involve inflammation resulting from oxidative stress [15].
Improving Hair and Skin Health
Basil and oregano are rich in antioxidants and minerals, which have beneficial health properties. Oregano is rich in zinc, which is an essential mineral for human health. This mineral may help to promote the formation of collagen to make healthy hair growth [16].
Basil antioxidants have a substantial impact on reducing free radicals, thus can decrease oxidative stress and keeping your skin healthy. According to the study, basil extract in skin creams may improve skin hydration and reduce wrinkling [17].
Weight loss
The calorie level of oregano is almost ten times higher than in basil. In the case of low calories diets, basil is a good choice. Basil also is good if you are in low fats or low carbs diets, such as the Keto diet or Dukan diet. At the same time, let's not forget that people usually consume spices in small quantities, so calories will not matter so much.
The glycemic index of oregano is lower, so you can choose it in the case of low glycemic index diets. However, basil can spice up your meals but not contribute significant nutrients to your diet. During diets, use it with other nutritious foods [18].
Mental Health
Basil leaves contain properties that may help alleviate stress, depression, and anxiety, increase thinking ability, improve stress-related sleep, and lower the risk of age-related memory loss. The study showed that using 500 mg of basil extract daily may lower depression, anxiety, and stress. Besides, people who used it daily felt more social [19].
Side Effects
Basil is high in vitamin K, which may help blood clots. High intakes of this vitamin can interfere with blood-thinning drugs, such as warfarin [20].
Try to avoid holy basil if you're pregnant or trying to get pregnant. According to studies, holy basil may negatively affect sperm and trigger contractions in pregnancy [21].
Allergy
The allergy to basil is the result of our immune system mistakenly identifying basil as a harmful invader. Basil allergy symptoms usually include tingling or itching in the mouth, runny nose, and itchy eyes, rarely diarrhea. Oregano allergy symptoms mainly include rash, rarely stomach distress, or trouble breathing. Some people may be allergic to oregano oil. In this case, using oregano may cause inflammation of the airways and quickly become dangerous [22].
References
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/B9780857090393500049
- https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1002/jsfa.2740330508
- https://academic.oup.com/ajcn/article/70/3/491s/4714940?login=true
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0260877404003875
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0968089619311368
- https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/abs/10.1017/S0043933918000454
- https://hort.purdue.edu/newcrop/ncnu02/pdf/juliani.pdf
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/24629960/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/19053389/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3210006/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/20448636/
- https://www.nature.com/articles/s41598-021-01713-5
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6542390/
- https://journals.sagepub.com/doi/abs/10.1177/0748233711403193
- https://www.koreascience.or.kr/article/JAKO201713647762249.page
- http://bergenhelse.no/wp-content/uploads/2019/06/A-potential-medicinal-importance-of-zinc-in-human-health-and-chronic-disease.pdf
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3304398/
- https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/abs/10.1080/10408398.2013.805713
- https://www.researchgate.net/publication/284800393_A_clinical_study_on_the_management_of_generalized_anxiety_disorder_with_Vaca_Acorus_calamus
- https://ods.od.nih.gov/factsheets/VitaminK-HealthProfessional/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/2844661/
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S1081120611004686
Infographic
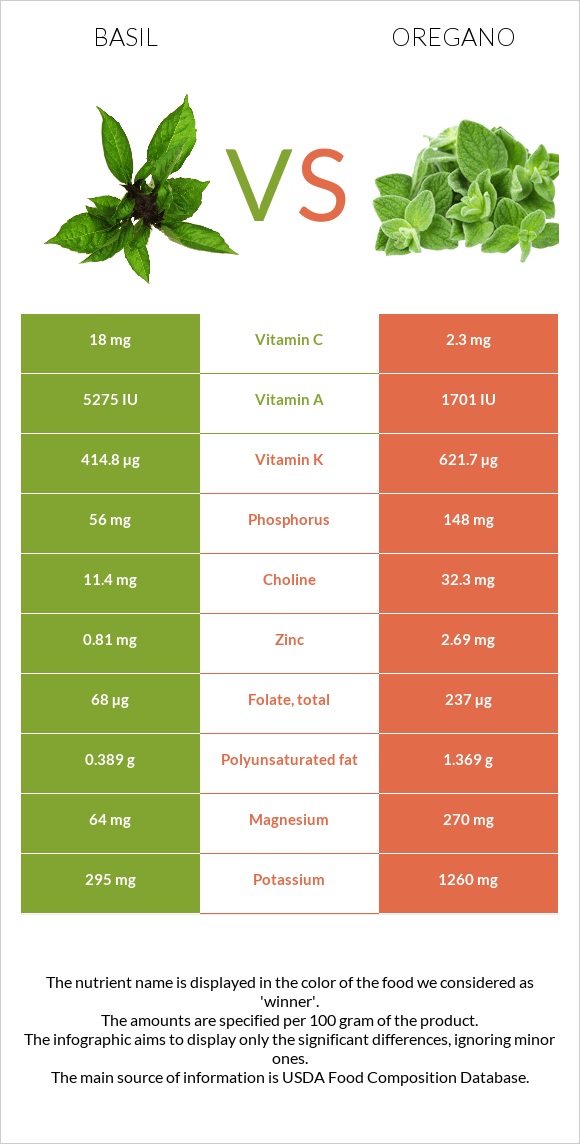
All nutrients comparison - raw data values
| Nutrient |  |
 |
DV% diff. |
| Iron | 3.17mg | 36.8mg | 420% |
| Vitamin K | 414.8µg | 621.7µg | 172% |
| Manganese | 1.148mg | 4.99mg | 167% |
| Fiber | 1.6g | 42.5g | 164% |
| Calcium | 177mg | 1597mg | 142% |
| Vitamin E | 0.8mg | 18.26mg | 116% |
| Vitamin B6 | 0.155mg | 1.044mg | 68% |
| Magnesium | 64mg | 270mg | 49% |
| Folate | 68µg | 237µg | 42% |
| Vitamin B2 | 0.076mg | 0.528mg | 35% |
| Potassium | 295mg | 1260mg | 28% |
| Copper | 0.385mg | 0.633mg | 28% |
| Vitamin B3 | 0.902mg | 4.64mg | 23% |
| Carbs | 2.65g | 68.92g | 22% |
| Vitamin A | 264µg | 85µg | 20% |
| Vitamin C | 18mg | 2.3mg | 17% |
| Zinc | 0.81mg | 2.69mg | 17% |
| Vitamin B5 | 0.209mg | 0.921mg | 14% |
| Phosphorus | 56mg | 148mg | 13% |
| Calories | 23kcal | 265kcal | 12% |
| Protein | 3.15g | 9g | 12% |
| Vitamin B1 | 0.034mg | 0.177mg | 12% |
| Selenium | 0.3µg | 4.5µg | 8% |
| Saturated fat | 0.041g | 1.551g | 7% |
| Polyunsaturated fat | 0.389g | 1.369g | 7% |
| Fats | 0.64g | 4.28g | 6% |
| Choline | 11.4mg | 32.3mg | 4% |
| Monounsaturated fat | 0.088g | 0.716g | 2% |
| Sodium | 4mg | 25mg | 1% |
| Fructose | 0.02g | 1.13g | 1% |
| Net carbs | 1.05g | 26.42g | N/A |
| Sugar | 0.3g | 4.09g | N/A |
| Tryptophan | 0.039mg | 0.203mg | 0% |
| Threonine | 0.104mg | 0.322mg | 0% |
| Isoleucine | 0.104mg | 0.441mg | 0% |
| Leucine | 0.191mg | 0.78mg | 0% |
| Lysine | 0.11mg | 0.5mg | 0% |
| Methionine | 0.036mg | 0.127mg | 0% |
| Phenylalanine | 0.13mg | 0.449mg | 0% |
| Valine | 0.127mg | 0.585mg | 0% |
| Histidine | 0.051mg | 0.144mg | 0% |
| Omega-3 - ALA | 0.621g | N/A |
Macronutrient Comparison
| Contains more WaterWater | +827.1% |
| Contains more ProteinProtein | +185.7% |
| Contains more FatsFats | +568.8% |
| Contains more CarbsCarbs | +2500.8% |
| Contains more OtherOther | +424.7% |
Fat Type Comparison
| Contains less Sat. FatSaturated fat | -97.4% |
| Contains more Mono. FatMonounsaturated fat | +713.6% |
| Contains more Poly. FatPolyunsaturated fat | +251.9% |
Carbohydrate type comparison
| Contains more GalactoseGalactose | +80% |
| Contains more SucroseSucrose | +∞% |
| Contains more GlucoseGlucose | +9400% |
| Contains more FructoseFructose | +5550% |
People also compare
References
All the values for which the sources are not specified explicitly are taken from FDA’s Food Central. The exact link to the food presented on this page can be found below.
- Basil - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/172232/nutrients
- Oregano - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/171328/nutrients
All the Daily Values are presented for males aged 31-50, for 2000-calorie diets.





