Feta vs. Ricotta — Health Impact and Nutrition Comparison


Summary
Feta is richer in proteins and has a higher fat content. Feta has richer and more versatile vitamin and mineral profiles. Ricotta is lower in calories, sodium, and carbs and is cheaper. Ricotta is lower in sodium which is a more important difference between them.
Introduction
Feta is a white cheese that originated in Greece in the 8th century BC. Feta cheese is usually made with sheep’s milk or goat’s milk, often it could be mixed. Nowadays, feta cheese is spread all over the world and it is part of different culinary cultures.
Ricotta cheese is a white cheese that has a sweeter taste than feta cheese. Ricotta can be made from cow’s milk, sheep’s milk, or goat’s milk. It is usually prepared from the remainder of milk products after being used to prepare different types of cheeses or yogurts. It originated in Italy, it is assumed that ricotta production dates back to around 200 AD.
What is the actual difference?
There are differences between feta and ricotta. These differences vary among different aspects that are price, shelf life, taste and flavor, and origin among other points that are discussed further in the article.
Price
Feta cheese is relatively cheaper than ricotta. The average price per pound of feta cheese is around $7 whereas ricotta costs 13$ on average. Of course, cheaper versions of the same cheeses are available in the market however, on average, feta is cheaper.
Shelf life
After being open ricotta and feta have similar shelf lives which are around 5 days in the refrigerator and properly stored. However, if unopened, feta cheese remains for up to 1 month whereas ricotta remains for about 2 weeks.
Taste and flavor
Relatively speaking, the taste and texture are different between feta and ricotta. Feta has a slightly more acidic taste with a crumbling texture. Whereas ricotta has a sweeter flavor and leans towards a creamier texture. Both kinds of cheese are white.
Origin
As mentioned in the introduction, feta and ricotta have different origins. Feta originated in Greece whereas ricotta originated in Italy.
Culinary world
Feta is a white cheese that is mostly associated with olive or tapenade, olive paste. It is usually considered a “refreshing cheese”, meaning that it can be served as a cold topping on a greek salad. In addition to that, feta can be served as a topping on pizza or even made as a pasta sauce base with olive oil and cherry tomatoes.
Ricotta has an advantage over feta in gastronomy. Ricotta is more versatile than feta. Mainly due to its slightly creamier texture and sweeter flavor. Ricotta can replace sweet yogurts, it can be served with pancakes for breakfast. Ricotta is also used as a base for cheesecake, ice cream, tart, and preparations of other types of sweets and desserts.
In this article, we are going to be comparing the difference between feta cheese and ricotta according to their nutritional content difference, diet and weight loss effects, and health impacts.
Nutritional content comparison
Glycemic index
Both feta and ricotta have the same glycemic index which is equal to 27. They are classified as low glycemic index foods.
Calories
Feta is higher in calories compared to ricotta. Feta contains 1.5 times more calories than ricotta.
Carbs
Feta contains more carbs than ricotta. However, feta and ricotta are not high in carbs.
Proteins
Feta is richer in proteins compared to ricotta. Also, it is important to mention that they are rich in proteins. In addition to that, feta has a complete essential amino acid profile that is richer and more complete than that of ricotta.
Fat
Feta is higher in fats compared to ricotta. Feta contains 1.6 times more fat than ricotta. It is important to mention that their fat content is mostly distributed as saturated fats. In addition to that, feta contains as much saturated fat as there are total fats in ricotta cheese. This is important to take into consideration when it comes to their comparison.
Cholesterol
Similar to the fat content, feta is also higher in cholesterol compared to ricotta. 100g of feta can fill ⅓ of the recommended daily value of cholesterol.
Trans fat
Feta is higher in trans fats than ricotta.
Mineral content
Feta is richer in vitamins than ricotta. Feta contains more phosphorus, zinc, and calcium. On the other hand, it is important to mention that feta is high in sodium. The sodium content of feta is very high compared to ricotta.
Mineral Comparison
Contains
more
MagnesiumMagnesium
+72.7%
Contains
more
CalciumCalcium
+138.2%
Contains
more
IronIron
+71.1%
Contains
more
CopperCopper
+52.4%
Contains
more
ZincZinc
+148.3%
Contains
more
PhosphorusPhosphorus
+113.3%
Contains
more
ManganeseManganese
+366.7%
Contains
more
PotassiumPotassium
+69.4%
Contains
less
SodiumSodium
-90.8%
Vitamins
Feta has a richer and more versatile vitamin content compared to ricotta. Feta is richer in B complex vitamins, B1, B2, B3, B5, B6, B12, and folate. The amounts of vitamins B2, B6, and B12 are very high thus making feta an important source of these vitamins.
Vitamin Comparison
Contains
more
Vitamin EVitamin E
+63.6%
Contains
more
Vitamin DVitamin D
+100%
Contains
more
Vitamin B1Vitamin B1
+1084.6%
Contains
more
Vitamin B2Vitamin B2
+332.8%
Contains
more
Vitamin B3Vitamin B3
+852.9%
Contains
more
Vitamin B5Vitamin B5
+354%
Contains
more
Vitamin B6Vitamin B6
+886%
Contains
more
Vitamin B12Vitamin B12
+397.1%
Contains
more
Vitamin KVitamin K
+63.6%
Contains
more
FolateFolate
+166.7%
Diet and weight loss
Feta and ricotta are well fit for diets that are aimed at losing weight. They are both flavor-rich and versatile in their usages for different types of dishes. It is important to take into consideration the sodium amounts of feta. Ricotta on the other hand doesn’t have high sodium levels and it provides good alternatives in dessert preparations and sweets.
Vegan
Both feta and ricotta are dairy products meaning that they cannot be consumed in the vegan diet.
Keto
Feta and ricotta are low in carbs and are categorized as low glycemic index foods. They can be consumed in the keto diet. However, as mentioned above feta contains elevated amounts of sodium which should be taken into consideration.
Health impacts
Cardiovascular health
Both feta and ricotta are dairy products that may contain saturated fats, which can increase the risk of cardiovascular disease by raising LDL ("bad" cholesterol) levels. Ricotta tends to be lower in saturated fat than feta (1).
Feta cheese is often high in sodium due to the brining process used in its preparation. High sodium intake is linked to hypertension and cardiovascular problems. On the other hand, ricotta typically has a lower sodium content, particularly if you choose low-sodium varieties (1, 2).
Both feta and ricotta cheese contain peptides that have been found to exhibit ACE (angiotensin-converting enzyme) inhibition activity, which can help lower blood pressure. However, the specific ACE inhibition activity of feta versus ricotta may vary depending on factors such as processing methods, fermentation duration, and the specific strains of bacteria used in production (3, 4).
Ricotta tends to be lower in calories compared to feta, making it a potentially better option for individuals looking to manage their weight, which is a risk factor for cardiovascular disease.
In summary, while both feta and ricotta can be part of a healthy diet, ricotta may have a slight advantage over feta in terms of its potential impact on cardiovascular health due to its lower saturated fat and sodium content. However, moderation and overall dietary balance are crucial, and individual health considerations should always be taken into account.
Diabetes
Low glycemic index cheese that contains low carbohydrates are not associated with an increased risk of developing type 2 diabetes. In this case, feta cheese and ricotta are both low in carbs and are categorized as low glycemic index foods, thus there is no association with developing type 2 diabetes. (5)
Cancer
Ricotta is associated with a decreased risk of developing breast cancer in women. Although there are many variables in factors of breast cancer development like age, number of pregnancies, etc... The ricotta was among the dairy foods that were negatively associated with the development of breast cancer. (6)
Prostate cancer is a concern in men, many factors have input in increasing or decreasing the risks of developing prostate cancer. In turn consumption of any type of dairy high fat or low fat, including feta and ricotta an increased risk of developing prostate cancer was observed. (7)
In cases of esophageal, gastric, pancreatic, and colorectal cancers there was no association of cancer development with dairy consumption, in this case, feta or ricotta. (8)
Intolerance and allergies
Feta and ricotta are not very high in carbs, their lactose levels are not elevated to cause issues in lactose-intolerant individuals. However, it could be that some individuals might have symptoms of lactose intolerance after eating feta or ricotta. To help with digestion, digestive enzymes can be taken to help digest them.
If the cheeses are made with goat’s milk, many individuals suffer from goat’s milk allergies and intolerances thus it might cause a problem for them. Similarly is the case of whey allergies. (9) (10)
References
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5867544/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/26997359/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/34828854/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC9855406/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5572495/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/12394243/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4754664/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6352799/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/12018807/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/17594876/
Infographic
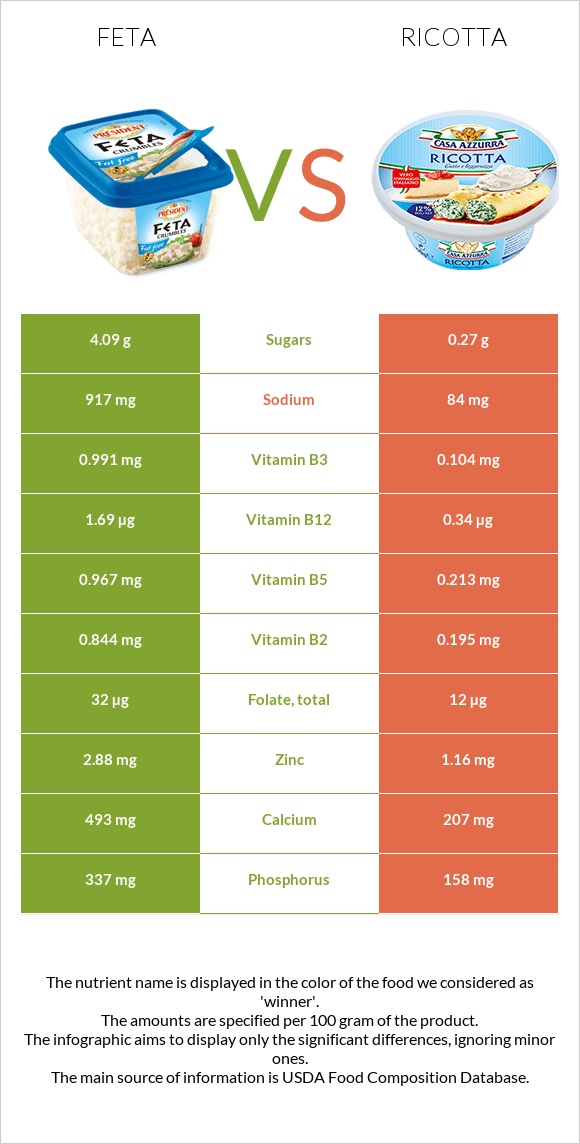
All nutrients comparison - raw data values
| Nutrient |  |
 |
DV% diff. |
| Vitamin B12 | 1.69µg | 0.34µg | 56% |
| Vitamin B2 | 0.844mg | 0.195mg | 50% |
| Sodium | 917mg | 84mg | 36% |
| Saturated fat | 14.946g | 8.295g | 30% |
| Calcium | 493mg | 207mg | 29% |
| Vitamin B6 | 0.424mg | 0.043mg | 29% |
| Phosphorus | 337mg | 158mg | 26% |
| Zinc | 2.88mg | 1.16mg | 16% |
| Vitamin B5 | 0.967mg | 0.213mg | 15% |
| Fats | 21.28g | 12.98g | 13% |
| Cholesterol | 89mg | 51mg | 13% |
| Vitamin B1 | 0.154mg | 0.013mg | 12% |
| Protein | 14.21g | 11.26g | 6% |
| Vitamin B3 | 0.991mg | 0.104mg | 6% |
| Calories | 264kcal | 174kcal | 5% |
| Folate | 32µg | 12µg | 5% |
| Iron | 0.65mg | 0.38mg | 3% |
| Magnesium | 19mg | 11mg | 2% |
| Monounsaturated fat | 4.623g | 3.627g | 2% |
| Vitamin D | 16 IU | 10 IU | 1% |
| Potassium | 62mg | 105mg | 1% |
| Copper | 0.032mg | 0.021mg | 1% |
| Vitamin A | 125µg | 120µg | 1% |
| Vitamin D | 0.4µg | 0.2µg | 1% |
| Manganese | 0.028mg | 0.006mg | 1% |
| Selenium | 15µg | 14.5µg | 1% |
| Vitamin K | 1.8µg | 1.1µg | 1% |
| Polyunsaturated fat | 0.591g | 0.385g | 1% |
| Net carbs | 4.09g | 3.04g | N/A |
| Carbs | 4.09g | 3.04g | 0% |
| Sugar | 4.09g | 0.27g | N/A |
| Vitamin E | 0.18mg | 0.11mg | 0% |
| Choline | 15.4mg | 17.5mg | 0% |
| Tryptophan | 0.2mg | 0.125mg | 0% |
| Threonine | 0.637mg | 0.517mg | 0% |
| Isoleucine | 0.803mg | 0.589mg | 0% |
| Leucine | 1.395mg | 1.221mg | 0% |
| Lysine | 1.219mg | 1.338mg | 0% |
| Methionine | 0.368mg | 0.281mg | 0% |
| Phenylalanine | 0.675mg | 0.556mg | 0% |
| Valine | 1.065mg | 0.692mg | 0% |
| Histidine | 0.397mg | 0.459mg | 0% |
Macronutrient Comparison
| Contains more ProteinProtein | +26.2% |
| Contains more FatsFats | +63.9% |
| Contains more CarbsCarbs | +34.5% |
| Contains more OtherOther | +409.8% |
| Contains more WaterWater | +29.8% |
Fat Type Comparison
| Contains more Mono. FatMonounsaturated fat | +27.5% |
| Contains more Poly. FatPolyunsaturated fat | +53.5% |
| Contains less Sat. FatSaturated fat | -44.5% |
People also compare
References
All the values for which the sources are not specified explicitly are taken from FDA’s Food Central. The exact link to the food presented on this page can be found below.
- Feta - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/173420/nutrients
- Ricotta - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/170851/nutrients
All the Daily Values are presented for males aged 31-50, for 2000-calorie diets.