Russet potato vs. Rutabagas — Health Impact and Nutrition Comparison


Summary
Russet potatoes are more nutrient-dense than rutabagas, containing 75% water compared to rutabagas' 90%. Both have no cholesterol and low fiber.
Russet potatoes are rich in iron, magnesium, phosphorus, potassium, sodium, zinc, copper, and manganese, while rutabagas are higher in calcium and selenium.
Russet potatoes have more vitamins K, A, and B compared to rutabagas. Rutabagas contain more vitamins B1, C, and E.
Introduction
Russet potatoes and rutabagas are widely used vegetables, both packed with vitamins and minerals. We'll discuss their differences, focusing on their nutritional value and health impact.
What's The Actual Difference?
Classification and Appearance
The potato plant belongs to the Solanaceae family, the Solanum genus, whereas rutabagas belong to the Cabbages genus. The Solanaceae family includes tomatoes, chili, and bell peppers.
The main difference is that rutabagas are purple on the outside, larger, and more bitter than russet potatoes. Russet potatoes usually have dark brown skin and few eyes.
Taste
Russet potato has an earthy, mild taste with a sweet aftertaste. In contrast, rutabagas have a strong smell and are bitter. They taste like a little sweet carrot.
Nutrition
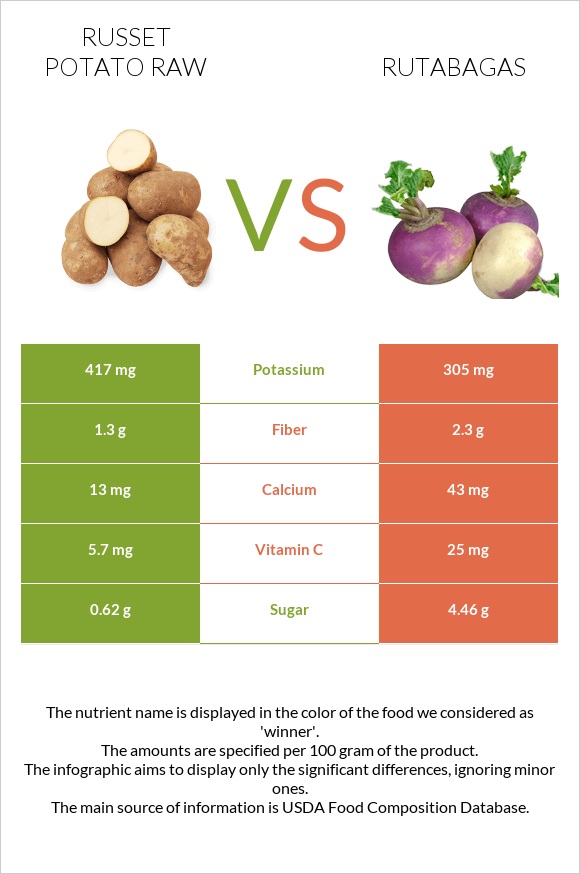
Below are infographics comparing baked russet potatoes and raw rutabagas for 100g servings. However, the average serving size per person for russet potatoes can vary depending on their size, with 138g, 173g, or 299g being typical. Similarly, rutabagas can range from 192g, 386g, 772g, or one cup weighing 140g.
Please note that these serving sizes are not recommendations but just typical amounts.
To better understand the nutritional differences between these two vegetables, please refer to our nutrition table at the bottom of the page.
Macronutrients and Calories
Russet potatoes are more nutrient-dense than rutabagas. Russet potatoes contain about 75% water, while rutabagas contain about 90%.
Rutabagas have fewer calories than russet potatoes, with 37 kcal per 100g for rutabagas and 97 kcal for russet potatoes.
Protein
Russet potatoes contain all essential amino acids, while rutabagas do not. Additionally, russet potatoes have 2.63g of protein per 100g, compared to 1.08g in rutabagas.
The dietary benefits and bodybuilding benefits will be discussed in the upcoming paragraphs.
Fat
Both russet potatoes and rutabagas have negligible amounts of fat. Russet potatoes contain 0.13g of fat per 100g, while rutabagas have 0.16g.
It's worth noting that rutabagas contain more beneficial mono- and polyunsaturated fats and fewer saturated fats than russet potatoes. Neither of them contains any cholesterol.
Carbohydrates
Russet potatoes have more carbs than rutabagas - 21.44g per 100g compared to 8.62g per 100g, respectively.
Russet potatoes contain around 44 times more starch than rutabagas.
Net Carbs
89% (19.14g) of russet potato carbs are net carbs, while rutabaga contains 73% (6.32g) of net carbs.
Dietary Fiber
It is important to note that russet potatoes and rutabagas contain only 2.3g of dietary fiber, which is considered low.
Consuming the recommended amount of fiber is essential for a healthy diet. Women should aim for 28g and men for 34g daily to meet the 2020-2025 Dietary Guidelines for Americans (1).
Minerals
It's important to note that russet potatoes have a more varied mineral profile than rutabaga.
Russet potatoes are rich in iron, magnesium, phosphorus, potassium, sodium, zinc, copper, and manganese, whereas rutabagas are higher in calcium and selenium.
Mineral Comparison
Contains
more
MagnesiumMagnesium
+15%
Contains
more
PotassiumPotassium
+36.7%
Contains
more
IronIron
+95.5%
Contains
more
CopperCopper
+221.9%
Contains
more
ZincZinc
+20.8%
Contains
less
SodiumSodium
-58.3%
Contains
more
ManganeseManganese
+19.8%
Contains
more
CalciumCalcium
+230.8%
Contains
more
SeleniumSelenium
+75%
Vitamins
Russet potatoes contain more lipid-soluble vitamins, such as vitamin A and vitamin K, than rutabagas. Besides, russet potatoes are high in vitamins B2, B3, B5, B6, and B9. Meanwhile, rutabaga is richer in vitamins E, C, and B1.
It is important to mention that eating 100g of russet potatoes can provide approximately 6.5% of the daily value (DV) required for vitamin B9 or folate, while 100g of rutabagas can provide 7.5% of the DV required for vitamin B1 or thiamin.
Vitamin Comparison
Contains
more
Vitamin B3Vitamin B3
+47.9%
Contains
more
Vitamin B5Vitamin B5
+88.1%
Contains
more
Vitamin B6Vitamin B6
+245%
Contains
more
Vitamin KVitamin K
+500%
Contains
more
Vitamin CVitamin C
+338.6%
Contains
more
Vitamin EVitamin E
+2900%
Contains
more
Vitamin B2Vitamin B2
+21.2%
Contains
more
FolateFolate
+50%
Glycemic Index
Boiled rutabaga has a glycemic index of 72 (2), while the glycemic index of a russet potato is unknown.
Health Impact
Cardiovascular Health
Potatoes are a good source of nutrients that can help improve blood pressure and promote fullness. However, the scientific evidence on the effects of eating whole potatoes on body weight and disease risk is inconsistent. Further studies, particularly randomized controlled trials, are required to determine the specific impact of potato consumption on health outcomes and disease states (3).
Research has shown that both rutabagas and russet potatoes contain potassium and fiber, which can effectively lower risk factors for cardiovascular disease. However, further research is required to establish the extent of their benefits (4,5).
Cancer
Rutabaga is high in glucosinolates and vitamin C, which have antioxidant properties. They've been shown to reduce inflammation and may even lower your risk of breast cancer (6).
There have been several test-tube studies on russet potatoes' antioxidants and cancer-prevention properties; however, more human-based research is required before making any health recommendations (7).
Bowel Health
As mentioned above, rutabaga is an excellent source of insoluble fiber. A diet rich in insoluble fiber may help soften stool and promote bowel movements. Besides, this type of fiber is a food for the gut microbiome. Hence, rutabaga consumption may also promote the growth of friendly bacteria in your large intestine (10).
Side Effects
Rutabagas are considered relatively safe vegetables but may not be suitable for people with gallstones. Goitrogenic foods can impair thyroid function by inhibiting thyroid hormone synthesis, leading to gland enlargement. Cooking and increasing selenium intake can lower the risk of side effects in people with thyroid dysfunction (8).
Because russet potatoes are high in starch, they can cause stomach pain if consumed in large quantities (9).
References
- https://www.dietaryguidelines.gov/sites/default/files/2020-12/Dietary_Guidelines_for_Americans_2020-2025.pdf
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/6259925/
- https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s12230-018-09705-4
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29066442/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4072837/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/23211939/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/19149749/
- https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s00394-012-0397-2
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31706777/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/22861801/
Infographic
All nutrients comparison - raw data values
| Nutrient |  |
 |
DV% diff. |
| Vitamin C | 5.7mg | 25mg | 21% |
| Vitamin B6 | 0.345mg | 0.1mg | 19% |
| Copper | 0.103mg | 0.032mg | 8% |
| Starch | 15.86g | 0.4g | 6% |
| Iron | 0.86mg | 0.44mg | 5% |
| Fiber | 1.3g | 2.3g | 4% |
| Carbs | 18.07g | 8.62g | 3% |
| Calcium | 13mg | 43mg | 3% |
| Potassium | 417mg | 305mg | 3% |
| Vitamin B5 | 0.301mg | 0.16mg | 3% |
| Calories | 79kcal | 37kcal | 2% |
| Protein | 2.14g | 1.08g | 2% |
| Vitamin E | 0.01mg | 0.3mg | 2% |
| Vitamin B3 | 1.035mg | 0.7mg | 2% |
| Folate | 14µg | 21µg | 2% |
| Fructose | 0.23g | 1.61g | 2% |
| Magnesium | 23mg | 20mg | 1% |
| Manganese | 0.157mg | 0.131mg | 1% |
| Selenium | 0.4µg | 0.7µg | 1% |
| Vitamin B1 | 0.082mg | 0.09mg | 1% |
| Vitamin B2 | 0.033mg | 0.04mg | 1% |
| Vitamin K | 1.8µg | 0.3µg | 1% |
| Fats | 0.08g | 0.16g | 0% |
| Net carbs | 16.77g | 6.32g | N/A |
| Sugar | 0.62g | 4.46g | N/A |
| Zinc | 0.29mg | 0.24mg | 0% |
| Phosphorus | 55mg | 53mg | 0% |
| Sodium | 5mg | 12mg | 0% |
| Choline | 12.6mg | 14.1mg | 0% |
| Saturated fat | 0.026g | 0.027g | 0% |
| Monounsaturated fat | 0.002g | 0.025g | 0% |
| Polyunsaturated fat | 0.043g | 0.088g | 0% |
Macronutrient Comparison
| Contains more ProteinProtein | +98.1% |
| Contains more CarbsCarbs | +109.6% |
| Contains more OtherOther | +59.2% |
| Contains more FatsFats | +100% |
| Contains more WaterWater | +13.8% |
Fat Type Comparison
| Contains more Mono. FatMonounsaturated fat | +1150% |
| Contains more Poly. FatPolyunsaturated fat | +104.7% |
Carbohydrate type comparison
| Contains more StarchStarch | +3865% |
| Contains more SucroseSucrose | +307.7% |
| Contains more GlucoseGlucose | +820% |
| Contains more FructoseFructose | +600% |
| Contains more MaltoseMaltose | +∞% |
References
All the values for which the sources are not specified explicitly are taken from FDA’s Food Central. The exact link to the food presented on this page can be found below.
- Russet potato raw - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/170027/nutrients
- Rutabagas - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/168454/nutrients
All the Daily Values are presented for males aged 31-50, for 2000-calorie diets.
