Saffron vs. Safflower — Health Impact and Nutrition Differences
Summary
Saffron contains more fiber and carbs, while safflower is higher in fats and proteins. Safflower seeds are naturally higher in B-complex vitamins. In contrast, saffron is higher in vitamins A and C.
Saffron has more iron, calcium, manganese, and potassium. At the same time, safflower is higher in magnesium, zinc, copper, and phosphorus.
Introduction
Saffron is the world's most expensive spice due to its labor-intensive harvesting method.
Talking about saffron, it's important to mention that it can be real or high-quality and fake or low-quality. Fake or poor quality saffron is safflower, sometimes called bastard saffron, poor men's, or false saffron. Many people may mistakenly use safflower instead of saffron.
The main differences between saffron and safflower and their impacts on health will be provided in this article.
What's The Actual Difference?
Saffron has a bitter taste and sweet aroma. Safflower has a mild sweet taste and almost no aroma. Besides, you need a pinch of saffron to give the food a rich yellow or orange color, whereas you will need to use more safflower for a similar effect.
Saffron has a more delicate color compared to safflower. High-quality saffron has deep red trumpet-shaped threads or stamens. Safflower or fake saffron consists of thistle-like petals instead of threads when comparing these two. The petals of safflower can vary in color in different shades of red.
Varieties
Saffron (Crocus sativus) belongs to the Crocus genus, related to ginger. The common saffron type is the Persian saffron, native to Ancient Persia. Saffron is the stigma of the plant flower.
Safflower (Carthamus tinctorius) belongs to the Carthamus genus. This herb produces two types of oil: one is high in monounsaturated oleic fatty acid, and the other is high in polyunsaturated linoleic fatty acid.
Uses
Saffron is used in medicine, culinary, as well as for dyes such as food coloring and cosmetics.
Saffron works great with rice dishes, stews, soups, and salads. Some of the dishes are bouillabaisse, Spanish paella, Tachin (Persian saffron rice), chicken and corn soup, Milanese risotto, some cakes, Swedish buns, rice pudding, spaghettoni, and others. One of the healthiest things to make from saffron is saffron tea.
Safflower is mostly cultivated for its seeds to make safflower oil. However, it can be used as a replacement for saffron, as a food coloring, and as tea as well.
Safflower is not the best saffron substitute if the taste matters, as safflower, has a mild taste and almost no aroma. Still, the blandness makes safflower a better choice for someone who doesn't like the taste but likes the color.
Safflower can be used along with saffron as well to use less saffron and save money.
Nutrition
The nutritional values are presented for saffron and dried safflower seeds.
A nutrition infographic at the bottom of this page visually shows the main differences between safflower and saffron.
Macronutrients
Macronutrient Comparison
Contains
more
CarbsCarbs
+90.6%
Contains
more
WaterWater
+111.7%
Contains
more
ProteinProtein
+41.6%
Contains
more
FatsFats
+557.3%
Comparing these spices, we can see that saffron contains more fiber and carbs, while safflower is higher in fats and protein.
Both contain no cholesterol.
Vitamins
Vitamin Comparison
Contains
more
Vitamin CVitamin C
+∞%
Contains
more
Vitamin AVitamin A
+800%
Contains
more
Vitamin B1Vitamin B1
+911.3%
Contains
more
Vitamin B2Vitamin B2
+55.4%
Contains
more
Vitamin B3Vitamin B3
+56.4%
Contains
more
Vitamin B6Vitamin B6
+15.8%
Contains
more
FolateFolate
+72%
Safflower seeds are naturally higher in most vitamins than saffron. Safflower contains more B-complex vitamins: vitamins B1, B2, B3, B6, and B9 (folate). On the other hand, saffron has more vitamins A and C.
Both lack Vitamin D, Vitamin E, Vitamin K, Vitamin B5, and Vitamin B12. In addition, safflower has no Vitamin C.
Minerals
Mineral Comparison
Contains
more
CalciumCalcium
+42.3%
Contains
more
PotassiumPotassium
+150.9%
Contains
more
IronIron
+126.5%
Contains
more
ManganeseManganese
+1310.5%
Contains
more
SeleniumSelenium
+∞%
Contains
more
MagnesiumMagnesium
+33.7%
Contains
more
CopperCopper
+432.6%
Contains
more
ZincZinc
+363.3%
Contains
more
PhosphorusPhosphorus
+155.6%
Contains
less
SodiumSodium
-98%
Both saffron and safflower are packed with minerals, but mineral amounts differ. Saffron has more iron, calcium, manganese, and potassium than safflower. On the other hand, safflower is higher in magnesium, zinc, copper, and phosphorus and contains less sodium than saffron.
Glycemic Index
No information is provided about the glycemic index values of saffron and safflower.
Acidity
There is no information provided about the pH of these foods as well.
However, the PRAL value or potential renal acid load value is calculated for these foods. The PRAL value shows the acidifying effect of the given food on the host's body.
The PRAL value of saffron is -29.6, making it base-producing, whereas the PRAL value of safflower is 7.1 making it acid-producing.
Diets
Saffron is a better choice for low-calorie and low-fat diets. On the other hand, safflower is the preferred choice for a low-carb diet.
Saffron is not strictly keto-friendly, but it can still be consumed in moderation during the keto diet.
As mentioned before, the two types of safflower produce either high oleic or high linoleic oils, and during the keto diet, high oleic safflower oil is the preferred choice. Safflower seeds are keto-friendly as well.
Safflower oil may be consumed during the DASH and Atkins diets.
Saffron and high oleic safflower oil can be consumed during the Mediterranean diet.
Health Benefits
Diabetes
According to research, safflower oil may help improve insulin sensitivity and reduce blood cholesterol and sugar levels in obese postmenopausal women with type 2 diabetes. What's more, safflower oil may reduce abdominal fat and increase muscle tissue in this group of women after 16 weeks, as it contains a polyunsaturated fatty acid called linoleic acid (1).
On the other hand, saffron may also be beneficial for type 2 diabetes. Research shows that hydroalcoholic saffron extract may significantly improve blood glucose control by lowering serum FBS levels in type 2 diabetic patients. However, more research is required (2).
Anti-inflammatory Effects
According to studies, safflower is an excellent source of polyphenolic compounds. These compounds inhibit nitric oxide synthase's pro-inflammatory activity and have anti-inflammatory, anti-bacterial, and antioxidant effects (3).
On the other hand, saffron also contains antioxidants, which have anti-inflammatory effects. This plant contains kaempferol, a compound that may help to reduce inflammation (4).
Weight Loss
In one eight-week study, women who took saffron supplements felt more satiated and lost significantly more weight than women in the placebo group.
Other research shows that saffron extract may help people with coronary heart disease by lowering body mass index, total fat mass, and waist circumference. The study found that people taking the supplement also had decreased appetite. Cooking saffron is an easy way to add it to your diet without the increasing risk of snacking (5).
Cancer
Saffron is an excellent source of potent antioxidants, including crocin, picrocrocin, and safranal, which help fight against oxidative stress and free radicals. Free radicals damage human cells, increasing the risk of several types of cancers. Besides, mentioned antioxidants can contribute to the death of cancer cells and reduce angiogenesis (6).
Research shows that safflower seeds inhibit the proliferation of human cancer cells, particularly breast cancer cells (7).
Cardiovascular Health
Saffron and safflower are two distinct plants with different properties, including potential effects on cardiovascular disease (CVD).
Studies have shown that saffron may have cardiovascular benefits. For example, research indicates that saffron may help lower blood pressure, improve lipid profile (including reducing LDL (“bad” cholesterol) and increasing HDL (“good” cholesterol) levels), and have antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects, which could potentially reduce the risk of CVD (8).
Safflower oil is rich in unsaturated fatty acids, particularly linoleic acid, which is an omega-6 fatty acid. Some studies suggest that replacing saturated fats with unsaturated fats, such as those found in safflower oil, can improve cardiovascular health by reducing LDL cholesterol levels. However, the evidence on safflower oil's specific effects on CVD is mixed, and more research is needed to fully understand its potential benefits (9).
To summarize, saffron and safflower both offer some cardiovascular benefits, but the reason behind saffron's positive impact is its antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties while safflower oil's benefits can be attributed to its unsaturated fatty acid content. It's important to keep in mind that as with any dietary component, it's crucial to consume these in moderation and as part of a balanced diet.
Aphrodisiac Effect
Research has shown that saffron has aphrodisiac effects, especially in people taking antidepressants. According to a study, a daily intake of 30 mg of saffron for four weeks may improve erectile function compared to a placebo in men with erectile dysfunction.
In addition, an analysis of six studies found that saffron supplementation significantly improved erectile function, libido, and overall satisfaction but did not improve sperm performance (10).
Digestion & Liver
Crocin found in saffron may show beneficial effects on patients with gastritis, peptic ulcer, and inflammatory bowel disease; curcurin shows similar effects in patients with irritable bowel syndrome or IBS. The hepatoprotective activity of saffron is mainly due to its antioxidant properties (11).
Safflower seed powder shows hepatoprotection against non-alcoholic fatty liver disease, the most common liver disease (12).
Neurological & Mental Health
Several studies have shown that saffron is as effective as Donepezil in the treatment of mild-to-moderate Alzheimer’s disease. Saffron may reduce neurodegeneration, improve learning ability and cognitive functions, and enhance memory (13).
In animal and human studies, saffron has shown anticonvulsant activities (prevention of seizures) and reduced withdrawal or discontinuation syndrome occurring in people who have a psychological dependence on alcohol or drugs (14).
Saffron may reduce anxiety and depression symptoms (15, 16). It has a significant effect on the severity of depression (17).
A study on 22 healthy elderly women and men shows that safflower oil can enhance memory performance and attention without enhancing blood sugar levels (18).
Ocular Health
Daily intake of 30mg saffron for 6 months may result in a significant improvement in retinal function in patients with age-related macular degeneration over the mid-term (19). Short-term saffron supplementation may improve retinal flicker sensitivity in patients as well (20).
Skin Health
Safflower seed oil, along with other vegetable oils, has anti-inflammatory and antioxidant effects on the skin and helps in wound healing and repairment of the skin barrier (21). It has antimicrobial and antifungal properties as well (22).
Safflower seed oil and its active compound acatecin inhibit ultraviolet-induced skin photoaging and may have the potential as an anti-wrinkle agent as well (23).
According to an animal study, safflower water extract may improve skin condition in systematic scleroderma patients due to reduced inflammatory response (24).
Downside and Risks
Small amounts of saffron are mainly safe to consume. However, too much consumption of saffron can cause an allergic reaction, vomiting, dizziness, and yellowing of the skin.
People with bleeding disorders who have had surgery should avoid excessive consumption of saffron. It can thin the blood and slow blood clotting, increasing the risk of bleeding (25, 26).
References
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/21295383/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/22980812/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7466186/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6535192/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/20579522/
- https://www.ingentaconnect.com/content/ben/acamc/2019/00000019/00000001/art00009
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/25673029/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3466873/
- https://www.spandidos-publications.com/10.3892/etm.2017.5414
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/22552758/
- https://www.mdpi.com/2072-6643/11/5/943/htm
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31930826/
- https://www.mdpi.com/2076-3921/5/4/40/htm
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/26468457/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29510352/
- https://academic.oup.com/nutritionreviews/article/77/8/557/5499264
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30036891/
- https://academic.oup.com/ajcn/article/74/5/687/4737528
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5342880/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/20688744/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29280987/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/33204394/
- https://www.jmb.or.kr/journal/view.html?doi=10.4014/jmb.2003.03064
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31701721/
- https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1111/j.1398-9995.1997.tb01042.x
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/0021870764900474
Infographic
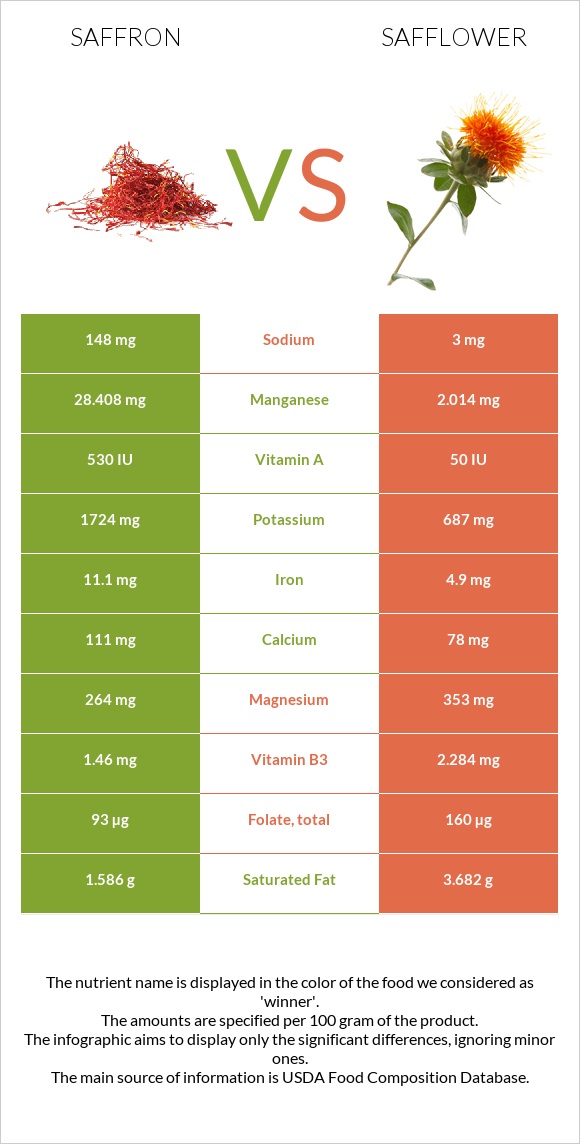
All nutrients comparison - raw data values
| Nutrient |  |
 |
DV% diff. |
| Manganese | 28.408mg | 2.014mg | 1148% |
| Polyunsaturated fat | 2.067g | 28.223g | 174% |
| Copper | 0.328mg | 1.747mg | 158% |
| Vitamin C | 80.8mg | 0mg | 90% |
| Vitamin B1 | 0.115mg | 1.163mg | 87% |
| Vitamin B5 | 4.03mg | 81% | |
| Iron | 11.1mg | 4.9mg | 78% |
| Phosphorus | 252mg | 644mg | 56% |
| Fats | 5.85g | 38.45g | 50% |
| Zinc | 1.09mg | 5.05mg | 36% |
| Potassium | 1724mg | 687mg | 31% |
| Magnesium | 264mg | 353mg | 21% |
| Folate | 93µg | 160µg | 17% |
| Fiber | 3.9g | 16% | |
| Vitamin B6 | 1.01mg | 1.17mg | 12% |
| Vitamin B2 | 0.267mg | 0.415mg | 11% |
| Monounsaturated fat | 0.429g | 4.848g | 11% |
| Calories | 310kcal | 517kcal | 10% |
| Protein | 11.43g | 16.18g | 10% |
| Carbs | 65.37g | 34.29g | 10% |
| Selenium | 5.6µg | 10% | |
| Saturated fat | 1.586g | 3.682g | 10% |
| Sodium | 148mg | 3mg | 6% |
| Vitamin B3 | 1.46mg | 2.284mg | 5% |
| Calcium | 111mg | 78mg | 3% |
| Vitamin A | 27µg | 3µg | 3% |
| Net carbs | 61.47g | 34.29g | N/A |
| Tryptophan | 0.183mg | 0% | |
| Threonine | 0.586mg | 0% | |
| Isoleucine | 0.717mg | 0% | |
| Leucine | 1.154mg | 0% | |
| Lysine | 0.534mg | 0% | |
| Methionine | 0.284mg | 0% | |
| Phenylalanine | 0.806mg | 0% | |
| Valine | 1.025mg | 0% | |
| Histidine | 0.452mg | 0% | |
| Omega-3 - DPA | 0.006g | N/A |
Fat Type Comparison
| Contains less Sat. FatSaturated fat | -56.9% |
| Contains more Mono. FatMonounsaturated fat | +1030.1% |
| Contains more Poly. FatPolyunsaturated fat | +1265.4% |
People also compare
References
All the values for which the sources are not specified explicitly are taken from FDA’s Food Central. The exact link to the food presented on this page can be found below.
- Saffron - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/170934/nutrients
- Safflower - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/170558/nutrients
All the Daily Values are presented for males aged 31-50, for 2000-calorie diets.






