Salmon oil vs. Fish oil — Health Impact and Nutrition Comparison


Summary
Although salmon oil and fish oil contain the exact amounts of fats, they differ in the types of fats they provide. Salmon oil mainly consists of polyunsaturated fats, while fish oil is significantly richer in monounsaturated fats.
Introduction
Frequently, edible oils cannot be distinguished because they have almost the same nutrient composition. Each oil, however, has its own unique characteristics. This article will compare salmon oil and fish oil made from herring fish.
Classification
Salmon oil and herring oil, described here as fish oil, are animal oils derived from oily fish.
Salmon oil is usually made from the heads of fresh salmons, while fish oil is harvested from the fatty tissues of herring fish.
The smoke point, taste, and use
One of the most essential characteristics of edible oils is the smoke point - the temperature at which the oil first breaks down and begins to smoke or burn.
The smoke point of salmon oil is about 460F /232C/, which is moderately high. Fish oil has a much higher smoke point, equalling 487F /250C/.
Fish oil has a distinct, intense spicy taste, while salmon oil usually does not taste fishy.
Since fish oil has not been refined, bleached, or deodorized to make it a safe cooking ingredient, it should never be used as cooking oil. Besides, some chemicals contained in these oils, such as omega-3 fatty acids, are very sensitive to high temperatures. Instead, fish oil and salmon oil are used as a supplement in the form of oil capsules.
Nutrition
The average serving size of fish oils is one tablespoon equalling 13.6g for fish and salmon oil. This article will compare nutritional values for 100g of these fish oils.
Macronutrient Comparison
Calories
Fish and salmon oil are classified as highly high-calorie foods, containing equal calories: 902 per 100g.
Average servings of fish oil and salmon oil contain 123 calories.
Fats
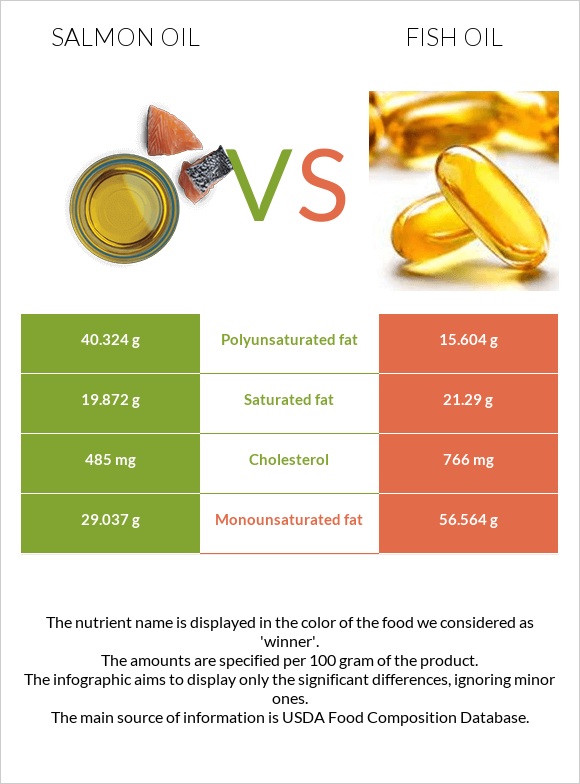
Fish and salmon oil's macronutrient content consists of 100% fats. However, they differ in the types of fats they provide.
Salmon oil consists of 45% of polyunsaturated fats, 30% of monounsaturated fats, and 22% of saturated fats, while fish oil is richer in monounsaturated fats, providing 61% of it, 23% saturated, and 17% of polyunsaturated fats. Salmon oil is significantly richer in all types of omega-3 fatty acids.
Fish oil is 281mg higher in cholesterol than salmon oil, providing 766mg per 100g compared to 485mg in the same amount of salmon oil.
The infographic below shows the visual representation of fat-type content.
@fattypeContent
Other nutrients
Salmon and fish oils contain no amounts of proteins, carbohydrates, minerals, or vitamins.
Health impact
As mentioned above, salmon oil is richer in omega-3 fatty acids than fish oil. They contain primarily eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) and docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) (1). These food supplements have similar impacts on different organs and systems of the human organism.
Cardiovascular health
Studies prove that fish oil supplements reduce heart disease risk factors. They can lower LDL cholesterol levels and increase HDL cholesterol concentrations in the blood flow at the same time (2). In the case of hyperlipidemia, fish oil and salmon oil consumption may lead to lower triglyceride levels (3). In hypertensive patients’ organisms, fish oil can reduce blood pressure (4).
Besides, these oils prevent plaque formation on the walls of arteries, thus reducing the risk of development of atherosclerosis (5).
Inflammation
Inflammation is something good, as it is the reaction of our immune system to infections, but chronic inflammation can cause serious health problems, such as diabetes, obesity, heart disease, etc.
Fish oil and salmon oil may have beneficial anti-inflammatory effects (6). Salmon oil omega-3 fatty acids reduce the quantities of inflammatory compounds produced by immune cells (7). Moreover, these oils may reduce joint pain during rheumatoid arthritis (8).
Skin health
Skin is the largest organ of the human organism and contains significant amounts of omega-3 fatty acids. Too much sun exposure and aging are related to reduced skin health. Supplements like fish oil are beneficial in conditions like dermatitis and psoriasis. Omega-3 fatty acids protect the skin from sun damage and improve wound healing (9).
Pregnancy and child development
Omega-3 fatty acids are crucial for fetal growth and development.
A study shows that children whose mothers took omega-3 supplements during pregnancy develop cognitive and motor skills easier than those whose mothers did not use any supplements (10).
Fish oil consumption during pregnancy and breastfeeding also lowers the risk of allergy development (11).
Side effects
Although fish oils have many beneficial health impacts, too much consumption may have some side effects.
Salmon oil overconsumption can cause headaches, diarrhea, nausea, and heartburn. Besides, in the case of using anticoagulants, salmon oil may become the cause of bleeding (12).
References
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/28900017/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/18774613/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/21924882/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/26817716/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/22317966/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30703872/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/22765297/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30213695/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6117694/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/21364848/
- https://academic.oup.com/jn/article/148/3/409/4930799
- https://www.nccih.nih.gov/health/omega3-supplements-in-depth#hed6
Infographic
Mineral Comparison
Vitamin Comparison
All nutrients comparison - raw data values
| Nutrient |  |
 |
DV% diff. |
| Polyunsaturated fat | 40.324g | 15.604g | 165% |
| Cholesterol | 485mg | 766mg | 94% |
| Monounsaturated fat | 29.037g | 56.564g | 69% |
| Saturated fat | 19.872g | 21.29g | 6% |
| Calories | 902kcal | 902kcal | 0% |
| Fats | 100g | 100g | 0% |
| Omega-3 - EPA | 13.023g | 6.273g | N/A |
| Omega-3 - DHA | 18.232g | 4.206g | N/A |
| Omega-3 - DPA | 2.991g | 0.619g | N/A |
Fat Type Comparison
| Contains more Poly. FatPolyunsaturated fat | +158.4% |
| Contains more Mono. FatMonounsaturated fat | +94.8% |
References
All the values for which the sources are not specified explicitly are taken from FDA’s Food Central. The exact link to the food presented on this page can be found below.
- Salmon oil - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/172343/nutrients
- Fish oil - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/172340/nutrients
All the Daily Values are presented for males aged 31-50, for 2000-calorie diets.
