Pastrami vs. Roast beef — Health Impact and Nutrition Comparison


Summary
Pastrami is a brisket deli cut. It is richer in proteins, selenium, choline, zinc, and iron. It also contains higher amounts of sodium. In comparison, roast beef is lower in fats and sodium. It is richer in phosphorus, potassium, and vitamins B2, B3, B5, B6, and B12.
Table of contents
Introduction
This article will compare two deli foods that are pastrami and roast beef. We will highlight the differences that exist between them, focusing on some general differences, nutritional content differences, and health impacts.
We will consider pastrami from beef, although different pastrami can also be prepared from different animals.
Pastrami is prepared by a brisket cut of beef, specifically the navel part of the brisket. Pastrami has several steps during preparation compared to roast beef, which is comparatively easier and quicker to prepare. Pastrami needs to be brined, seasoned, and finally smoked. Thus, the process takes several days.
In comparison, roast beef is simpler and quicker to prepare. Roast beef can be prepared from different cuts of beef. It is roasted for a couple of hours and ready to be served. The golden rule is to brown the outside and keep the inside moist and pink.
Nutritional content comparison
In this section, we will compare pastrami to roast beef based on 100g of each in cooked forms.
Calories
Pastrami has slightly higher calories in comparison to roast beef. Pastrami has 147 calories, and roast beef has 115 calories.
Carbs
Their carbohydrate content is negligible.
Protein
Pastrami has a higher protein content in comparison to roast beef. Pastrami contains 22g of protein, and roast beef contains 18.6g of protein.
Fats
Both of them are, on average leaner cuts. Pastrami contains slightly higher amounts of fats compared to roast beef. However, both contain low amounts of fat. Pastrami contains 5.8g of fat. In comparison, roast beef contains 3.7g of fat.
Although it is important to mention that since roast beef can be prepared from different cuts of beef, we can have leaner or slightly higher fat cuts.
Minerals
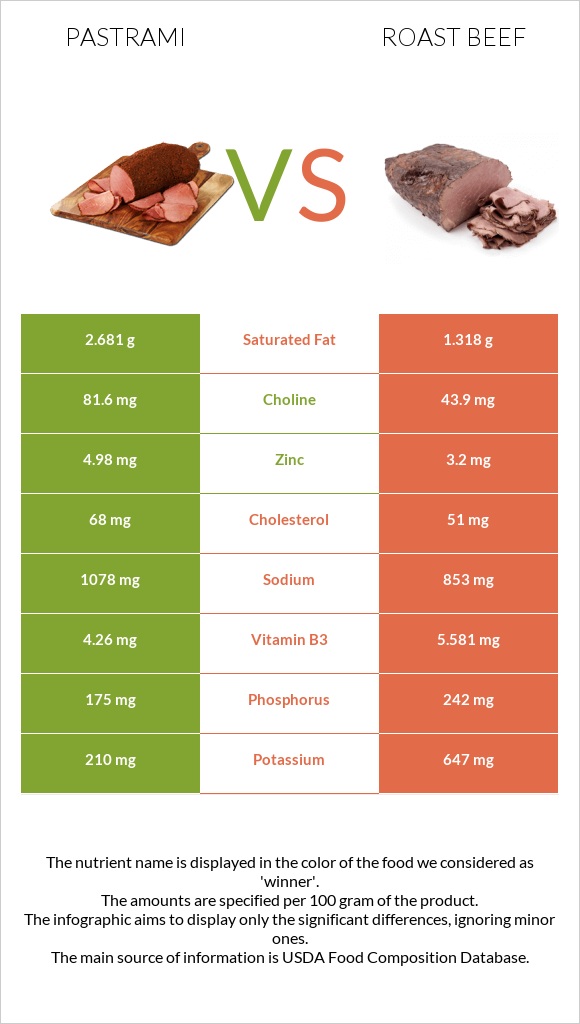
Pastrami is richer in selenium, choline, zinc, and iron. Pastrami is also higher in sodium. In comparison, roast beef is richer in potassium and phosphorus.
Pastrami and roast beef are high in sodium. The amount of sodium present in 100g of each is very high and must be considered.
In the diagram below, we can visualize their difference in mineral distributions.
Mineral Comparison
Vitamins
Roast beef is richer in all vitamins compared to pastrami. Roast beef is richer in vitamins B2, B3, B5, B6, and B12.
Noting that pastrami also contains high amounts of most of these vitamins, however, comparatively, roast beef is richer.
In the diagram below, we can visualize their difference in vitamin distributions.
Vitamin Comparison
Health impacts
Considering these are red meats, they have several adverse health impacts when over-consumed. To read in detail about those impacts, this article covers all the important features of red meat on overall health.
These articles also discuss in detail meat intolerance and meat allergy.
Anemia
Considering that both of these are red meat, they are packed with vitamin B12 and iron which decrease overall risks of vitamin B12 deficiency (megaloblastic) anemia and iron deficiency anemia. (1) (2)
Cancer
Red meat is considered a carcinogenic compound, and in addition to that, pastrami specifically contains preservatives such as nitrites and nitrates to increase their shelf lives. Roast beef can also contain preservatives since they are both deli cuts.
Nitrogen compounds that are used as food preservatives increase the risks of breast, prostate, and pancreatic cancers.
In addition, red meat increases the risk of colorectal cancer, lung cancer, and renal cancer. (3)(4)(5)(6)
Cardiovascular health
One of the main risks of increasing risks of mortality from cardiovascular diseases is hypertension. Long-term consumption of sodium in high amounts increases the risk of developing hypertension. In this case, pastrami and roast beef are high in sodium. In specific, the pastrami is even higher in sodium (7). To lower the risk of high blood pressure, you should consider consuming foods low in sodium.
References
Infographic
Macronutrient Comparison
Fat Type Comparison
Carbohydrate type comparison
Comparison summary table
 |
 |
||
| Lower in Sodium |
|
||
| Lower in Cholesterol |
|
||
| Lower in Saturated Fat |
|
||
| Lower in Glycemic Index |
|
||
| Lower in price |
|
||
| Lower in Sugar |
|
||
| Rich in minerals |
|
||
| Rich in vitamins | Equal | ||
All nutrients comparison - raw data values
| Nutrient |  |
 |
Opinion |
| Net carbs | 0.36g | 0.64g |
 |
| Protein | 21.8g | 18.62g |
 |
| Fats | 5.82g | 3.69g |
 |
| Carbs | 0.36g | 0.64g |
 |
| Calories | 147kcal | 115kcal |
 |
| Fructose | 0.01g | 0g |
 |
| Sugar | 0.1g | 0.29g |
 |
| Calcium | 10mg | 5mg |
 |
| Iron | 2.22mg | 2.05mg |
 |
| Magnesium | 17mg | 20mg |
 |
| Phosphorus | 175mg | 242mg |
 |
| Potassium | 210mg | 647mg |
 |
| Sodium | 1078mg | 853mg |
 |
| Zinc | 4.98mg | 3.2mg |
 |
| Copper | 0.091mg | 0.086mg |
 |
| Manganese | 0.027mg | 0.015mg |
 |
| Selenium | 17.7µg | 14.7µg |
 |
| Vitamin A | 42IU | 11IU |
 |
| Vitamin A RAE | 2µg | 3µg |
 |
| Vitamin E | 0.12mg | 0.49mg |
 |
| Vitamin D | 4IU | 1IU |
 |
| Vitamin D | 0.1µg | 0µg |
 |
| Vitamin C | 0.3mg | 0mg |
 |
| Vitamin B1 | 0.052mg | 0.043mg |
 |
| Vitamin B2 | 0.161mg | 0.213mg |
 |
| Vitamin B3 | 4.26mg | 5.581mg |
 |
| Vitamin B5 | 0.265mg | 0.566mg |
 |
| Vitamin B6 | 0.221mg | 0.46mg |
 |
| Folate | 6µg | 5µg |
 |
| Vitamin B12 | 1.87µg | 2.04µg |
 |
| Vitamin K | 0.7µg | 1.6µg |
 |
| Tryptophan | 0.141mg |
 |
|
| Threonine | 0.857mg |
 |
|
| Isoleucine | 0.976mg |
 |
|
| Leucine | 1.706mg |
 |
|
| Lysine | 1.812mg |
 |
|
| Methionine | 0.558mg |
 |
|
| Phenylalanine | 0.847mg |
 |
|
| Valine | 1.065mg |
 |
|
| Histidine | 0.684mg |
 |
|
| Cholesterol | 68mg | 51mg |
 |
| Trans Fat | 0.148g |
 |
|
| Saturated Fat | 2.681g | 1.318g |
 |
| Omega-3 - DHA | 0g | 0.001g |
 |
| Omega-3 - EPA | 0g | 0.007g |
 |
| Omega-3 - DPA | 0g | 0.012g |
 |
| Monounsaturated Fat | 2.118g | 1.521g |
 |
| Polyunsaturated fat | 0.145g | 0.27g |
 |
| Omega-6 - Eicosadienoic acid | 0.002g |
 |
|
| Omega-6 - Linoleic acid | 0.14g |
 |
|
| Omega-6 - Gamma-linoleic acid | 0.001g |
 |
|
| Omega-3 - ALA | 0.017g |
 |
|
| Omega-6 - Dihomo-gamma-linoleic acid | 0.011g |
 |
Which food is preferable for your diet?
 |
 |
|
| Low Fats diet |
|
|
| Low Carbs diet |
|
|
| Low Calories diet |
|
|
| Low Glycemic Index diet |
|
People also compare
Vitamins & Minerals Daily Need Coverage Score
Comparison summary
References
All the values for which the sources are not specified explicitly are taken from FDA’s Food Central. The exact link to the food presented on this page can be found below.
- Pastrami - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/170204/nutrients
- Roast beef - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/174570/nutrients
All the Daily Values are presented for males aged 31-50, for 2000-calorie diets.






