Apple vs. Pineapple — Health Impact and Nutrition Comparison

Summary
When compared, pineapples have a better nutritional profile than apples. Pineapples are overall richer in vitamins, minerals, and proteins. However, apples are higher in dietary fiber.
They have varying health benefits on different organ systems.
Overall, apples are cheaper and more available compared to pineapples which are more of a luxury fruit.
Introduction
Pineapples and apples can be used as fresh raw fruits or jams. They can also be used in manufactured foods or beverages, such as fruit juices or alcoholic beverages.
Apples are one of the most popular and loved fruits worldwide. The apple tree is one of the earliest trees to be cultivated. Apples even appear in art and religious traditions as a mystical fruit.
On the other hand, pineapples are considered an exotic fruit. In European iconography, it was a symbol of welcome and hospitality. Nowadays, it can be commonly found in any grocery store, but usually for a high price.
Nutritional Comparison
Apple is popular among health-conscious people. They are known to have health-promoting and disease-preventing properties.
If we compare their nutritional content, pineapple is richer in vitamins and minerals. It contains approximately 5 times more vitamins and 2 times more minerals than an apple does.
When looking at the coverage of our daily vitamins needs, we see that pineapple covers 3.5 times more of it. Pineapple also covers 6 times more of our daily minerals needs as it contains more iron, calcium, magnesium, copper, and zinc.
Vitamins
It is enough to mention that pineapple contains 11 times more vitamin C, 5 times more vitamin B1, and two times more vitamins B3, B5, B6 than apple.
Vitamin Comparison
| Contains more Vitamin EVitamin E | +800% |
| Contains more Vitamin KVitamin K | +214.3% |
| Contains more Vitamin CVitamin C | +939.1% |
| Contains more Vitamin B1Vitamin B1 | +364.7% |
| Contains more Vitamin B2Vitamin B2 | +23.1% |
| Contains more Vitamin B3Vitamin B3 | +449.5% |
| Contains more Vitamin B5Vitamin B5 | +249.2% |
| Contains more Vitamin B6Vitamin B6 | +173.2% |
| Contains more FolateFolate | +500% |
Minerals
Pineapples are 3 times richer in zinc and 4 times higher in copper. They also contain more calcium, iron, and magnesium.
Nevertheless, apples are richer in phosphorus.
Mineral Comparison
| Contains more PhosphorusPhosphorus | +37.5% |
| Contains more MagnesiumMagnesium | +140% |
| Contains more CalciumCalcium | +116.7% |
| Contains more IronIron | +141.7% |
| Contains more CopperCopper | +307.4% |
| Contains more ZincZinc | +200% |
| Contains more ManganeseManganese | +2548.6% |
| Contains more SeleniumSelenium | +∞% |
Macronutrients
Pineapple contains fewer carbohydrates but more sugar overall due to lower dietary fiber content. Pineapples also contain a little more protein and a little less fat.
Apples have a low glycemic index of 36, while the glycemic index of pineapples is 66.
Health Impact
Health Benefits of Apples
The old saying is true: An apple a day keeps the doctor away. Apple truly has many health benefits, no less than pineapple.
- Whiter and healthier teeth
Biting and chewing one apple a day reduces tooth decay by lowering bacteria levels (1). - Prevention of Alzheimer’s
Studies showed that its juice has the ability to prevent Alzheimer’s and fight the aging of the brain (2). - Protect against Parkinson’s
Due to the free radical-fighting power of its antioxidants, apples have a certain amount of protection against Parkinson’s (2). - Curb all sorts of cancers
Research has shown that they can reduce the risk of developing pancreatic cancer by up to 23% (3). - Decrease the risk of diabetes
Thanks to the soluble fiber in this fruit, women who eat at least one apple a day are 28% less likely to develop diabetes (4). - Reduce cholesterol
They contain soluble fiber that binds with fats in the intestine, which reduces cholesterol levels in the blood (5). - A healthier heart
Apple skin contains a phenolic compound, which prevents the cholesterol that gets into the system from solidifying on the artery walls (5). - Preventing gallstones
To prevent gallstones, doctors recommend a diet high in fiber (6). - Neutralize irritable bowel syndrome
To control the symptoms of irritable bowel, doctors recommend eating apples (7). - Boost the immune system
Studies have shown that red apples contain quercetin that can boost and fortify the immune system (8).
Health Benefits of Pineapples
- Age-related macular degeneration
Pineapples decrease the risk of age-related macular degeneration (9). - Asthma prevention
Pineapples prevent asthma attacks (10). - Blood pressure and cardiovascular health
It is high in potassium and has anti-hypertensive characteristics. It also has protective characteristics for cardiovascular health (11). - Cancer
Pineapples can play a protective role from the free radicals, which can cause cancer, as they are a good source of antioxidants - vitamin C and beta-carotene. Research has shown that they contain bromelain and other enzymes that can be used in the treatment of cancer for reducing the side effects (12). - Diabetes
One pineapple contains approximately 13g of fiber, which is known to lower blood glucose levels (12). - Healing and Inflammation
The antioxidants present in pineapples reduce overall inflammation in the body (12). - Skin
Skin damage can be caused by the sun or pollution, and pineapple can help fight these skin damages and improve overall skin texture (12).
References
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6051571/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3183591/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/27000627/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/28186516/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6997084/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/10609857/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5777282/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC442131/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7355812/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/22894886/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6464871/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3529416/
Infographic
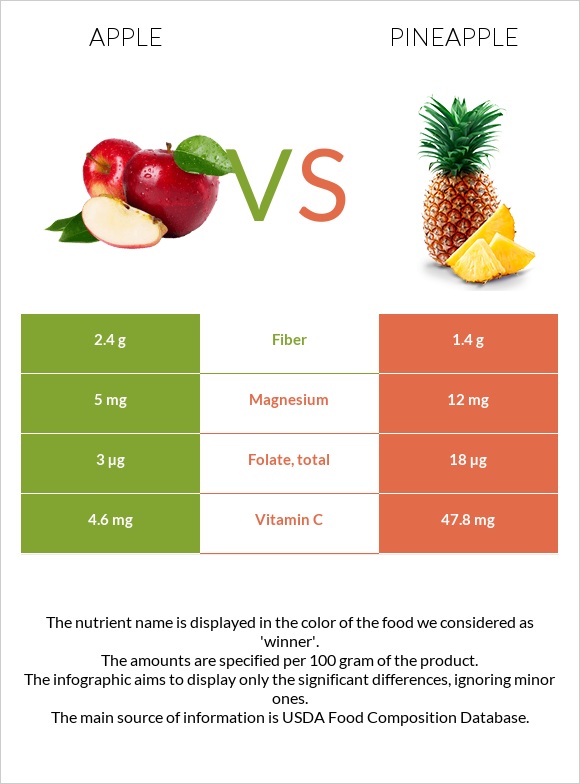
All nutrients comparison - raw data values
| Nutrient |  |
 |
DV% diff. |
| Vitamin C | 4.6mg | 47.8mg | 48% |
| Manganese | 0.035mg | 0.927mg | 39% |
| Copper | 0.027mg | 0.11mg | 9% |
| Vitamin B1 | 0.017mg | 0.079mg | 5% |
| Vitamin B6 | 0.041mg | 0.112mg | 5% |
| Fructose | 5.9g | 2.12g | 5% |
| Fiber | 2.4g | 1.4g | 4% |
| Folate | 3µg | 18µg | 4% |
| Vitamin B3 | 0.091mg | 0.5mg | 3% |
| Vitamin B5 | 0.061mg | 0.213mg | 3% |
| Magnesium | 5mg | 12mg | 2% |
| Iron | 0.12mg | 0.29mg | 2% |
| Protein | 0.26g | 0.54g | 1% |
| Calcium | 6mg | 13mg | 1% |
| Zinc | 0.04mg | 0.12mg | 1% |
| Vitamin E | 0.18mg | 0.02mg | 1% |
| Vitamin K | 2.2µg | 0.7µg | 1% |
| Calories | 52kcal | 50kcal | 0% |
| Fats | 0.17g | 0.12g | 0% |
| Net carbs | 11.41g | 11.72g | N/A |
| Carbs | 13.81g | 13.12g | 0% |
| Potassium | 107mg | 109mg | 0% |
| Sugar | 10.39g | 9.85g | N/A |
| Starch | 0.05g | 0g | 0% |
| Phosphorus | 11mg | 8mg | 0% |
| Sodium | 1mg | 1mg | 0% |
| Vitamin A | 3µg | 3µg | 0% |
| Selenium | 0µg | 0.1µg | 0% |
| Vitamin B2 | 0.026mg | 0.032mg | 0% |
| Choline | 3.4mg | 5.5mg | 0% |
| Saturated fat | 0.028g | 0.009g | 0% |
| Monounsaturated fat | 0.007g | 0.013g | 0% |
| Polyunsaturated fat | 0.051g | 0.04g | 0% |
| Tryptophan | 0.001mg | 0.005mg | 0% |
| Threonine | 0.006mg | 0.019mg | 0% |
| Isoleucine | 0.006mg | 0.019mg | 0% |
| Leucine | 0.013mg | 0.024mg | 0% |
| Lysine | 0.012mg | 0.026mg | 0% |
| Methionine | 0.001mg | 0.012mg | 0% |
| Phenylalanine | 0.006mg | 0.021mg | 0% |
| Valine | 0.012mg | 0.024mg | 0% |
| Histidine | 0.005mg | 0.01mg | 0% |
Macronutrient Comparison
| Contains more FatsFats | +41.7% |
| Contains more ProteinProtein | +107.7% |
Fat Type Comparison
| Contains more Poly. FatPolyunsaturated fat | +27.5% |
| Contains less Sat. FatSaturated fat | -67.9% |
| Contains more Mono. FatMonounsaturated fat | +85.7% |
Carbohydrate type comparison
| Contains more StarchStarch | +∞% |
| Contains more GlucoseGlucose | +40.5% |
| Contains more FructoseFructose | +178.3% |
| Contains more SucroseSucrose | +189.4% |
People also compare
References
All the values for which the sources are not specified explicitly are taken from FDA’s Food Central. The exact link to the food presented on this page can be found below.
- Apple - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/171688/nutrients
- Pineapple - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/169124/nutrients
All the Daily Values are presented for males aged 31-50, for 2000-calorie diets.




