Barley vs. Bulgur — Health Impact and Nutrition Comparison


Summary
Barley is denser in nutrients, containing more net carbs and protein. Barley provides two times more vitamin B3 and two and a half times more vitamin A, while bulgur contains higher amounts of dietary fiber. Barley is a better source of minerals, including iron, phosphorus, potassium, zinc, and copper.
Introduction
Bulgur and barley are different grains with significant nutrient content. In this article, we will discuss their nutrition and health impact differences.
Bulgur is a ground, cracked wheat that is partially cooked and dried for easy preparation. It is a well-known whole grain in Middle Eastern cuisine used to prepare pilaf or tabbouleh.
Barley belongs to the grass family. It is a famous cereal grain cultivated worldwide, usually in regions with a temperate climate. Barley is commonly used for making bread, soups, and alcoholic beverages, especially beer.
According to classification, bulgur and barley are two species from the same family - Poaceae.
Actual differences
Bulgur and barley differ in taste, texture, and use.
Technically, bulgur is wheat that is parboiled, dried, then cracked into smaller pieces. Bulgur has two common varieties: yellow and dark. The first has a coarse texture, while the dark bulgur's texture is softer.
On the other hand, barley can be yellow, brown, or purple, depending on its flavonoid content. This whole grain has a chewy texture.
Bulgur has an earthy and nutty flavor, while barley tastes lighter and mild. Bulgur can be an excellent substitute for quinoa and rice. Check the bulgur vs. quinoa comparison article for more information. Barley can be used as a substitute for farro, buckwheat, or quinoa.
Nutrition
In the sections below, you will find information about the nutritional content of 100g servings of cooked barley and bulgur.
The average serving size for these grains is one cup, equalling 182g for bulgur and 157g for barley.
Macronutrients
Barley is denser in nutrients than bulgur. Bulgur contains 78% of water, 19% of carbs, and 3% of other nutrients, while barley comprises 69% of water, 28% of carbohydrates, and 3% of other nutrients.
Macronutrient Comparison
Contains
more
FatsFats
+83.3%
Contains
more
CarbsCarbs
+51.9%
Contains
more
ProteinProtein
+36.3%
Contains
more
WaterWater
+13%
Contains
more
OtherOther
+21.4%
Calories
Bulgur can be classified as a low-calorie food, while barley fits in the medium-calorie foods group.
Barley is notably higher in calories, containing 40 more calories per every 100g. Per 100g, bulgur contains 83 calories, while barley provides 123 calories.
Carbohydrates
Barley is 10g higher in net carbs than bulgur in each 100g serving, while bulgur is 0.7g richer in dietary fiber, resulting in barley being higher in overall carbs.
100g serving size of bulgur contains 18.6g of carbs, 76% of which are net carbs and 24% - dietary fiber, while the same size of barley provides 28.3g of carbs, 86% of which are net carbs and 14% - dietary fiber.
Barley is an excellent source of dietary fiber. It contains nearly three times more of this nutrient than oats. Barley is especially rich in soluble fiber.
Protein
Bulgur is slightly higher in protein, containing 3.1g per 100g, while barley has 2.3g. These grains contain some amounts of essential amino acids. However, they are relatively low in proteins.
Fats
Bulgur and barley contain less than one gram of fat per 100g. Most of the fats present in these grains are unsaturated. Hence, the fat content can be neglected.
Fat Type Comparison
Contains
more
Mono. FatMonounsaturated fat
+83.9%
Contains
more
Poly. FatPolyunsaturated fat
+118.4%
Contains
less
Sat. FatSaturated fat
-54.8%
Vitamins
Barley is more affluent in most vitamins, containing two times more vitamin B3, two and a half times more vitamin A, and overall more vitamins B1, B2, B6, and K.
Bulgur has more than two times more vitamin B5 and more folate /vitamin B9/ than barley.
Vitamin Comparison
Contains
more
Vitamin B1Vitamin B1
+45.6%
Contains
more
Vitamin B2Vitamin B2
+121.4%
Contains
more
Vitamin B3Vitamin B3
+106.3%
Contains
more
Vitamin B6Vitamin B6
+38.6%
Contains
more
Vitamin KVitamin K
+60%
Contains
more
Vitamin B5Vitamin B5
+154.8%
Contains
more
FolateFolate
+12.5%
Minerals
Barley is the absolute winner in this section. It is notably higher in most minerals: iron, phosphorus, potassium, zinc, and copper.
Barley covers 50% of the DV for iron.
Bulgur is richer in magnesium. Barley contains less sodium.
Glycemic index
According to measurements, bulgur has an average GI of 47, falling into the list of low-glycemic index foods (1). Barey's average glycemic index equals 28, suggesting it to be a low-glycemic index food too.
For more information, please read these in-depth articles: the glycemic index of barley and the glycemic index of bulgur.
You can also check our glycemic index chart page to learn more about other foods' glycemic indexes.
Health impact
Diabetes
Both bulgur and barley, as was already mentioned, have low glycemic index values. However, barley's GI tends to be lower. These low values show that consuming these grains causes blood glucose levels to rise gradually rather than rapidly.
As a study indicates, whole grains, such as bulgur and barley, can lower the risk of development of type 2 diabetes. Type 2 diabetes and obesity are two metabolic diseases that whole-grain phytochemicals may help treat (2). Whole grain consumption improves insulin sensitivity, which is damaged during type two diabetes. Thus, whole grains can protect from the development of metabolic diseases (3).
Gluten intolerance
Gluten is a protein in grains such as wheat, barley, bulgur, etc. People with gluten-related disorders, such as celiac disease and non-celiac gluten sensitivity, must avoid consuming these foods as they will likely trigger the disease (4) (5). The most common symptoms of these diseases include diarrhea, stomach pain, and bloating.
Both barley and bulgur are not gluten-free. Hence, people with gluten intolerance should avoid eating these grains.
FODMAPs
Barley and one serving of bulgur are high in FODMAPs - poorly absorbed carbohydrates, causing abdominal pain, bloating, flatulence, and diarrhea. Half-serving bulgur is considered low FODMAP and may be consumed during such diets.
Cardiovascular health
Whole grain consumption (such as barley and bulgur) is linked to a lower cardiovascular disease risk (6).
Whole grain food products have high dietary fiber content, which results in a higher potential for cardiovascular disease prevention and a lower risk of atherosclerosis development (7).
References
- https://academic.oup.com/ajcn/article/114/5/1625/6320814?login=false
- https://www.researchgate.net/publication/361575031_Biochemical_nutritional_properties_of_wheat_bulgur_a_review
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/28944285/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6630947/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6258800/
- https://www.researchgate.net/publication/361575031_Biochemical_nutritional_properties_of_wheat_bulgur_a_review
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6566984/
Infographic
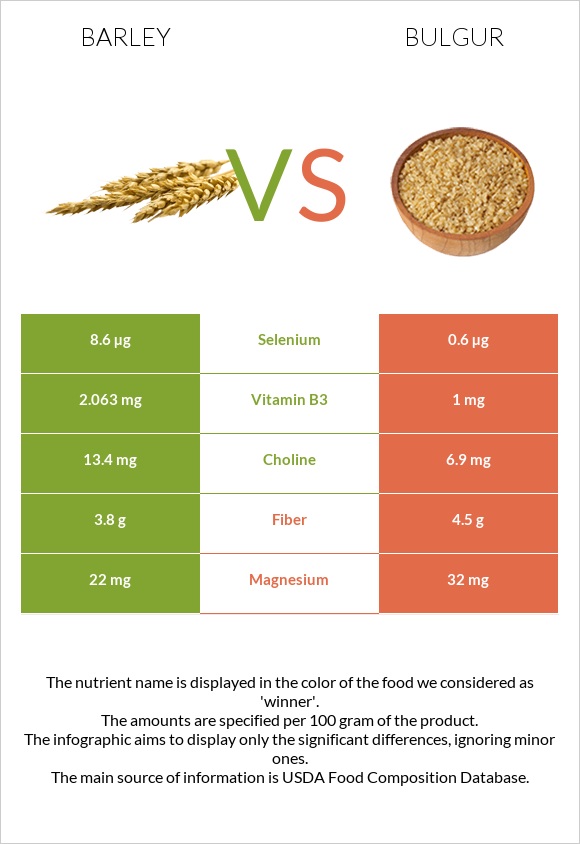
Mineral Comparison
| Contains more PotassiumPotassium | +36.8% |
| Contains more IronIron | +38.5% |
| Contains more CopperCopper | +40% |
| Contains more ZincZinc | +43.9% |
| Contains more PhosphorusPhosphorus | +35% |
| Contains less SodiumSodium | -40% |
| Contains more SeleniumSelenium | +1333.3% |
| Contains more MagnesiumMagnesium | +45.5% |
| Contains more ManganeseManganese | +135.1% |
All nutrients comparison - raw data values
| Nutrient |  |
 |
DV% diff. |
| Manganese | 0.259mg | 0.609mg | 15% |
| Selenium | 8.6µg | 0.6µg | 15% |
| Vitamin B3 | 2.063mg | 1mg | 7% |
| Iron | 1.33mg | 0.96mg | 5% |
| Vitamin B5 | 0.135mg | 0.344mg | 4% |
| Carbs | 28.22g | 18.58g | 3% |
| Fiber | 3.8g | 4.5g | 3% |
| Copper | 0.105mg | 0.075mg | 3% |
| Vitamin B2 | 0.062mg | 0.028mg | 3% |
| Calories | 123kcal | 83kcal | 2% |
| Protein | 2.26g | 3.08g | 2% |
| Magnesium | 22mg | 32mg | 2% |
| Zinc | 0.82mg | 0.57mg | 2% |
| Phosphorus | 54mg | 40mg | 2% |
| Vitamin B1 | 0.083mg | 0.057mg | 2% |
| Vitamin B6 | 0.115mg | 0.083mg | 2% |
| Potassium | 93mg | 68mg | 1% |
| Folate | 16µg | 18µg | 1% |
| Choline | 13.4mg | 6.9mg | 1% |
| Polyunsaturated fat | 0.214g | 0.098g | 1% |
| Fats | 0.44g | 0.24g | 0% |
| Net carbs | 24.42g | 14.08g | N/A |
| Calcium | 11mg | 10mg | 0% |
| Sugar | 0.28g | 0.1g | N/A |
| Sodium | 3mg | 5mg | 0% |
| Vitamin E | 0.01mg | 0.01mg | 0% |
| Vitamin K | 0.8µg | 0.5µg | 0% |
| Saturated fat | 0.093g | 0.042g | 0% |
| Monounsaturated fat | 0.057g | 0.031g | 0% |
| Tryptophan | 0.038mg | 0.048mg | 0% |
| Threonine | 0.077mg | 0.089mg | 0% |
| Isoleucine | 0.083mg | 0.114mg | 0% |
| Leucine | 0.154mg | 0.208mg | 0% |
| Lysine | 0.084mg | 0.085mg | 0% |
| Methionine | 0.043mg | 0.048mg | 0% |
| Phenylalanine | 0.127mg | 0.145mg | 0% |
| Valine | 0.111mg | 0.139mg | 0% |
| Histidine | 0.051mg | 0.071mg | 0% |
People also compare
References
All the values for which the sources are not specified explicitly are taken from FDA’s Food Central. The exact link to the food presented on this page can be found below.
- Barley - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/170285/nutrients
- Bulgur - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/170287/nutrients
All the Daily Values are presented for males aged 31-50, for 2000-calorie diets.





