Canola Oil vs Coconut oil - Nutrition and Health Impact Comparison


Summary
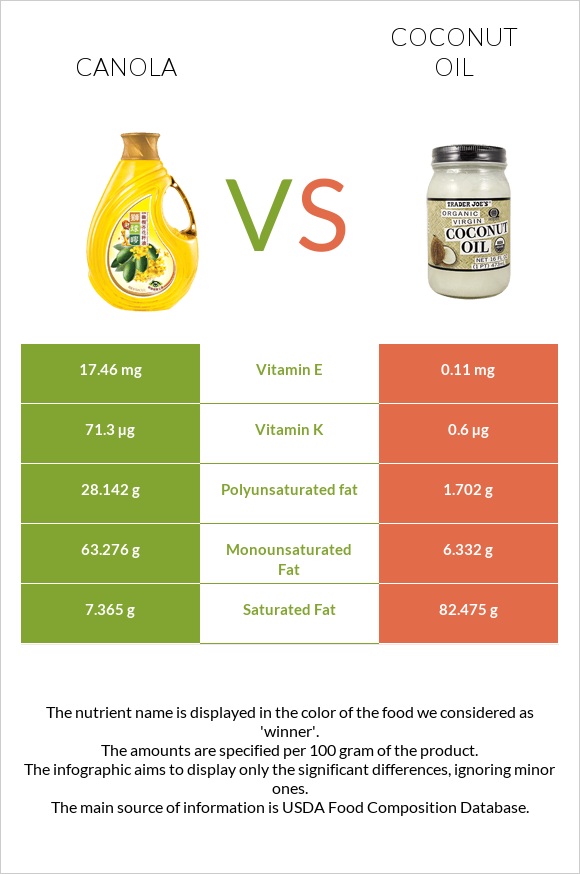
Canola oil is richer in vitamin E and vitamin K. The fat profile of canola oil is richer in monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fats. In comparison, coconut oil is higher in saturated fats and has more negative health impacts.
Introduction
Canola oil is a variety of rapeseed oil. Unlike rapeseed oil, canola oil or double-zero rapeseed oil contains less than 2% erucic acid, high levels of which may cause adverse health effects. Coconut oil or coconut butter is an edible oil that is solid at room temperature and liquid in warmer climates.
In this article, we will compare the general differences, nutritional content, and health impacts of both oils.
Taste and Use
Vegetable oils are used in numerous ways and in different industries.
Canola and coconut oils are used as cooking oils, hair and skin oils, and industrial oils.
Some of the other uses of canola oil are its use in the production of margarine, dairy blends, emulsifiers, animal feed, vitamin E, candles, cosmetics, plastics, inks, etc.
Coconut oil is used in the production of soap, shampoos, detergents, emulsifiers, pesticides, and cosmetics, and it can also be an alternative fuel source.
Virgin or unrefined coconut oil has a coconut scent and flavor, whereas refined coconut oil and canola oil have a neutral flavor.
Varieties
Canola oil can be virgin or refined.
Refined canola oil is chemically extracted using a solvent, commonly hexane. The heat during this process can affect the stability of oil molecules, leading to omega-3 fatty acids being destroyed and trans fats being produced (1). Canola oil can be extracted by the cold-press method as well.
Virgin canola oil is an expeller-pressed oil that has been mechanically pressed or squeezed.
Canola oil can be genetically modified or non-GMO. However, most canola crops are genetically modified to be herbicide-tolerant.
The two kinds of coconut oil are refined and unrefined.
Unrefined, also known as a virgin, extra virgin, or pure coconut oil, is produced by pressing the coconut meat. No further processing undergoes this oil; therefore, it keeps its flavor.
Refined coconut oil is derived from dried coconut meat, known as copra. The copra goes through a process of refining, bleaching, and deodorizing, which leads to a loss of coconut flavor.
Refined edible coconut oil can be partially hydrogenated as well. Hydrogenation transforms unsaturated or “good” fats into saturated or trans fats, known as “bad” fats.
Nutrition
Nutritional values in this article are presented for canola oil and coconut oil.
Macronutrients and Calories
Canola oil and coconut oil are devoid of protein and carbohydrates. They are 100% made of fats. However, there is a difference in their fat composition.
The serving size of the oils is one tablespoon, which equals 14 grams of canola oil and 13.6 grams of coconut oil.
Calories
The edible oils are very high in calories. Canola and coconut oils provide more calories than most foods. Per 100g of coconut oil, there is 892, and in comparison, 100g of canola oil contains 884 calories.
One serving of canola oil provides 124 calories, while one serving of coconut oil provides 121 calories.
Fats
More than 99% of the macronutrient content of coconut oil belongs to fat, whereas canola oil consists of almost 100% fats.
Nearly 63% of the fats in canola oil are monounsaturated fatty acids, 28% are polyunsaturated fatty acids, and only 7% are saturated fatty acids.
The predominant monounsaturated fatty acid in canola oil is omega-9 oleic acid. The polyunsaturated fatty acid is omega-6 linoleic or omega-3 α-linolenic acid.
On the other hand, coconut oil contains more than 82% saturated fatty acids. Next by portion are monounsaturated fatty acids and only then polyunsaturated fatty acids.
More than half of the saturated fatty acids are medium-chain triglycerides or MCT. The predominant MCT found in coconut oil is lauric acid.
The oils contain some levels of trans fats as well and are absent in cholesterol.
Vitamins
Canola oil contains only high amounts of fat-soluble vitamins E and K. One serving size of canola oil covers the daily needs of vitamin E by 25% and vitamin K by almost 50%.
Coconut oil contains the same vitamins but in insignificant amounts.
Vitamin Comparison
Contains
more
Vitamin EVitamin E
+15772.7%
Contains
more
Vitamin KVitamin K
+11783.3%
Minerals
Their mineral composition is insignificant.
Glycemic Index
The glycemic indices of coconut and canola oils are 0, as they contain no carbs.
Acidity
Virgin coconut oil has a pH of 6.4 to 6.5, making it slightly acidic, whereas refined coconut oil has a pH of 6.9, making it neutral (2).
The pH of canola oil is neutral; it ranges from 6.9 to 6.7. A decrease in the number appears during the heating of the oil (3).
The PRAL or potential renal acid load value shows how much acid or base the given food produces in the organism.
The PRAL value of canola and coconut oils is 0, making them neutral.
Weight Loss & Diets
A meta-analysis including 25 studies has revealed that canola oil consumption leads to a modest decrease in body weight. However, changes in body mass index, waist and hip circumference, body lean, and fat mass were insignificant; when it comes to weight loss, a caloric deficit is what matters (4).
A study on mice suggests that cold-pressed canola oil is a better oil when compared with refined canola oil, as it may lower the risk of obesity and “bad” fat content in the blood (5).
However, another study on mice claims that a canola-rich diet leads to an increase in body weight (6).
A clinical trial performed with 29 obese men has concluded that coconut oil increases high-density lipoprotein levels and decreases total cholesterol / high-density lipoprotein ratio levels without changes in anthropometric variables (7).
A study suggests that daily intake of coconut oil may reduce body weight and fat accumulation as it is rich in MCT or medium-chain triglycerides. However, another study claims that coconut oil should not be promoted as having similar effects as MCT oil. Nevertheless, there is not enough consistent evidence on the topic of satiety and weight loss; further research needs to be done (8, 9, 10).
Health Impact
It’s important to mention that most of the research is done on less refined and unrefined or virgin canola oil, whereas most canola oil in the market is refined.
Health Benefits & Downsides
Cardiovascular Health
Many canola and coconut oil studies show contradictory results, making it unclear whether these oils are good or bad for heart health.
Canola oil may have cardioprotective, antithrombotic, antiarrhythmic, and anti-inflammatory effects and promote cardiovascular health. Due to the high level of monounsaturated fatty acids, canola oil has a beneficial effect on the regulation of plasma lipids and lipoproteins, leading to the reduction of coronary heart disease risk (11, 12).
However, another study on rats has suggested that canola oil is pro-inflammatory and increases plasma lipid levels, risk factors for heart disease (13). Similar results were achieved when rats were given repeatedly heated oil, which induced inflammatory stress and even negatively affected the liver (14).
A study has demonstrated that overweight or obese people continuously consuming canola oil have higher scores of metabolic syndrome (including diabetes, high blood pressure, obesity, and high risk of coronary heart disease, stroke, and atherosclerosis) than those who rarely or never use it. However, other studies suggest that canola oil reduces the risk of metabolic syndrome (15, 16, 17).
Although more often, we see that coconut oil is marketed as safe for the heart and even advertised as better than vegetable oils. However, that's not the case. Coconut oil is high in saturated fats, and it is associated with increased risks of cardiovascular diseases because it increases levels of LDL cholesterol. This, in turn, will increase risks of atherosclerosis and cardiovascular mortality (18, 19, 20, 21).
Diabetes
A 3-month ongoing controlled trial has shown that canola oil-enriched low glycemic load diets improve glycemic control in people with type 2 diabetes, particularly those with high systolic blood pressure (24).
Several studies suggest that canola oil, along with sesame and sesame-canola oils, may beneficially affect diabetes carrying different genotypes (25, 26).
Other studies speak in favor of canola oil and diabetes, suggesting improvements in fatty liver, lipid profile, measures of insulin resistance, and lower levels of fasting blood glucose (11, 27, 28, 29).
On the other hand, refined canola oil is associated with a higher risk of type 2 diabetes (30).
A case has been presented where a 66-year-old man with type 2 diabetes managed with insulin developed recurrent hypoglycemia due to coconut oil supplementation. However, this case was not a controlled experimental trial, and the primary source of data was the patient’s report. A review of the literature showed that coconut oil might positively affect blood sugar control, but more studies are required to confirm this (31).
In one study, animals were fed a high-calorie, fat, cholesterol, and fructose diet rich in coconut oil and developed obesity but had normal blood glucose levels and decreased markers of inflammation (32).
Cancer
Several animal studies suggest that canola oil may be chemoprotective against colon cancer (33, 34).
Canola oil can potentially suppress the growth of breast cancer cells as well. In a study, canola oil has shown synergistic effects on cancer cell growth suppression with some chemotherapeutic drugs (35, 36, 37).
Canola oil has some amounts of PAH or polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons, which increase after heating the oil. PAH may potentially increase the risk of cancer (38, 39, 40).
A study has shown that virgin, processed, and fractionated coconut oils have anti-cancer properties against oral and liver cancers (41).
As mentioned before, coconut oil is rich in lauric acid, which has been shown to have antiproliferative and pro-apoptotic effects in breast and endometrial cancer cells (42).
Neurological Health
Studies have shown that coconut oil improves cognitive functions in patients with Alzheimer’s disease. MCT metabolism leads to ketone body production, which can potentially serve as an alternative energy source and compensate for the lack of glucose utilization in the brain and stop the progression of neural death occurring in Alzheimer’s disease. Coconut oil has significantly improved orientation and language-construction areas of the brain (43, 44, 45, 46).
On the other hand, chronic consumption of canola oil in mouse models had a negative effect on memory and synaptic integrity (normal functioning synaptic unit); however, the limitation is that rat neurophysiology is not similar (47).
Another study on rats and their offspring has shown that a maternal high-fat diet enriched with canola oil can lead to neurodevelopmental issues in the offspring (48).
References
- Ask the Expert: Concerns about canola oil
- https://www.mdpi.com/2227-9717/8/4/402/pdf
- Heating Effect on Quality Characteristics of Mixed Canola Cooking Oils
- https://academic.oup.com/advances/article/10/3/419/5365770
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31183867/
- https://www.nature.com/articles/s41598-017-17373-3
- https://pubs.rsc.org/en/content/articlelanding/2020/fo/d0fo00872a/unauth
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0031938417302111
- COCONUT OIL – A REVIEW OF POTENTIAL APPLICATIONS
- https://www.nature.com/articles/ejcn201786
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3746113/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/15259529/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3215974/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/33278395/
- https://www.mdpi.com/2072-6643/10/8/972/htm
- https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/abs/10.1080/07315724.2010.10719844
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/27804268/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31928080/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29974400/
- https://bmjopen.bmj.com/content/8/3/e020167
- https://www.ahajournals.org/doi/full/10.1161/CIR.0000000000000510
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5719422/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31676261/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/24929428/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/33123324/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32690147/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/24625239/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/27055960/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/9506190/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32364230/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7781718/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5509134/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/21264790/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/24761850/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/23859037/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/17571951/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/20730604/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/34145544/
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0956713517302967
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32162691/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31736449/
- https://www.nature.com/articles/cddiscovery201763
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/28421789/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6885391/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30056419/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31953123/
Infographic
Mineral Comparison
| Contains more CalciumCalcium | +∞% |
| Contains more IronIron | +∞% |
| Contains more ZincZinc | +∞% |
All nutrients comparison - raw data values
| Nutrient |  |
 |
DV% diff. |
| Saturated fat | 7.365g | 82.475g | 341% |
| Polyunsaturated fat | 28.142g | 1.702g | 176% |
| Monounsaturated fat | 63.276g | 6.332g | 142% |
| Vitamin E | 17.46mg | 0.11mg | 116% |
| Vitamin K | 71.3µg | 0.6µg | 59% |
| Fats | 100g | 99.06g | 1% |
| Iron | 0mg | 0.05mg | 1% |
| Calories | 884kcal | 892kcal | 0% |
| Calcium | 0mg | 1mg | 0% |
| Zinc | 0mg | 0.02mg | 0% |
| Trans fat | 0.395g | 0.028g | N/A |
| Choline | 0.2mg | 0.3mg | 0% |
| Omega-3 - ALA | 9.137g | 0.019g | N/A |
| Omega-6 - Linoleic acid | 18.64g | 1.676g | N/A |
Macronutrient Comparison
| Contains more WaterWater | +∞% |
| Contains more OtherOther | +∞% |
Fat Type Comparison
| Contains less Sat. FatSaturated fat | -91.1% |
| Contains more Mono. FatMonounsaturated fat | +899.3% |
| Contains more Poly. FatPolyunsaturated fat | +1553.5% |
People also compare
References
All the values for which the sources are not specified explicitly are taken from FDA’s Food Central. The exact link to the food presented on this page can be found below.
- Canola oil - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/172336/nutrients
- Coconut oil - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/171412/nutrients
All the Daily Values are presented for males aged 31-50, for 2000-calorie diets.






