Cottage cheese vs. Cream cheese — Health Impact and Nutrition Comparison


Summary
Cottage cheese is richer in proteins, vitamin B12, phosphorus, and sodium. It is lower in calories, fats, and carbs. On the other hand, cream cheese is richer in calcium, selenium, and vitamins A, B2, and E.
Introduction
Cottage cheese and cream cheese are dairy products obtained after processing milk with an acidic product, also known as the curdling process. The difference is that cream cheese retains most water and keeps its spreadable texture. On the other hand, cottage cheese is drained after processing, and solid chunks remain in curdles.
Taste and flavor
Cottage cheese is solid and curdled; however, the texture is soft and creamy. It often has a milky taste. In comparison, cream cheese has a spreadable texture with a creamy flavor. Cream cheese is often found mixed with herbs and garlic.
Cottage cheese is moister compared to cream cheese.
Uses in the culinary world
Cottage cheese and cream changes have a wide range of versatility and are often used in the culinary world. They are used in baking, breakfast preparations, sauce and dip preparations, desserts, and main dishes like pasta, sushi, and soups.
Baking
Cream cheese and cottage cheese are good alternatives to use during baking. They are often used to alter the flavor and texture of cookies and cakes. The difference between cream cheese and cottage cheese is that it is the low-fat alternative between them, and it tastes closer to milk.
Breakfast preparations
Cream cheese is a famous spread that goes along with bagels. On the other hand, cottage cheese can go along with a healthy avocado and toast breakfast.
Desserts
Cream cheese is the main ingredient in the preparation of cheesecakes. On the other hand, cottage cheese is often used to prepare a dessert bowl, which can also be a breakfast alternative. A wide range of toppings can be added to a bowl of cottage cheese, like honey, fruits, and syrup.
However, when it comes to added toppings, we must consider the extra calories, sugars, and additives.
Crepe filling
Cream cheese and cottage cheese are often used in crepe fillings. They are mixed with vanilla and sugar to add a sweet flavor. The difference between them would be in the texture and taste. Cream cheese is creamy and denser, whereas cottage cheese is less creamy with a taste close to milk.
Sauces and dips
Cream cheese is a famous base for dipping sauce preparations that dip in vegetables and chips. However, cottage cheese can also be used as an alternative to it.
Taco dip
We can use cream cheese and cottage cheese to prepare the famous taco-layered dip. It is a popular snack with various layers of elements such as beef, avocados, etc. The main element is the taco and the sauce. The sauce is often prepared with cream cheese; we can add cottage cheese to give the sauce a more solid texture.
Main dishes
Pasta
We can use cream cheese and cottage cheese in the preparations of pasta. In this case, the difference between them is taste and texture related.
Soup
Cream cheese can also be used as a base in preparation for creamy soups.
Lasagna
Cream cheese makes lasagna even better than it is. We can use it between the layers, providing a creamier taste with a broader range of flavors. We can also use it on the top layer instead of mozzarella or other cheeses to provide a melting creamy flavor and texture. Also, cottage cheese is often used as an alternative between the layers.
Home Preparation
We can prepare cottage cheese at home. It is quite easy to make. While heating milk, acids are added (vinegar, citric acid), which causes the protein elements of milk to curdle up. This is then rinsed so that any acidic flavors are removed. Afterward, starch is added to keep the curdles from crumbling or sticking to each other.
We can also prepare cream cheese at home. Acid is added to a combination of milk and cream or only milk. The curdling process starts taking place. The curdled mixture is then taken and processed into a creamy texture. We can add various herbs and spices to make it more flavorful.
Shelf life
Cream cheese, if opened, has a shelf life of 10 days. On the other hand, it can last up to 1 month in the fridge when not opened.
On the other hand, cottage cheese lasts for up to 7 days in the fridge. However, if frozen, it can last for three months.
Nutrition
In this part of the article, the nutritional data of cottage cheese and cream cheese are assessed.
You can check this article, cottage cheese vs. greek yogurt, to get an idea about other comparative foods with cottage cheese.
100g of each will be considered while comparing their nutritional data.
It is important to note that cottage cheese and cream cheese have different water contents. Cottage cheese constitutes 80% water, meaning that 80g of the 100g is water. On the other hand, cream cheese has only 52.6% water, meaning 52.6g of the 100 is water.
Calories
Cottage cheese contains 95 calories. On the other hand, cream cheese contains much higher calories compared to cottage cheese. It contains 350 calories. Cream cheese has 368% more calories than cottage cheese.
Carbs
Cottage cheese has lower amounts of carbs compared to cream cheese. Cottage cheese contains 3.38g of carbohydrates compared to cream cheese which contains 5.52g.
Proteins
Cottage cheese is richer in protein compared to cream cheese. Cottage cheese contains 11.12g of proteins compared to cream cheese which contains 6.15g.
Fats
Cottage cheese is lower in fats compared to cream cheese. Cream cheese has its consistency due to its higher amounts of fats.
Monounsaturated fats and polyunsaturated fat amounts are higher in cream cheese.
Cream cheese has high amounts of cholesterol, 101mg. This is 34% of the recommended daily values.
Glycemic index
Cottage and cream cheese have equal glycemic indices, equal to 10.
Vitamins
Cottage cheese is richer in vitamin B12. On the other hand, cream cheese is richer in vitamins A, B2, and E.
Vitamin Comparison
Contains
more
Vitamin DVitamin D
+∞%
Contains
more
Vitamin B1Vitamin B1
+17.4%
Contains
more
Vitamin B12Vitamin B12
+95.5%
Contains
more
FolateFolate
+33.3%
Contains
more
Vitamin AVitamin A
+732.4%
Contains
more
Vitamin EVitamin E
+975%
Contains
more
Vitamin B2Vitamin B2
+41.1%
Contains
more
Vitamin B6Vitamin B6
+21.7%
Contains
more
Vitamin KVitamin K
+∞%
Minerals
Cottage cheese is richer in sodium and phosphorus. In comparison, cream cheese is richer in selenium.
Calcium
Cottage and cream cheese are among the top 25% of foods rich in calcium. Yet, there is a slight difference between them. Cream cheese is slightly richer in calcium compared to cottage cheese.
Mineral Comparison
Contains
more
CopperCopper
+61.1%
Contains
more
PhosphorusPhosphorus
+48.6%
Contains
more
SeleniumSelenium
+12.8%
Contains
more
MagnesiumMagnesium
+12.5%
Contains
more
CalciumCalcium
+16.9%
Contains
more
PotassiumPotassium
+26.9%
Contains
more
IronIron
+57.1%
Contains
more
ZincZinc
+25%
Contains
less
SodiumSodium
-13.7%
Contains
more
ManganeseManganese
+450%
Weight loss and diets
Keto
Cottage cheese and cream cheese are considered low-carb foods. They are keto diet foods.
However, it is important to note that in the case of cottage cheese, it has to be consumed without additional toppings and syrups.
Vegan
Vegans cannot consume cottage cheese and cream cheese for vegan diets because they are dairy products - animal derivatives.
Dairy-free
The low amounts of carbs (lactose) in cottage cheese and cream cheese do not trigger an intolerance response in most lactose-intolerant individuals. However, this is on the individual level and only a standard for some lactose-intolerant individuals. In cases of need, lactase enzymes can facilitate the digestion of cottage cheese and cream cheese.
Another reason to follow a dairy-free diet is milk allergy.
Health impacts
Health benefits
Cardiovascular health
The inhibition of the angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) is the most studied mechanism underlying the antihypertensive effects of cheese peptides (1). ACE-inhibitor medications (Captopril, Lisinopril, etc.) also work by this mechanism (2). As a result, both of these products have antihypertensive effects.
People taking MAO inhibitors (particularly antidepressants) may experience a hypertensive crisis when eating cheeses, including these cheeses, which contain tyramine (3).
This study shows that moderate amounts of cream-based dairy products positively affect cardiovascular health. (4)
Diabetes
There is a direct relationship between the reduction of developing type 2 diabetes and moderate consumption of dairy without additives and sugars. (5)
Studies highlight the association between the reduction of risks of developing metabolic disorders and diabetes. (6)
Downsides & Risks
Cancer
This article shows a positive association between the development of breast cancer and the consumption of cream cheese and cottage cheese when consumed in high amounts. (7)
There is a direct association between the development of prostate cancer and the consumption of high-calcium diets. (8)
Diabetes
Full-fat dairy consumption is associated with pre-diabetes development. If pre-diabetes is not controlled in the long run, it develops into diabetes. (9)
Intolerance and allergy
As previously mentioned, people with lactose intolerance or milk allergy should avoid cottage cheese and cream cheese.
Common symptoms of lactose intolerance are abdominal cramps, diarrhea, bloating, and flatulence. In contrast, milk allergy may manifest with digestive symptoms such as abdominal cramps, diarrhea, and bloody stools or non-specific allergic reactions such as hives, wheezing, itching, vomiting, etc.
References
- https://academic.oup.com/jn/article/137/3/825S/4664770
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/18843651/
- https://europepmc.org/article/med/3283290
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/25476191/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3719038/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5367265/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5998914/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/22081693/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29498341/
Infographic
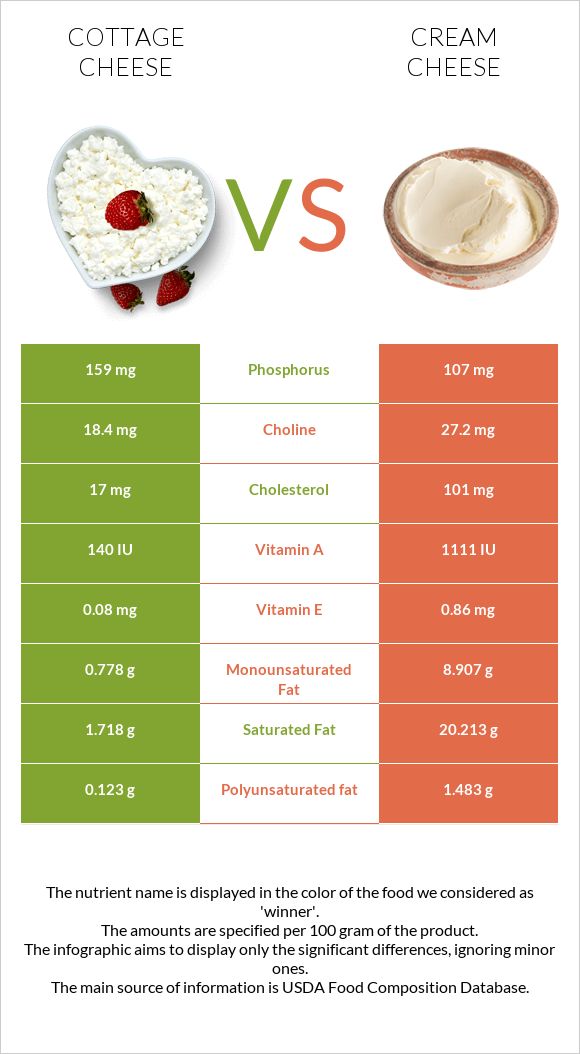
All nutrients comparison - raw data values
| Nutrient |  |
 |
DV% diff. |
| Saturated fat | 1.718g | 20.213g | 84% |
| Fats | 4.3g | 34.44g | 46% |
| Vitamin A | 37µg | 308µg | 30% |
| Cholesterol | 17mg | 101mg | 28% |
| Monounsaturated fat | 0.778g | 8.907g | 20% |
| Calories | 98kcal | 350kcal | 13% |
| Protein | 11.12g | 6.15g | 10% |
| Vitamin B12 | 0.43µg | 0.22µg | 9% |
| Polyunsaturated fat | 0.123g | 1.483g | 9% |
| Phosphorus | 159mg | 107mg | 7% |
| Vitamin E | 0.08mg | 0.86mg | 5% |
| Vitamin B2 | 0.163mg | 0.23mg | 5% |
| Sodium | 364mg | 314mg | 2% |
| Selenium | 9.7µg | 8.6µg | 2% |
| Vitamin K | 0µg | 2.1µg | 2% |
| Choline | 18.4mg | 27.2mg | 2% |
| Carbs | 3.38g | 5.52g | 1% |
| Calcium | 83mg | 97mg | 1% |
| Potassium | 104mg | 132mg | 1% |
| Iron | 0.07mg | 0.11mg | 1% |
| Copper | 0.029mg | 0.018mg | 1% |
| Zinc | 0.4mg | 0.5mg | 1% |
| Vitamin D | 0.1µg | 0µg | 1% |
| Vitamin B5 | 0.557mg | 0.517mg | 1% |
| Vitamin B6 | 0.046mg | 0.056mg | 1% |
| Folate | 12µg | 9µg | 1% |
| Net carbs | 3.38g | 5.52g | N/A |
| Vitamin D | 3 IU | 0 IU | 0% |
| Magnesium | 8mg | 9mg | 0% |
| Sugar | 2.67g | 3.76g | N/A |
| Starch | 0.35g | 0% | |
| Manganese | 0.002mg | 0.011mg | 0% |
| Vitamin B1 | 0.027mg | 0.023mg | 0% |
| Vitamin B3 | 0.099mg | 0.091mg | 0% |
| Tryptophan | 0.147mg | 0.069mg | 0% |
| Threonine | 0.5mg | 0.233mg | 0% |
| Isoleucine | 0.591mg | 0.324mg | 0% |
| Leucine | 1.116mg | 0.657mg | 0% |
| Lysine | 0.934mg | 0.567mg | 0% |
| Methionine | 0.269mg | 0.191mg | 0% |
| Phenylalanine | 0.577mg | 0.291mg | 0% |
| Valine | 0.748mg | 0.395mg | 0% |
| Histidine | 0.326mg | 0.175mg | 0% |
| Omega-3 - EPA | 0g | 0.01g | N/A |
| Omega-3 - ALA | 0.125g | N/A | |
| Omega-3 - DPA | 0g | 0.02g | N/A |
| Omega-3 - Eicosatrienoic acid | 0.002g | N/A | |
| Omega-6 - Gamma-linoleic acid | 0.002g | N/A | |
| Omega-6 - Dihomo-gamma-linoleic acid | 0.036g | N/A | |
| Omega-6 - Eicosadienoic acid | 0.007g | N/A | |
| Omega-6 - Linoleic acid | 0.807g | N/A |
Macronutrient Comparison
| Contains more ProteinProtein | +80.8% |
| Contains more WaterWater | +51.6% |
| Contains more FatsFats | +700.9% |
| Contains more CarbsCarbs | +63.3% |
Fat Type Comparison
| Contains less Sat. FatSaturated fat | -91.5% |
| Contains more Mono. FatMonounsaturated fat | +1044.9% |
| Contains more Poly. FatPolyunsaturated fat | +1105.7% |
Carbohydrate type comparison
| Contains more StarchStarch | +∞% |
| Contains more LactoseLactose | +40.8% |
People also compare
References
All the values for which the sources are not specified explicitly are taken from FDA’s Food Central. The exact link to the food presented on this page can be found below.
- Cottage cheese - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/172179/nutrients
- Cream cheese - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/173418/nutrients
All the Daily Values are presented for males aged 31-50, for 2000-calorie diets.



