Coconut Oil vs. Coconut Milk — What’s the Difference?


Summary
While coconut oil is 99% fat, coconut milk contains 68% water and 24% fat and small amounts of protein and carbohydrates.
Coconut oil is very high in calories and saturated fats and is nearly absent in vitamins and minerals. In comparison, coconut milk is a source of several vitamins and minerals, such as copper, manganese, and iron; however, it has a high glycemic index of 97.
Introduction
Coconut (Cocos nucifera) products, such as coconut oil and coconut milk, are widely available in many parts of the world and can be found on the shelves of many supermarkets. Other coconut products are coconut butter, coconut cream, and coconut water.
Coconut oil is a tropical oil derived from the white parts of the coconut, known as coconut meat or coconut flesh. It is solid or semi-solid at room temperature and liquid at higher temperatures.
Coconut milk is a white opaque liquid that has the same consistency as any other milk. Coconut milk can be made from dried or fresh coconut meat.
In this article, we will discuss the difference between coconut oil and coconut milk according to their main differences, nutritional content, diet and weight loss, health impacts, and myths.
What Are the Actual Differences?
There are many differences, including shelf life, availability, and usage.
Shelf Life
Coconut oil has a longer shelf life compared to coconut milk. Mainly because it is an oil that ultimately has a longer shelf life. Often preservatives are added to coconut milk to extend its shelf life.
Price
Coconut oil is more expensive, and it is considered one of the most expensive oils compared to other cooking oils. The comparison with other oils will not be discussed in this article, but it is important to highlight that notion.
Availability
Coconut oil and milk are mostly available and cheaper in tropical regions mainly because they are harvested there. Coconut milk is more easily prepared even at home if there is a mature coconut, although many coconuts are required for a decent amount of coconut milk.
Usage
Coconut milk is more versatile in the culinary world. Cooking, drinking as an alternative to milk, and preparing various breakfast meals. Coconut milk is used in Asian cuisine, mostly in Filipino, Indian, and other countries. On the other hand, coconut oil is mostly used in cooking.
Nutrition
This article compares 100g of coconut oil and coconut milk. Both have a serving size of 1 tbsp, equal to 13.6g for coconut oil and 15g for coconut milk.
While coconut oil is 99% fat, coconut milk contains 68% water and 24% fat, and small amounts of protein and carbohydrates.
Macronutrient Comparison
Contains
more
FatsFats
+315.5%
Contains
more
OtherOther
+28.2%
Contains
more
ProteinProtein
+∞%
Contains
more
CarbsCarbs
+∞%
Contains
more
WaterWater
+225300%
Calories
When it comes to calories, coconut oil is very high in calories as compared to coconut milk. A 100g of coconut oil provides 892 calories, whereas coconut milk provides 230.
1 tbsp of coconut oil and coconut milk provides 121 and 34.5 calories, respectively.
Carbs
Coconut oil contains 0g of carbs, whereas coconut milk has higher carbs, equal to 5.5g.
Fats
The fat profile of both is the most important nutritional feature.
Coconut oil is an oil food meaning that most of its weight is made of fat. It contains 99g of fat per 100g. On the other hand, coconut milk contains less fat. Coconut milk contains 24g of fat per 100g.
Over 90% of fats in both coconut milk and coconut oil are saturated or “bad” fats. More than half of the saturated fats are medium-chain triglycerides (MCTs or MCFAs), predominantly in the form of lauric acid.
In the second place are polyunsaturated fats, leaving monounsaturated fats in the last place.
Fat Type Comparison
Contains
more
Mono. FatMonounsaturated fat
+524.5%
Contains
more
Poly. FatPolyunsaturated fat
+552.1%
Contains
less
Sat. FatSaturated fat
-74.4%
Coconuts and coconut products are naturally absent in cholesterol. Coconut oil contains some amounts of trans fats.
Vitamins
Coconut milk contains some amounts of vitamins B1, B3, B5, B6, B9 (folate), C, E, and K.
Coconut oil contains fat-soluble vitamins E and K in negligible amounts.
Vitamin Comparison
Contains
more
Vitamin KVitamin K
+500%
Contains
more
Vitamin CVitamin C
+∞%
Contains
more
Vitamin EVitamin E
+36.4%
Contains
more
Vitamin B1Vitamin B1
+∞%
Contains
more
Vitamin B3Vitamin B3
+∞%
Contains
more
Vitamin B5Vitamin B5
+∞%
Contains
more
Vitamin B6Vitamin B6
+∞%
Contains
more
FolateFolate
+∞%
Minerals
Coconut oil is almost absent in minerals, whereas coconut milk is rich in copper, manganese, and iron. Coconut milk is also a source of phosphorus, selenium, magnesium, zinc, choline, and calcium.
Mineral Comparison
Contains
less
SodiumSodium
-100%
Contains
more
MagnesiumMagnesium
+∞%
Contains
more
CalciumCalcium
+1500%
Contains
more
PotassiumPotassium
+∞%
Contains
more
IronIron
+3180%
Contains
more
CopperCopper
+∞%
Contains
more
ZincZinc
+3250%
Contains
more
PhosphorusPhosphorus
+∞%
Contains
more
ManganeseManganese
+∞%
Contains
more
SeleniumSelenium
+∞%
Glycemic Index
The glycemic index difference between coconut milk and coconut oil is very remarkable.
The glycemic index of coconut oil is 0, as it is 99% fat and contains no carbs.
The glycemic index of coconut milk is 97, and it is classified as a high glycemic index food.
Diets And Weight Loss
Vegan & Dairy-free
Coconut milk and coconut oil are used during the vegan diet. Coconut oil can replace butter in cooking as it gives a dense texture to food due to its high saturated fat content.
On the other hand, coconut milk is a good alternative to dairy milk; however, better alternatives are available that are low in saturated fats, such as soy milk and almond milk.
Keto
Coconut oil and coconut milk are low in carbs and can be part of the keto diet. Most importantly, here we have coconut milk which is a lower-carb version of nearly any non-dairy milk. In addition to that, coconut milk can be used in cooking.
Health Impact: Benefits & Risks
Cancer
Coconut oil and coconut milk contain lauric acid, a fatty acid that decreases the risk of developing an enlarged prostate and prostate cancer. The lauric acid may also induce apoptosis in breast and endometrial cancer cells (1, 2).
Neurological Health
According to a study, a diet high in coconut oil may improve the cognitive skills of those with Alzheimer's disease (3). Coconut oil may improve orientation and language-construction areas of the brain
The lauric acid present in coconut milk and oil may also promote healthy cognitive development (4).
Cardiovascular Health
Both coconut oil and coconut milk contain saturated fat, which, in excess, can contribute to CVD risk by raising LDL (“bad” cholesterol) levels. However, coconut milk contains less saturated fat due to its dilution with water and the fiber from the coconut meat (5).
Additionally, coconut milk provides various essential nutrients (including vitamin E, which may help reduce the risk of atherosclerosis), making it a more balanced option than coconut oil. When consumed in moderation as part of a balanced diet, coconut milk may offer potential health benefits without significantly increasing the risk of CVD.
It is recommended by the American Heart Association to reduce the intake of dietary saturated fats (up to 5-6% of total calorie intake) and replace them with unsaturated fats to lower the risk of cardiovascular disease (6, 7).
Miscellaneous
As a vegan cooking oil, coconut oil may be used in cooking. It is also used in cooking for the preparation of vegan mayonnaise.
Coconut oil has an advantage over other oils in that it may be safely used for high-temperature cooking.
Another benefit of coconut oil is that it may be used as a skin moisturizer and UV protection. Although using coconut oil as a moisturizer has no nutritional advantages, it does have medicinal significance.
Myths
Coconut oil is a nutritious and risk-free oil to consume: incorrect
Coconut oil is well known in the vegan world and among those who follow the keto diet. It is promoted as a healthy fat to ingest. However, increased daily consumption of coconut oil over a large period of time may increase the risk of developing metabolic syndrome, including obesity, high blood pressure, stroke, and liver diseases.
Replace carbs with fats: incorrect
This is heavily emphasized in the keto community. When carbohydrates are removed from the diet and replaced with lipids that are primarily saturated fats, such as butter or coconut oil, the risk of metabolic syndrome increase (8).
References
- https://www.researchgate.net/publication/6201718
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5601385/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30056419/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/28421789/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31928080/
- https://www.heart.org/en/healthy-living/healthy-eating/eat-smart/fats/saturated-fats
- https://www.ahajournals.org/doi/full/10.1161/CIR.0000000000000510
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5492032/
Infographic
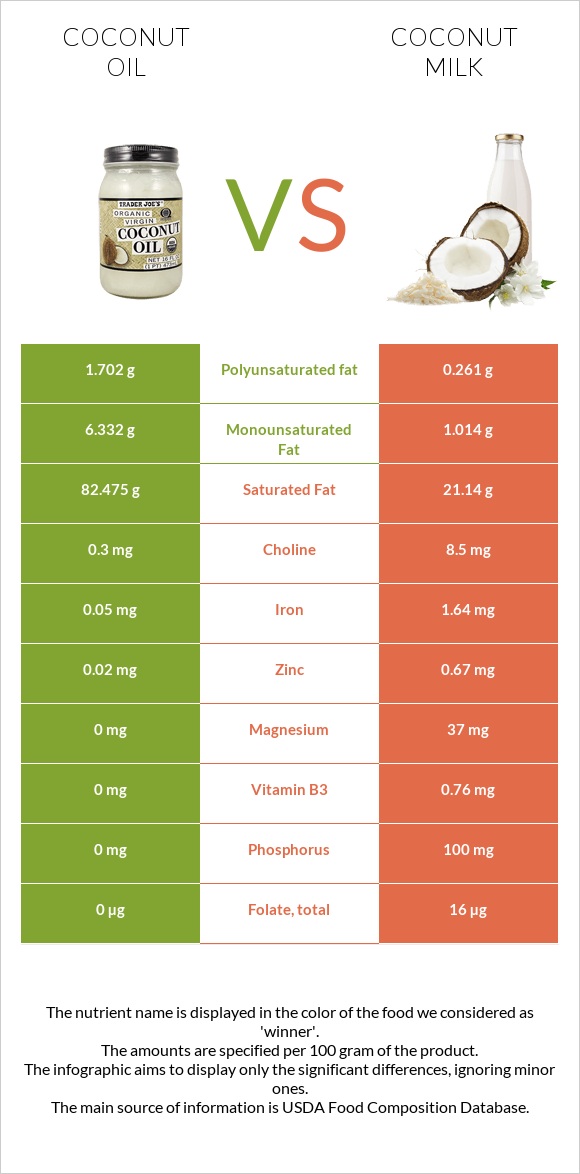
All nutrients comparison - raw data values
| Nutrient |  |
 |
DV% diff. |
| Saturated fat | 82.475g | 21.14g | 279% |
| Fats | 99.06g | 23.84g | 116% |
| Manganese | 0mg | 0.916mg | 40% |
| Calories | 892kcal | 230kcal | 33% |
| Copper | 0mg | 0.266mg | 30% |
| Iron | 0.05mg | 1.64mg | 20% |
| Phosphorus | 0mg | 100mg | 14% |
| Monounsaturated fat | 6.332g | 1.014g | 13% |
| Selenium | 0µg | 6.2µg | 11% |
| Polyunsaturated fat | 1.702g | 0.261g | 10% |
| Magnesium | 0mg | 37mg | 9% |
| Fiber | 0g | 2.2g | 9% |
| Potassium | 0mg | 263mg | 8% |
| Zinc | 0.02mg | 0.67mg | 6% |
| Protein | 0g | 2.29g | 5% |
| Vitamin B3 | 0mg | 0.76mg | 5% |
| Vitamin B5 | 0mg | 0.183mg | 4% |
| Folate | 0µg | 16µg | 4% |
| Vitamin C | 0mg | 2.8mg | 3% |
| Vitamin B6 | 0mg | 0.033mg | 3% |
| Carbs | 0g | 5.54g | 2% |
| Calcium | 1mg | 16mg | 2% |
| Vitamin B1 | 0mg | 0.026mg | 2% |
| Sodium | 0mg | 15mg | 1% |
| Choline | 0.3mg | 8.5mg | 1% |
| Net carbs | 0g | 3.34g | N/A |
| Sugar | 0g | 3.34g | N/A |
| Vitamin E | 0.11mg | 0.15mg | 0% |
| Vitamin K | 0.6µg | 0.1µg | 0% |
| Trans fat | 0.028g | N/A | |
| Tryptophan | 0mg | 0.027mg | 0% |
| Threonine | 0mg | 0.083mg | 0% |
| Isoleucine | 0mg | 0.09mg | 0% |
| Leucine | 0mg | 0.17mg | 0% |
| Lysine | 0mg | 0.101mg | 0% |
| Methionine | 0mg | 0.043mg | 0% |
| Phenylalanine | 0mg | 0.116mg | 0% |
| Valine | 0mg | 0.139mg | 0% |
| Histidine | 0mg | 0.053mg | 0% |
| Omega-3 - ALA | 0.019g | N/A | |
| Omega-6 - Linoleic acid | 1.676g | N/A |
People also compare
References
All the values for which the sources are not specified explicitly are taken from FDA’s Food Central. The exact link to the food presented on this page can be found below.
- Coconut oil - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/171412/nutrients
- Coconut milk - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/170172/nutrients
All the Daily Values are presented for males aged 31-50, for 2000-calorie diets.






