Cucumber vs. Bell pepper — Health Impact and Nutrition Comparison


Summary
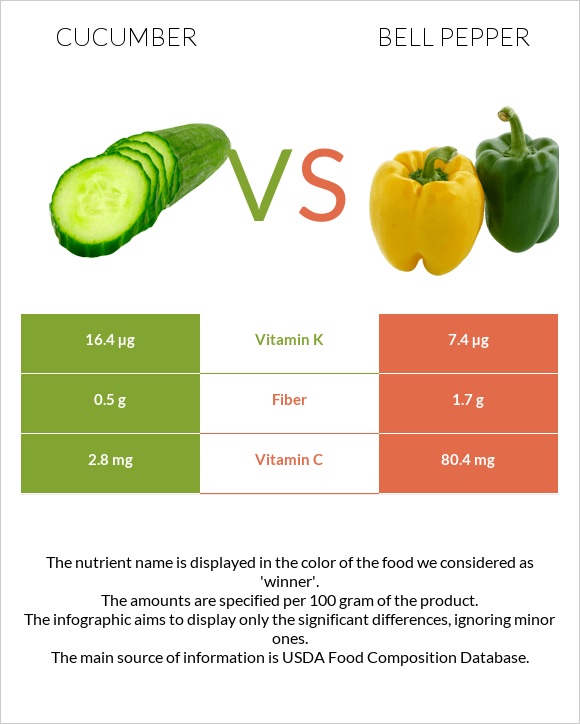
Bell peppers contain 80.4 mg of vitamin C, around 29 times more than cucumbers, which contain 2.8mg. However, cucumbers are 9mg richer in vitamin K content. Bell peppers are also higher in fiber, folate, and vitamin A. Cucumbers are low in calories, and Bell pepper has a higher oxalate content.
Introduction
Bell peppers and cucumbers are widespread and commonly used vegetables. This article will review their key differences, focusing on their nutrition and health impacts.
Actual Differences
Classification and Varieties
Cucumbers and bell peppers are popular vegetables that come in a variety of types, each with distinct characteristics. Cucumbers, classified scientifically as Cucumis sativus, are part of the Cucurbitaceae family. They are typically categorized into slicing, pickling, and seedless or burpless varieties. Slicing cucumbers, such as the Marketmore, are long and smooth-skinned, ideal for fresh consumption. Pickling cucumbers, like the Boston Pickling, are shorter, with a bumpy exterior suited for brining. Seedless cucumbers, including the English cucumber, are used for minimal seeds and a milder taste.
Bell peppers, or Capsicum annuum, belong to the Solanaceae family. Varieties include the classic California Wonder, known for its blocky shape and thick walls, and the elongated, sweet Corno di Toro.
Appearance
Cucumbers are typically elongated and cylindrical. Their skin can be smooth or bumpy and varies in color from light to dark green. Some varieties, like the English cucumber, are thinner with fewer seeds. Inside, cucumbers have a pale green, watery flesh with small, edible seeds arranged in a central cavity.
In contrast, bell peppers are short and famous for their blocky, square shape. They have a glossy, firm exterior that comes in various colors, including green, yellow, orange, red, and even purple. The interior of a bell pepper consists of a hollow cavity filled with small, white seeds attached to a pithy rib. The flesh of bell pepper is thick, crisp, and juicy, contrasting the more delicate, watery texture of cucumber flesh.
Taste and Use
Bell peppers have a sweet, slightly tangy flavor that intensifies as they ripen from green to red. Green bell peppers are more bitter and less sweet, while red, orange, and yellow peppers are sweeter and fruitier. Their crisp texture makes them ideal for a variety of dishes, both raw and cooked. Raw bell peppers are commonly added to salads, salsas, and crudité platters. When cooked, they can be roasted, grilled, sautéed, or stuffed and added to dishes like stir-fries, fajitas, and casseroles.
Cucumbers, on the other hand, have a mild, refreshing taste with a watery and crisp texture. They can be added to salads, sandwiches, and sauces like tzatziki. Slicing cucumbers are perfect for fresh consumption while pickling cucumbers are used to make tangy, crunchy pickles. Seedless varieties, with their tender skin and fewer seeds, are ideal for snacking and garnishing. Unlike bell peppers, cucumbers are less commonly cooked, as their high water content can make them mushy, but they are sometimes lightly sautéed or incorporated into warm dishes in Asian cuisines.
Nutrition
In this article, we will compare the nutritional composition of raw cucumbers and sweet, green, raw Bell peppers. The nutritional values for 100g servings of these vegetables are presented here.
Macronutrients and Calories
Both vegetables are low in nutrients; however, Bell peppers are slightly denser in nutrients compared to cucumbers. The protein content of these vegetables is nearly identical; each contains less than one gram of protein. They both provide more than 90% of water.
Macronutrient Comparison
Contains
more
ProteinProtein
+32.3%
Contains
more
FatsFats
+54.5%
Contains
more
CarbsCarbs
+27.8%
Contains
more
OtherOther
+15.8%
Carbohydrates
Cucumbers are lower in carbs, containing 3.63g of carbohydrates compared to 4.64g in Bell peppers. However, Bell peppers are lower in net carbs. Cucumbers are higher in starch, whereas Bell peppers are higher in sucrose, fructose, and glucose.
Fiber
Bell peppers are around 3.5 times richer in dietary fiber, containing 1.7 grams, while cucumbers provide only 0.5 grams of it. Bell peppers are especially richer in insoluble fiber.
Carbohydrate type comparison
Contains
more
StarchStarch
+∞%
Contains
more
MaltoseMaltose
+∞%
Contains
more
SucroseSucrose
+266.7%
Contains
more
GlucoseGlucose
+52.6%
Contains
more
FructoseFructose
+28.7%
Calories
Cucumbers provide 15 kcal per 100g, while the same amount of Bell peppers contains 20 kcal. Cucumbers and Bell peppers are classified as low-calorie foods.
Vitamins
Cucumbers contain higher amounts of vitamin K than Bell peppers, providing 16.4mg compared to 7.4mg in Bell peppers. On the other hand, Bell peppers are notably richer in vitamin C, with 80.4mg compared to 2.8mg in cucumbers.
Bell peppers also contain more vitamins A, E, B1, B3, B6, and folate. However, cucumbers contain higher amounts of vitamins B2 and B5.
Both vegetables do not provide vitamin D and B12.
Vitamin Comparison
Contains
more
Vitamin B2Vitamin B2
+17.9%
Contains
more
Vitamin B5Vitamin B5
+161.6%
Contains
more
Vitamin KVitamin K
+121.6%
Contains
more
Vitamin CVitamin C
+2771.4%
Contains
more
Vitamin AVitamin A
+260%
Contains
more
Vitamin EVitamin E
+1133.3%
Contains
more
Vitamin B1Vitamin B1
+111.1%
Contains
more
Vitamin B3Vitamin B3
+389.8%
Contains
more
Vitamin B6Vitamin B6
+460%
Contains
more
FolateFolate
+42.9%
Minerals
Cucumbers are the winners in this category. They provide more calcium, magnesium, phosphorus, zinc, and selenium than Bell peppers. On the other hand, Bell peppers contain more amounts of iron, potassium, copper, and manganese. Also, cucumbers are 1mg lower in sodium.
Mineral Comparison
Contains
more
MagnesiumMagnesium
+30%
Contains
more
CalciumCalcium
+60%
Contains
more
ZincZinc
+53.8%
Contains
more
PhosphorusPhosphorus
+20%
Contains
less
SodiumSodium
-33.3%
Contains
more
SeleniumSelenium
+∞%
Contains
more
PotassiumPotassium
+19%
Contains
more
IronIron
+21.4%
Contains
more
CopperCopper
+61%
Contains
more
ManganeseManganese
+54.4%
Oxalates
Bell peppers are slightly higher in oxalates than cucumbers. The Bell pepper oxalate content equals 10mg, while the oxalate content of cucumber is 4mg. Both are considered low-oxalate foods.
Glycemic Index
Cucumbers and Bell peppers are considered low-GI foods. The GI value of Bell peppers is 32, and the GI value of cucumber equals 21.
Acidity
Bell pepper is alkaline, having a PRAL value of -2.9, while cucumber is alkaline, with a PRAL value of -2.4.
Health impact
Eye Health
Bell peppers significantly impact eye health due to their high content of vitamins and antioxidants, particularly vitamin A and carotenoids like lutein and zeaxanthin.
Vitamin A, derived from the beta-carotene in bell peppers, is essential for maintaining good vision, especially in low-light conditions. Beta-carotene is converted into retinol, a form of vitamin A, which is a component of rhodopsin, a protein in the eyes that absorbs light (1). Furthermore, lutein and zeaxanthin, two carotenoids present in bell peppers, are known to filter harmful blue light and protect the retina. Studies have shown that these carotenoids accumulate in the retina, where they help to prevent oxidative stress and inflammation, thereby reducing the risk of chronic eye diseases like age-related macular degeneration (2).
Diabetes
Bell peppers and cucumbers can positively impact diabetes management due to their nutritional profiles and low glycemic index. A study suggests that the antioxidant properties of bell peppers may improve insulin sensitivity and glycemic control in diabetic patients (3). Furthermore, the fiber content in bell peppers aids in slowing down glucose absorption, helping maintain stable blood sugar levels.
Cucumbers also benefit diabetes management. They are high in water and contain compounds like cucurbitacins and lignans with anti-inflammatory and antidiabetic properties. According to a study, cucumber extracts exhibit hypoglycemic effects, which can help lower blood sugar levels (4).
Infographic
All nutrients comparison - raw data values
| Nutrient |  |
 |
DV% diff. |
| Vitamin C | 2.8mg | 80.4mg | 86% |
| Vitamin B6 | 0.04mg | 0.224mg | 14% |
| Vitamin K | 16.4µg | 7.4µg | 8% |
| Fiber | 0.5g | 1.7g | 5% |
| Copper | 0.041mg | 0.066mg | 3% |
| Vitamin B1 | 0.027mg | 0.057mg | 3% |
| Vitamin B5 | 0.259mg | 0.099mg | 3% |
| Vitamin E | 0.03mg | 0.37mg | 2% |
| Manganese | 0.079mg | 0.122mg | 2% |
| Vitamin B3 | 0.098mg | 0.48mg | 2% |
| Magnesium | 13mg | 10mg | 1% |
| Calcium | 16mg | 10mg | 1% |
| Potassium | 147mg | 175mg | 1% |
| Iron | 0.28mg | 0.34mg | 1% |
| Zinc | 0.2mg | 0.13mg | 1% |
| Phosphorus | 24mg | 20mg | 1% |
| Vitamin A | 5µg | 18µg | 1% |
| Selenium | 0.3µg | 0µg | 1% |
| Folate | 7µg | 10µg | 1% |
| Calories | 15kcal | 20kcal | 0% |
| Protein | 0.65g | 0.86g | 0% |
| Fats | 0.11g | 0.17g | 0% |
| Net carbs | 3.13g | 2.94g | N/A |
| Carbs | 3.63g | 4.64g | 0% |
| Sugar | 1.67g | 2.4g | N/A |
| Starch | 0.83g | 0g | 0% |
| Sodium | 2mg | 3mg | 0% |
| Vitamin B2 | 0.033mg | 0.028mg | 0% |
| Choline | 6mg | 5.5mg | 0% |
| Saturated fat | 0.037g | 0.058g | 0% |
| Monounsaturated fat | 0.005g | 0.008g | 0% |
| Polyunsaturated fat | 0.032g | 0.062g | 0% |
| Tryptophan | 0.005mg | 0.012mg | 0% |
| Threonine | 0.019mg | 0.036mg | 0% |
| Isoleucine | 0.021mg | 0.024mg | 0% |
| Leucine | 0.029mg | 0.036mg | 0% |
| Lysine | 0.029mg | 0.039mg | 0% |
| Methionine | 0.006mg | 0.007mg | 0% |
| Phenylalanine | 0.019mg | 0.092mg | 0% |
| Valine | 0.022mg | 0.036mg | 0% |
| Histidine | 0.01mg | 0.01mg | 0% |
| Fructose | 0.87g | 1.12g | 0% |
Fat Type Comparison
| Contains less Sat. FatSaturated fat | -36.2% |
| Contains more Mono. FatMonounsaturated fat | +60% |
| Contains more Poly. FatPolyunsaturated fat | +93.8% |
People also compare
References
All the values for which the sources are not specified explicitly are taken from FDA’s Food Central. The exact link to the food presented on this page can be found below.
- Cucumber - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/168409/nutrients
- Bell pepper - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/170427/nutrients
All the Daily Values are presented for males aged 31-50, for 2000-calorie diets.




