Cucumber vs. Eggplant — Health Impact and Nutrition Comparison


Summary
Eggplant contains more Vitamin E, Vitamin B3, Vitamin B6, folate, potassium, and copper than cucumber. Eggplant is also lower in saturated fat.
Cucumber contains higher amounts of calcium, iron, zinc, Vitamin A, Vitamin C, and Vitamin K. It is also lower in sugar and glycemic index.
Introduction
In this article, you can find a detailed description of the differences between eggplant and cucumber.
What's The Actual Difference?
Eggplant belongs to the Solanum genus, and cucumber belongs to the Cucumis genus. Eggplant is a dark purple or brownish-purple color, whereas regular cucumbers have green stripes on darker green skin.
Cucumbers are commonly green but can also be white, yellow, or orange. Cucumbers' flavor is all about their texture and water content; they are sweet and plumpy. Eggplant has a tender, mild, and sweet flavor.
Nutrition
Below are the nutrition infographics that visually show the differences between cucumber and eggplant. This article discusses the food varieties raw cucumber and raw eggplant.
Calories
Both cucumber and eggplant are low in calories. Cucumber contains 15 calories per 100g, whereas eggplant contains 25 calories per 100g. They can both be excellent additions to low-calorie diets.
Fats
Both plants have fats of less than 1g. Cucumbers contain 0.11g of fat, and the eggplant has 0.18g of fat. Due to their low-fat content, cucumber and eggplant can be added to the list of recommended foods for low-fat diets, such as The Paleo Diet and The Vegan Diet.
Carbs
Eggplants have two times more carbs than cucumbers; however, the carb content of both plants is shallow. Eggplant contains 5.88g of carbs per 100g, whereas cucumber contains 3.63g of carbs per 100g. Eggplant has 3g fiber and 2.88g net carbs. In addition, eggplant falls in the top 27% of foods as a source of fiber.
Cucumber provides 0.5g of fiber and 3.13g of net carbs.
Both are considered low-carb foods.
Cholesterol
Both plants have no cholesterol.
Protein
Cucumbers and eggplant have tiny and equal amounts of protein.
Vitamins
Eggplant contains nine times more Vitamin E and five times more Vitamin B3 than cucumber. Vitamin B1, Vitamin B2, Vitamin B6, and folate are also higher in eggplant.
On the other hand, cucumber contains more Vitamin A, Vitamin C, and Vitamin K.
Both eggplant and cucumber have an equal amount of Vitamin B5.
Vitamin Comparison
Contains
more
Vitamin CVitamin C
+27.3%
Contains
more
Vitamin AVitamin A
+400%
Contains
more
Vitamin KVitamin K
+368.6%
Contains
more
Vitamin EVitamin E
+900%
Contains
more
Vitamin B1Vitamin B1
+44.4%
Contains
more
Vitamin B2Vitamin B2
+12.1%
Contains
more
Vitamin B3Vitamin B3
+562.2%
Contains
more
Vitamin B6Vitamin B6
+110%
Contains
more
FolateFolate
+214.3%
Minerals
Cucumber is relatively higher in calcium, zinc, and iron, whereas eggplant provides more potassium and copper.
Both plants have equal amounts of magnesium, phosphorus, and sodium.
Small mention: both plants are deficient in sodium: 2mg per 100g.
Mineral Comparison
Contains
more
CalciumCalcium
+77.8%
Contains
more
IronIron
+21.7%
Contains
more
ZincZinc
+25%
Contains
more
PotassiumPotassium
+55.8%
Contains
more
CopperCopper
+97.6%
Contains
more
ManganeseManganese
+193.7%
Glycemic Index
Overall, vegetables are considered low-glycemic-index foods. However, the glycemic index of cucumber is slightly lower than that of eggplant.
Cucumber has a glycemic index of 21 and a glycemic load of 1.5.
Eggplant has a GI of 30 and a glycemic load of 1. This means that consumption of both plants will not raise your blood sugar levels.
Health Impact
Cardiovascular Health
Cucumbers contain antioxidants such as beta-carotene, flavonoids, and tannins, which can help reduce oxidative stress and inflammation, potentially slowing the development of atherosclerosis, the main cause of coronary artery disease. However, eggplants have a higher concentration of potent antioxidants such as nasunin (anthocyanin) and chlorogenic acid, which are more effective in reducing oxidative stress and inflammation. This makes eggplants more beneficial in potentially preventing the development of atherosclerosis.
Blood Pressure Regulation
Cucumbers are highly hydrated because they have a water content of about 95%, which is vital in maintaining proper hydration levels and regulating blood pressure. In addition to their high water content, cucumbers also contain potassium, which contributes to lowering blood pressure. On the other hand, eggplants are rich in polyphenols, compounds found to improve endothelial function, a crucial factor in blood pressure regulation. Furthermore, eggplants also provide significant amounts of potassium and magnesium, both of which are essential for maintaining healthy blood pressure levels. Therefore, while both vegetables contribute to blood pressure regulation, eggplants offer additional benefits due to their polyphenol content (1, 2).
LDL Cholesterol Levels
Both cucumbers and eggplants contain dietary fiber that can help lower LDL (“bad” cholesterol) levels by promoting its excretion from the body. However, eggplants have a higher fiber content compared to cucumbers. Additionally, eggplants contain chlorogenic acid, which has been shown to reduce LDL cholesterol levels and improve lipid profiles more effectively than the fiber in cucumbers. This makes eggplants more effective in lowering LDL cholesterol levels (2).
In conclusion, while both cucumbers and eggplants contribute to cardiovascular health, eggplants may have a slight edge due to their higher fiber content, more potent antioxidants, and additional bioactive compounds, making them particularly beneficial for reducing LDL cholesterol and overall cardiovascular risk.
Cancer
Research shows that cucurbitacins inhibit tumor cell growth and signaling pathways and cause cancer cells to die. Cucurbitacins have antitumor activity against lung, pancreatic, colon, breast, and cervical cancers (3). Triterpenes and lignans isolated from cucumber have shown anticancer activity against liver cancer by inducing cancer cell death (4).
Solasodine rhamnosyl glycosides (SRGs) are compounds found in nightshade plants such as eggplant. SRGs have been shown in animal studies (5) to cause cancer cell death and may also help reduce the recurrence of certain types of cancer.
Diabetes
Eggplants are high in phenolic compounds, which, according to research, may regulate carbohydrate metabolism in the body. This mechanism gives insulin more time to digest the carbohydrates, mostly from refined foods with little fiber or vitamin content (6).
Another study found that polyphenols can help lower blood sugar by reducing sugar absorption and increasing insulin secretion. Eating eggplant inhibits the enzyme that converts starch into blood sugar, making it one of the most effective foods for diabetes prevention (7).
Skin Health
Keeping your skin hydrated helps to improve elasticity and firmness. Lack of hydration can cause your skin to appear dry and flaky and more prone to fine lines and wrinkles. Cucumbers are high in polysaccharides, which can help to keep the skin elastic and healthy. Cucumbers are mostly water; in fact, they are 96 percent water. Cucumber's high water content is a crucial benefit because it allows them to provide superior hydration to the skin (8).
Other Health Benefits
Cucumbers are high in water (96%), which may help to keep you hydrated. Dehydration is a risk factor for constipation because it may make your stool passage difficult. Staying hydrated can help with softer stools, relieve constipation, and improve regularity if the constipation is due to dehydration (9).
Eggplant is rich in dietary fiber. It may beneficially affect chronic functional constipation and IBS and lower the risk of hemorrhoids and diverticulosis (10).
Animal studies (11) suggest that nasunin, an anthocyanin found in eggplant skin, may help protect brain cell membranes from free radical damage.
Anthocyanins also help to reduce neuroinflammation and increase blood flow to the brain. This may aid in preventing memory loss and other aspects of aging-related mental decline (12).
Side Effects
Allergy
Cucurbits have been linked to oral allergy syndrome (itching, burning, redness, and swelling of the lips), nausea, diarrhea, asthma, rhinitis, watery eyes, and contact urticaria. Eggplant belongs to a family of plants known as nightshades. People may be more likely to develop an eggplant allergy if allergic to other nightshades, including tomatoes, potatoes, or peppers.
Cucumbers and eggplants contain salicylate, so people allergic to Aspirin should avoid cucumbers, apples, almonds, oranges, berries, tomatoes, and other foods (13).
References
- https://www.health.harvard.edu/heart-health/potassium-lowers-blood-pressure
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7927207/
- https://cancerres.aacrjournals.org/content/69/14/5876
- https://www.nature.com/articles/srep36594
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/22399274/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2871121/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6981492/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6356561/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7987589/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/24876314/
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0300483X0000202X
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5613902/
- https://www.jstage.jst.go.jp/article/allergolint/64/1/64_S1323-8930-14-00013-6/_article/-char/ja/
Infographic
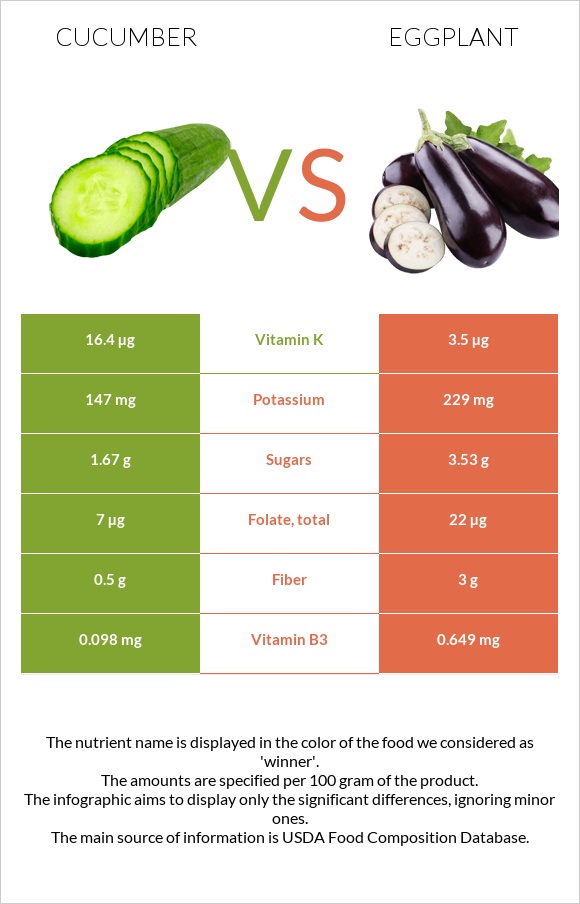
All nutrients comparison - raw data values
| Nutrient |  |
 |
DV% diff. |
| Vitamin K | 16.4µg | 3.5µg | 11% |
| Fiber | 0.5g | 3g | 10% |
| Manganese | 0.079mg | 0.232mg | 7% |
| Copper | 0.041mg | 0.081mg | 4% |
| Folate | 7µg | 22µg | 4% |
| Vitamin B3 | 0.098mg | 0.649mg | 3% |
| Vitamin B6 | 0.04mg | 0.084mg | 3% |
| Potassium | 147mg | 229mg | 2% |
| Vitamin E | 0.03mg | 0.3mg | 2% |
| Calories | 15kcal | 25kcal | 1% |
| Protein | 0.65g | 0.98g | 1% |
| Vitamin C | 2.8mg | 2.2mg | 1% |
| Carbs | 3.63g | 5.88g | 1% |
| Calcium | 16mg | 9mg | 1% |
| Iron | 0.28mg | 0.23mg | 1% |
| Vitamin B1 | 0.027mg | 0.039mg | 1% |
| Fructose | 0.87g | 1.54g | 1% |
| Fats | 0.11g | 0.18g | 0% |
| Net carbs | 3.13g | 2.88g | N/A |
| Magnesium | 13mg | 14mg | 0% |
| Sugar | 1.67g | 3.53g | N/A |
| Zinc | 0.2mg | 0.16mg | 0% |
| Starch | 0.83g | 0% | |
| Phosphorus | 24mg | 24mg | 0% |
| Sodium | 2mg | 2mg | 0% |
| Vitamin A | 5µg | 1µg | 0% |
| Selenium | 0.3µg | 0.3µg | 0% |
| Vitamin B2 | 0.033mg | 0.037mg | 0% |
| Vitamin B5 | 0.259mg | 0.281mg | 0% |
| Choline | 6mg | 6.9mg | 0% |
| Saturated fat | 0.037g | 0.034g | 0% |
| Monounsaturated fat | 0.005g | 0.016g | 0% |
| Polyunsaturated fat | 0.032g | 0.076g | 0% |
| Tryptophan | 0.005mg | 0.009mg | 0% |
| Threonine | 0.019mg | 0.037mg | 0% |
| Isoleucine | 0.021mg | 0.045mg | 0% |
| Leucine | 0.029mg | 0.064mg | 0% |
| Lysine | 0.029mg | 0.047mg | 0% |
| Methionine | 0.006mg | 0.011mg | 0% |
| Phenylalanine | 0.019mg | 0.043mg | 0% |
| Valine | 0.022mg | 0.053mg | 0% |
| Histidine | 0.01mg | 0.023mg | 0% |
Macronutrient Comparison
| Contains more ProteinProtein | +50.8% |
| Contains more FatsFats | +63.6% |
| Contains more CarbsCarbs | +62% |
| Contains more OtherOther | +73.7% |
Fat Type Comparison
| Contains more Mono. FatMonounsaturated fat | +220% |
| Contains more Poly. FatPolyunsaturated fat | +137.5% |
Carbohydrate type comparison
| Contains more StarchStarch | +∞% |
| Contains more MaltoseMaltose | +∞% |
| Contains more SucroseSucrose | +766.7% |
| Contains more GlucoseGlucose | +107.9% |
| Contains more FructoseFructose | +77% |
People also compare
References
All the values for which the sources are not specified explicitly are taken from FDA’s Food Central. The exact link to the food presented on this page can be found below.
- Cucumber - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/168409/nutrients
- Eggplant - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/169228/nutrients
All the Daily Values are presented for males aged 31-50, for 2000-calorie diets.



