Feta vs. Cottage cheese — Health Impact and Nutrition Comparison


Summary
Feta provides more calcium, phosphorus, magnesium, zinc, protein, monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fats, and carbs, whereas cottage cheese contains more potassium and choline. Compared to cottage cheese, feta is high in all vitamins. On the other hand, cottage cheese provides fewer calories, cholesterol, saturated fats, and sodium.
Introduction
Feta cheese and cottage cheese are both popular types of cheese but have some key differences. Feta is typically made from sheep's milk or a combination of goat's and sheep's milk. However, it can also be made from cow and buffalo milk. Cottage cheese is traditionally made from cow's milk. Feta cheese is aged and cured in a brine solution, giving it a distinct flavor and texture. Cottage cheese is produced by curdling milk with an acidic substance such as vinegar or lemon juice, and then the whey is drained.
Nutrition
This section of the article will compare the nutritional information of feta and cottage cheese.
Macronutrients and Calories
Feta is denser than cottage cheese. Cottage cheese contains 80% water, whereas feta contains 55% water.
Macronutrient Comparison
Contains
more
ProteinProtein
+27.8%
Contains
more
FatsFats
+394.9%
Contains
more
CarbsCarbs
+21%
Contains
more
OtherOther
+268.8%
Contains
more
WaterWater
+44.5%
Calories
Feta provides over 2.7 times more calories per hundred grams than cottage cheese. A hundred grams of feta has 264 calories, whereas cottage cheese has 98 calories.
One serving of feta (1 oz or 28.35g ) has 75 kcal, whereas one serving of cottage cheese (4 oz or 113g) provides 111 kcal.
Protein
Feta has a high protein content. In a 100g serving, feta and cottage cheese have 14.21g and 11.12g of protein, respectively. Both provide all amino acids, feta being higher.
Fats
Feta provides over five times more total fats. In a 100g serving, feta and cottage cheese have 21.28g and 4.3g of fats, respectively.
Cottage cheese has over 8.7 times less saturated fats, whereas feta has over six times more monounsaturated fats and five times more polyunsaturated fats. In a 100g serving, feta and cottage cheese have 15g and 1.7g of saturated fats, respectively.
Cholesterol
Feta has significantly higher cholesterol levels compared to cottage cheese.
A hundred grams of feta has 89 milligrams of cholesterol, whereas cottage cheese provides 17 milligrams.
Fat Type Comparison
Contains
more
Mono. FatMonounsaturated fat
+494.2%
Contains
more
Poly. FatPolyunsaturated fat
+380.5%
Contains
less
Sat. FatSaturated fat
-88.5%
Carbohydrates
Compared to cottage cheese, feta provides more carbs. In a 100g serving, feta and cottage cheese have 4.09g and 3.38g of net carbs, respectively. Both lack dietary fiber.
Lactose
The lactose content of cottage cheese and feta can vary depending on the preparation method and brand. Generally, feta cheese contains very little lactose, typically 1.4 g per 100 grams. Cottage cheese, on the other hand, can contain more lactose, usually 3.2 g per 100 grams (1).
Vitamins
Feta is the winner in this category. Feta has over five times more vitamin B2, three times more vitamin A, nine times more vitamin B6, and four times more vitamin B12. It also has more vitamins B1, B3, B5, E, and folate.
Vitamin Comparison
Contains
more
Vitamin AVitamin A
+237.8%
Contains
more
Vitamin EVitamin E
+125%
Contains
more
Vitamin DVitamin D
+300%
Contains
more
Vitamin B1Vitamin B1
+470.4%
Contains
more
Vitamin B2Vitamin B2
+417.8%
Contains
more
Vitamin B3Vitamin B3
+901%
Contains
more
Vitamin B5Vitamin B5
+73.6%
Contains
more
Vitamin B6Vitamin B6
+821.7%
Contains
more
Vitamin B12Vitamin B12
+293%
Contains
more
Vitamin KVitamin K
+∞%
Contains
more
FolateFolate
+166.7%
Minerals
Feta has over six times more calcium, two times more phosphorus, two times more magnesium, seven times more zinc, and 1.5 times more selenium. Both contain high amounts of sodium, feta being higher.
In a 100g serving, feta and cottage cheese have 917 mg and 364mg of sodium, respectively. Feta also provides more iron, copper, and manganese. In contrast, cottage cheese has more choline and potassium.
Mineral Comparison
Contains
more
MagnesiumMagnesium
+137.5%
Contains
more
CalciumCalcium
+494%
Contains
more
IronIron
+828.6%
Contains
more
ZincZinc
+620%
Contains
more
PhosphorusPhosphorus
+111.9%
Contains
more
ManganeseManganese
+1300%
Contains
more
SeleniumSelenium
+54.6%
Contains
more
PotassiumPotassium
+67.7%
Contains
less
SodiumSodium
-60.3%
Oxalate
Feta and cottage cheese are oxalate-free.
Glycemic Index
Feta has a higher glycemic index than cottage cheese. Feta has a glycemic index of 27. The glycemic index of cottage cheese is equal to 10. However, the glycemic index of both falls in the low category.
Acidity
The potential renal acid load (PRAL) indicates the food's capacity to degrade into bases or acids within the body. Cottage cheese has a PRAL value of 7.9. The PRAL level for feta is 11.2. That indicates that feta is more acid-forming than cottage cheese.
Weight Loss & Diets
- Vegan: Vegans should avoid all animal products. Feta and cottage cheese are not vegan-friendly.
- Paleo: The paleo diet typically excludes dairy products, so feta and cottage cheese are not paleo-friendly.
- Keto: The keto diet focuses on low-carb, high-fat, and moderate-protein foods. Feta and cottage cheese are low in carbohydrates, making them suitable for a keto diet.
- Mediterranean: The Mediterranean diet emphasizes the consumption of different plant-based foods, along with moderate amounts of dairy, fish, and poultry. Feta cheese, a traditional cheese in Mediterranean cuisine, can be enjoyed in moderation. Cottage cheese can also be a part of the Mediterranean diet.
Health Benefits
Cardiovascular Health
There is moderate-quality evidence indicating that cheese consumption is inversely associated with cardiovascular disease (CVD) mortality and overall incidences of CVD, coronary heart disease (CHD), and stroke (2).
Cheese intake may significantly increase HDL-cholesterol (high-density lipoprotein cholesterol) and decrease the LDL-C/HDL-C ratio (3).
Low-fat dairy products like cottage cheese may lower LDL-C levels, but there is no significant independent association with HDL-C or triglycerides (4).
Bone Health
Dairy products like cottage cheese and feta are optimal sources of calcium and protein, which are highly bioavailable and essential for bone health. Osteoporosis is a disorder marked by the loss of bone mass, weakened bones, and deterioration of bone tissue, leading to an increased risk of fractures. A diet rich in calcium may prevent and manage osteoporosis (5).
Cancer
The findings suggest that consuming cheese, especially 40 grams or more daily, can have neutral to moderate health benefits. There is no significant association between cheese consumption and cancer mortality and prostate cancer incidence (2, 6).
According to the study, there is a protective association between cottage cheese and ricotta cheese consumption and estrogen receptor-negative (ER-) breast cancer incidence (2).
Conjugated linoleic acid (CLA) found in feta cheese is known for its anticarcinogenic properties, especially in combating breast cancer (7).
Downsides and Risks
Allergy
Cottage cheese is made from cow's milk and can be allergic. Cow's milk allergy is a frequent condition in infants and children, characterized by an allergic reaction to the protein in cow's milk. Symptoms can vary and may appear in infancy, potentially resolving by age 6. Managing this allergy involves a milk-free diet. Symptoms of cow's milk allergy can be classified into rapid onset, typically IgE-mediated, where symptoms occur within an hour after ingestion, and slow-onset, non-IgE mediated, where symptoms take hours or days to present. Rapid onset symptoms may include urticaria/hives, wheezing, itching around the mouth or lips, angioedema, coughing or shortness of breath, vomiting, and anaphylaxis (severe allergic reaction). Slow-onset symptoms may include diarrhea, hematochezia, abdominal cramps, and colic (8, 9, 10). Alternative milk options, such as sheep's and goat's milk, are often not recommended due to their high cross-reactivity with cow's milk protein. Individuals with milk allergies should avoid dairy products like cottage cheese and feta (8).
Lactose Intolerance
Lactose, a disaccharide found in dairy products and milk, is hydrolyzed by the enzyme lactase in the gastrointestinal tract into glucose and galactose, which are absorbed. Most people have lactose intolerance. Symptoms of lactose intolerance include diarrhea, flatulence, bloating, and abdominal pain, which occur when lactose reaches the large intestine. Individuals with lactose intolerance should avoid dairy products like cottage cheese and feta (11, 12).
Classification
Feta and cottage cheese are classified as fresh cheeses due to their minimal aging compared to cheddar cheese, parmesan cheese, and blue cheese.
Appearance
Feta cheese is often sold in blocks or as crumbles. The blocks are usually white and compact, with a slightly crumbly texture. When crumbled, feta cheese has a granular appearance, resembling small chunks or crumbles. While feta cheese is typically white, it may occasionally exhibit a slightly creamy or yellowish tint. Feta cheese is stored in brine, which can give it a slightly wet or moist appearance. Cottage cheese has a more varied appearance compared to feta. It consists of lumpy curds suspended in a creamy liquid. The curds can vary in size, ranging from small to large, and they are usually soft and moist. The color of cottage cheese is generally white, but it can sometimes have a slightly creamy or off-white appearance. Cottage cheese is often sold in containers with the curds floating in the creamy liquid.
Taste
Feta cheese offers a tangy, salty flavor and a crumbly texture. The intensity of its taste varies from mild to sharp, influenced by the duration of aging. The brining process gives it a unique and slightly tangy flavor distinct from other cheeses. Cottage cheese, on the other hand, has a mild and sweet flavor. It is creamy and lumpy in texture, with a fresh and milky taste. The curds are soft and moist, providing a unique texture compared to other cheeses. Feta cheese has a crumbly texture, while cottage cheese has a creamy and lumpy texture.
Uses
Feta cheese and cottage cheese are versatile ingredients that you can use in different dishes. Feta cheese is a popular topping for salads, adding a tangy flavor and creamy texture. It is used in pastries such as spanakopita (spinach pie) or tiropita (cheese pie). Feta cheese can be added to sandwiches and wraps. Feta cheese is a great pizza topping, especially with vegetables like spinach or bell peppers. In contrast, cottage cheese pairs well with fruits like pineapple, peaches, or berries for a sweet and savory snack. It can be used in baking, such as pancakes, muffins, or cheesecakes, to add moisture and protein. You can use cottage cheese as a dip and spread or in stuffed pasta shells.
Sources
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7318541/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC10509445/
- https://www.researchgate.net/publication/320177687
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/24002126/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/22461827/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/38042408/
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK542243/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31194400/
- https://www.allergy.org.au/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/9467238/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7318541/
Infographic
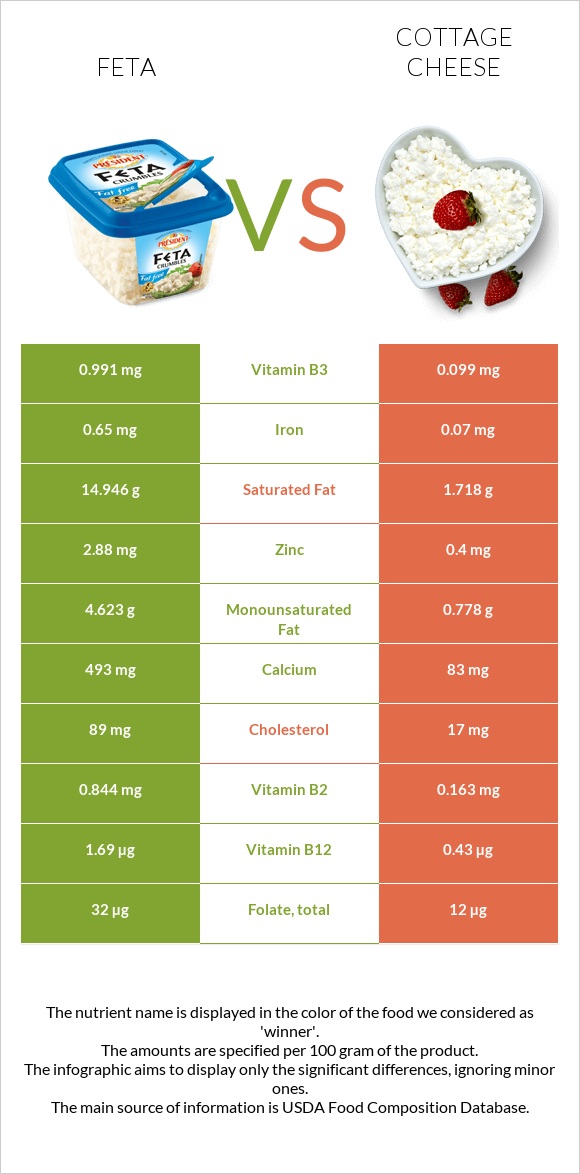
All nutrients comparison - raw data values
| Nutrient |  |
 |
DV% diff. |
| Saturated fat | 14.946g | 1.718g | 60% |
| Vitamin B12 | 1.69µg | 0.43µg | 53% |
| Vitamin B2 | 0.844mg | 0.163mg | 52% |
| Calcium | 493mg | 83mg | 41% |
| Vitamin B6 | 0.424mg | 0.046mg | 29% |
| Fats | 21.28g | 4.3g | 26% |
| Phosphorus | 337mg | 159mg | 25% |
| Cholesterol | 89mg | 17mg | 24% |
| Sodium | 917mg | 364mg | 24% |
| Zinc | 2.88mg | 0.4mg | 23% |
| Vitamin B1 | 0.154mg | 0.027mg | 11% |
| Vitamin A | 125µg | 37µg | 10% |
| Selenium | 15µg | 9.7µg | 10% |
| Monounsaturated fat | 4.623g | 0.778g | 10% |
| Calories | 264kcal | 98kcal | 8% |
| Vitamin B5 | 0.967mg | 0.557mg | 8% |
| Iron | 0.65mg | 0.07mg | 7% |
| Protein | 14.21g | 11.12g | 6% |
| Vitamin B3 | 0.991mg | 0.099mg | 6% |
| Folate | 32µg | 12µg | 5% |
| Magnesium | 19mg | 8mg | 3% |
| Polyunsaturated fat | 0.591g | 0.123g | 3% |
| Vitamin D | 16 IU | 3 IU | 2% |
| Vitamin D | 0.4µg | 0.1µg | 2% |
| Vitamin K | 1.8µg | 0µg | 2% |
| Potassium | 62mg | 104mg | 1% |
| Vitamin E | 0.18mg | 0.08mg | 1% |
| Manganese | 0.028mg | 0.002mg | 1% |
| Choline | 15.4mg | 18.4mg | 1% |
| Net carbs | 4.09g | 3.38g | N/A |
| Carbs | 4.09g | 3.38g | 0% |
| Sugar | 4.09g | 2.67g | N/A |
| Copper | 0.032mg | 0.029mg | 0% |
| Tryptophan | 0.2mg | 0.147mg | 0% |
| Threonine | 0.637mg | 0.5mg | 0% |
| Isoleucine | 0.803mg | 0.591mg | 0% |
| Leucine | 1.395mg | 1.116mg | 0% |
| Lysine | 1.219mg | 0.934mg | 0% |
| Methionine | 0.368mg | 0.269mg | 0% |
| Phenylalanine | 0.675mg | 0.577mg | 0% |
| Valine | 1.065mg | 0.748mg | 0% |
| Histidine | 0.397mg | 0.326mg | 0% |
People also compare
References
All the values for which the sources are not specified explicitly are taken from FDA’s Food Central. The exact link to the food presented on this page can be found below.
- Feta - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/173420/nutrients
- Cottage cheese - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/172179/nutrients
All the Daily Values are presented for males aged 31-50, for 2000-calorie diets.



