Honey vs. Sugar — What's The Healthier Choice?


Summary
Honey is the healthier and more nutritious choice you should make when it comes to honey vs sugar. Honey is lower in calories and carbs, yet it’s sweeter. In addition, it contains flavonoids and polyphenols that positively impact our health. In comparison, table sugar is made of sucrose and does not positively impact our health. In high amounts, it is associated with adverse health impacts.
Introduction
We all consume honey and sugar daily. Even if we don’t know it directly, we always consume something containing it. When consuming sugary foods, such as sugar and honey, it is important to know how they impact our health.
This article compares honey and sugar with an in-depth comparison of their health impacts.
Nutrition
When it comes to sugar, it’s 100% carbs. There are no vitamins, minerals, fats, and proteins.
Sugar is made of sucrose.
Regarding the nutritional profile of honey, we have a more nutrient-dense food.
Honey is lower in calories; there are 304 calories in 100g of honey, whereas sugar contains 386 calories. The main reason is that honey comprises 82g of carbs and 17g of water.
Honey is richer in vitamins and minerals, such as vitamin B2 and magnesium. However, their amount is not so remarkable.
In the charts below, you can visualize their distribution.
Mineral Comparison
Contains
more
MagnesiumMagnesium
+∞%
Contains
more
CalciumCalcium
+500%
Contains
more
PotassiumPotassium
+2500%
Contains
more
IronIron
+740%
Contains
more
CopperCopper
+414.3%
Contains
more
ZincZinc
+2100%
Contains
more
PhosphorusPhosphorus
+∞%
Contains
more
ManganeseManganese
+1900%
Contains
more
SeleniumSelenium
+33.3%
Contains
less
SodiumSodium
-75%
Vitamin Comparison
Contains
more
Vitamin CVitamin C
+∞%
Contains
more
Vitamin B2Vitamin B2
+100%
Contains
more
Vitamin B3Vitamin B3
+∞%
Contains
more
Vitamin B5Vitamin B5
+∞%
Contains
more
Vitamin B6Vitamin B6
+∞%
Contains
more
FolateFolate
+∞%
You can read about honey vs brown sugar in this article.
Glycemic Index
Contrary to the more common belief that sugar has a glycemic index of 100. The glycemic index of sugar is 65.
The glycemic index of sugar being 65 is that it only made 50% of glucose, and the other 50% is fructose.
In comparison, the glycemic index of honey is 60.
For a deep dive into the glycemic index of honey, you can read this article.
Sweetness
Honey is sweeter than table sugar. This means consuming less honey and fewer calories for the sweetness needed than sugar.
Quality
Ideally, the best honey that you should consume is from trusted beekeepers who don’t mix sugar with their honey. It’s best to get seasonal honey aswell since beekeepers often feed their bees sugary water to produce honey quickly and in higher amounts.
So find a trusted beekeeper and get the honey from there.
You won’t find them on supermarket shelves.
Health Impacts
Considering sugar and honey in a comparison regarding health impacts. Honey is a healthier option when it comes to that comparison.
The reason is that honey is more of a nutritious food that contains micronutrients, enzymes, and other bioactive compounds such as polyphenols and flavonoids that positively impact our health.
Diabetes
In diabetic patients, it’s best if they do not consume excess sugar. In cases of insulin resistance, whatever the source of glucose, if post-prandial, there are frequent spikes for long durations. Diabetic complications will start to appear.
In this case, sugar is a major red flag. Consumption of table sugar, especially in higher amounts, is associated with increased risks of diabetes (1).
It is important to note that occasionally consuming 1 teaspoon of sugar will not cause diabetes. The dose matters.
In comparison, honey can be used as an alternate sugar since it is sweeter. However, it’s best to reduce overall foods that would cause glucose spikes in diabetes.
Overall, some data indicates that the consumption of honey positively affects diabetes. However, it’s best to keep it in low-moderate amounts (2).
Anti-Inflammatory Effects
Honey contains polyphenols and flavonoids that have antioxidative effects. Sugar doesn’t have these properties. Honey is not refined; especially good honey from a trusted beekeeper is ideal (3).
Some references indicate that high sugar consumption in parallel with processed food has detrimental effects on our bodies by increasing risks of inflammatory damage (4).
Cancer
Honey has been shown to have cytotoxic effects on cancer cells. This doesn’t indicate that you can treat cancer, but having proper nutrition on a lifelong basis can decrease your risks of carcinogenesis (5).
Epidemiological studies have found an association with high sugar intake in high frequencies with the development of cancer (6).
Botulism
There are many cases of botulism in pediatric ages. Raw honey shouldn't be given to babies up to 12 months because it can contain botulinum toxin that can cause botulism in babies (7).
Allergies
Honey is derived from pollen, which is highly allergic to most people. However, honey has been shown to positively affect allergic rhinitis symptoms by decreasing its symptoms (8).
You can read about brown sugar vs. sugar in this article.
References
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3584048/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5817209/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/28539734/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/24566317/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/36119103/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/36551528/
- https://www.cdc.gov/botulism/prevention.html
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/24188941/
Infographic
All nutrients comparison - raw data values
| Nutrient |  |
 |
DV% diff. |
| Fructose | 40.94g | 0g | 51% |
| Carbs | 82.4g | 99.98g | 6% |
| Iron | 0.42mg | 0.05mg | 5% |
| Calories | 304kcal | 387kcal | 4% |
| Copper | 0.036mg | 0.007mg | 3% |
| Manganese | 0.08mg | 0.004mg | 3% |
| Zinc | 0.22mg | 0.01mg | 2% |
| Vitamin B6 | 0.024mg | 0mg | 2% |
| Protein | 0.3g | 0g | 1% |
| Vitamin C | 0.5mg | 0mg | 1% |
| Calcium | 6mg | 1mg | 1% |
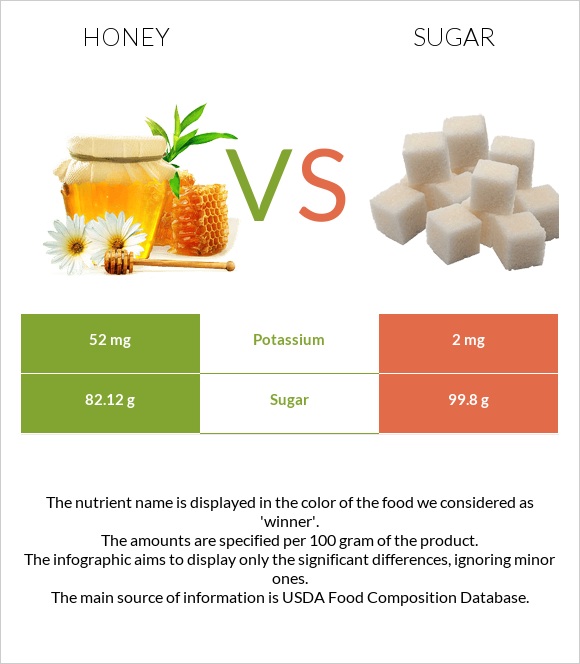
| Potassium | 52mg | 2mg | 1% |
| Fiber | 0.2g | 0g | 1% |
| Phosphorus | 4mg | 0mg | 1% |
| Vitamin B2 | 0.038mg | 0.019mg | 1% |
| Vitamin B3 | 0.121mg | 0mg | 1% |
| Vitamin B5 | 0.068mg | 0mg | 1% |
| Folate | 2µg | 0µg | 1% |
| Net carbs | 82.2g | 99.98g | N/A |
| Magnesium | 2mg | 0mg | 0% |
| Sugar | 82.12g | 99.8g | N/A |
| Sodium | 4mg | 1mg | 0% |
| Selenium | 0.8µg | 0.6µg | 0% |
| Choline | 2.2mg | 0mg | 0% |
| Tryptophan | 0.004mg | 0% | |
| Threonine | 0.004mg | 0% | |
| Isoleucine | 0.008mg | 0% | |
| Leucine | 0.01mg | 0% | |
| Lysine | 0.008mg | 0% | |
| Methionine | 0.001mg | 0% | |
| Phenylalanine | 0.011mg | 0% | |
| Valine | 0.009mg | 0% | |
| Histidine | 0.001mg | 0% |
Macronutrient Comparison
| Contains more ProteinProtein | +∞% |
| Contains more WaterWater | +85400% |
| Contains more OtherOther | +∞% |
| Contains more CarbsCarbs | +21.3% |
Carbohydrate type comparison
| Contains more GlucoseGlucose | +∞% |
| Contains more FructoseFructose | +∞% |
| Contains more MaltoseMaltose | +∞% |
| Contains more GalactoseGalactose | +∞% |
| Contains more SucroseSucrose | +11113.5% |
People also compare
References
All the values for which the sources are not specified explicitly are taken from FDA’s Food Central. The exact link to the food presented on this page can be found below.
- Honey - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/169640/nutrients
- Sugar - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/169655/nutrients
All the Daily Values are presented for males aged 31-50, for 2000-calorie diets.





