Lettuce vs. Brussels sprouts — Health Impact and Nutrition Comparison


Summary
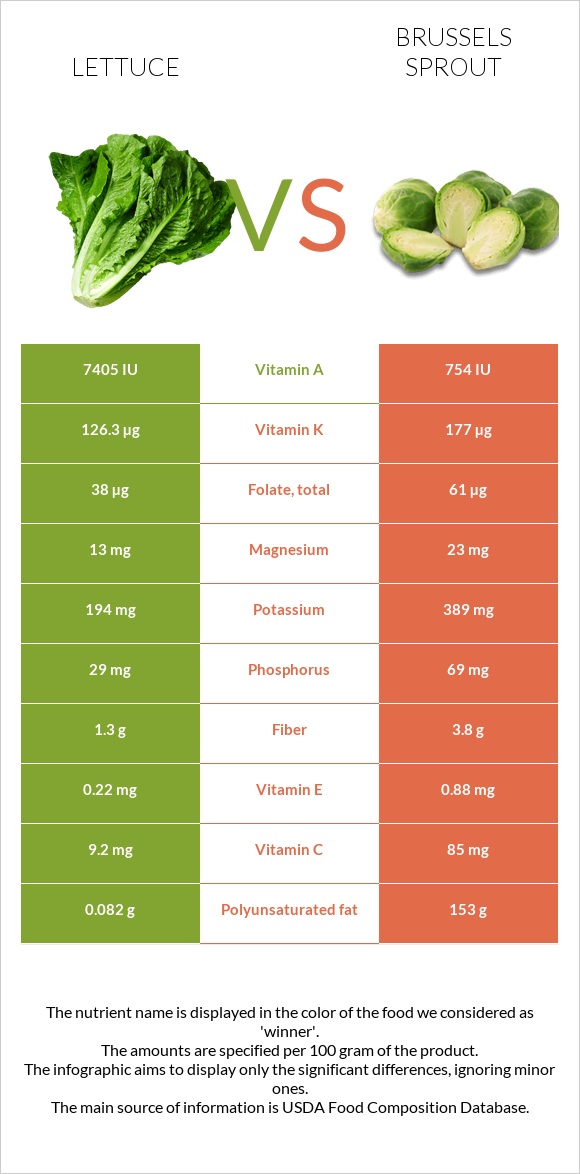
Lettuce is an excellent source of vitamin A, containing nearly 10 times more of it than Brussels sprouts. On the other hand, Brussels sprouts provide more than 9 times more vitamin C.
Brussels sprouts are richer in minerals than lettuce. Specifically, they provide more amounts of magnesium, potassium, and phosphorus. Moreover, they are higher in fiber and polyunsaturated fats.
Introduction
Both lettuce and Brussels sprouts are some of the healthiest vegetables worldwide. They are commonly used in a fresh form in salads and are an important part of a healthy lifestyle. In this article, we will give an overview of lettuce and Brussels sprouts, compare their nutritional profile, and discuss their potential effects on human health.
What Is the Actual Difference?
Lettuce and Brussels sprouts belong to the Brassicaceae family, but they have many differences.
Lettuce, known for its leafy texture and crispness, is primarily consumed raw and often used as a base in salads and added to sandwiches. Brussels sprouts are small, compact cabbages that grow along a thick stalk. These cruciferous vegetables have a distinctive nutty flavor and are often cooked by roasting or steaming.
Additionally, Brussels sprouts contain compounds like glucosinolates, known for their potential health benefits, including antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties. Thus, while lettuce delights in its refreshing crunch, Brussels sprouts offer a healthy and nutritious addition to culinary creations.
Nutrition
In this article, we will compare the nutritional compositions of raw lettuce and raw Brussels sprouts.
The recommended serving sizes for Brussels sprouts and lettuce are equal to one cup, which corresponds to 88g of Brussels sprouts and 36g of lettuce.
Macronutrients and Calories
As shown in the chart below, Brussels sprouts are denser in nutrients than lettuce. Lettuce contains 95% water per 100g, while the same serving of Brussels provides 86%. Additionally, sprouts contain more proteins and carbohydrates.
Macronutrient Comparison
Contains
more
ProteinProtein
+148.5%
Contains
more
FatsFats
+100%
Contains
more
CarbsCarbs
+211.8%
Contains
more
OtherOther
+114.1%
Calories
Brussels sprouts and lettuce are low-calorie vegetables, but Brussels sprouts have around three times more calories per 100g. A 100g serving of Brussels sprouts contains 43 calories, while lettuce contains 15 calories.
Protein and Fats
Brussels sprouts contain 2.5 times more protein than lettuce. Brussels sprouts have 3.38g of protein per 100g serving, whereas the same size of lettuce contains 1.36g.
Both vegetables have less than 1g of fat per 100g. However, Brussels sprouts have slightly higher quantities of fats. They are especially higher in polyunsaturated fats. None of these vegetables contains cholesterol.
Fat Type Comparison
Contains
less
Sat. FatSaturated fat
-67.7%
Contains
more
Mono. FatMonounsaturated fat
+283.3%
Contains
more
Poly. FatPolyunsaturated fat
+186485.4%
Carbohydrates
Brussels sprouts and lettuce are classified as low-carb vegetables. However, Brussels sprouts contain more carbohydrates than lettuce, with 8.95g compared to 2.87g respectively. They are richer in sucrose, glucose, and fructose.
Fiber
Brussels sprouts contain three times more amounts of dietary fiber. They provide 3.8g, while lettuce has only 1.3g of fiber per 100g. Sprouts are especially rich in soluble fiber.
Vitamins
Brussels sprouts are the winner in this category. They contain higher amounts of almost all vitamins. Sprouts are 9 times higher in vitamin C and around 2 times higher in folate compared to lettuce. They are also richer in B-complex vitamins, vitamins E and K.
On the other hand, lettuce provides 10 times more vitamin A, with 7405IU per 100g, while the same serving of Brussels contains only 754IU of it.
Vitamin Comparison
Contains
more
Vitamin AVitamin A
+873.7%
Contains
more
Vitamin CVitamin C
+823.9%
Contains
more
Vitamin EVitamin E
+300%
Contains
more
Vitamin B1Vitamin B1
+98.6%
Contains
more
Vitamin B2Vitamin B2
+12.5%
Contains
more
Vitamin B3Vitamin B3
+98.7%
Contains
more
Vitamin B5Vitamin B5
+130.6%
Contains
more
Vitamin B6Vitamin B6
+143.3%
Contains
more
Vitamin KVitamin K
+40.1%
Contains
more
FolateFolate
+60.5%
Minerals
Brussels sprouts are richer in minerals than lettuce. They contain 195mg more potassium, 10mg more magnesium, and 40mg more phosphorus. Lettuce is also lower in calcium, iron, zinc, copper, manganese, and selenium.
Mineral Comparison
Contains
more
MagnesiumMagnesium
+76.9%
Contains
more
CalciumCalcium
+16.7%
Contains
more
PotassiumPotassium
+100.5%
Contains
more
IronIron
+62.8%
Contains
more
CopperCopper
+141.4%
Contains
more
ZincZinc
+133.3%
Contains
more
PhosphorusPhosphorus
+137.9%
Contains
less
SodiumSodium
-10.7%
Contains
more
ManganeseManganese
+34.8%
Contains
more
SeleniumSelenium
+166.7%
Oxalate content
The oxalate content of lettuce is 16mg per 100g, while the oxalate content of Brussels sprouts equals 13mg.
Although both are classified as low-oxalate foods, lettuce has a lower oxalate content.
Glycemic Index
Both lettuce and Brussels sprouts are low in carbs. Thus, both vegetables are classified as low-GI foods. While the glycemic index of Brussels sprouts is not calculated yet, the GI value of lettuce equals 32.
Acidity
The PRAL values of Brussels sprouts and lettuce are -5.1 and -3.1, respectively. Both are alkaline, but Brussels sprouts have a higher potential to alkalize the organism compared to lettuce.
Health Impact
Cardiovascular Health
Lettuce and Brussels sprouts offer valuable cardiovascular health benefits due to their nutrient profiles. Lettuce, particularly varieties like romaine, provides significant amounts of vitamin K, which plays a crucial role in blood clotting and may help reduce the risk of arterial calcification, a factor associated with cardiovascular disease (1). Moreover, the high water content of lettuce contributes to hydration, promoting overall cardiovascular health.
On the other hand, Brussels sprouts are rich in antioxidants such as vitamin C and vitamin E, as well as dietary fiber, which can help lower cholesterol levels and improve heart health by reducing the risk of coronary artery disease and stroke (2) (3). Additionally, Brussels sprouts contain compounds called glucosinolates, which have been linked to anti-inflammatory and anti-atherosclerotic effects, further supporting cardiovascular health (4).
Diabetes
Lettuce and Brussels sprouts are two vegetables that offer potential benefits for individuals managing diabetes. Lettuce is low in carbohydrates and this low-glycemic index food can help stabilize blood sugar levels, making it a suitable choice for individuals with diabetes (5).
Brussels sprouts, similarly, are low in carbohydrates and high in fiber, making them a valuable addition to a diabetic-friendly diet. The fiber content helps slow down the absorption of glucose, preventing spikes in blood sugar levels (6).
Cancer
Lettuce, particularly darker varieties like romaine, contains antioxidants such as vitamin C and beta-carotene, which may help neutralize harmful free radicals in the body and reduce the risk of certain cancers, including lung and bladder cancer (7). Additionally, lettuce is rich in fiber, which can aid in digestive health and potentially lower the risk of colorectal cancer (9).
Brussels sprouts, on the other hand, contain compounds like glucosinolates, which can be converted into bioactive compounds with anti-cancer effects. Studies have suggested that regular consumption of Brussels sprouts may reduce the risk of various cancers, including lung, breast, prostate, and colorectal cancer (8).
References
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/18729924/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3249911/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3257631/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/19079898/
- https://www.researchgate.net/publication/312930285
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/26778708/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/22391648/
- https://www.cancer.gov/about-cancer/causes-prevention/risk/diet/cruciferous-vegetables-fact-sheet
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5394516/
Infographic
All nutrients comparison - raw data values
| Nutrient |  |
 |
DV% diff. |
| Polyunsaturated fat | 0.082g | 153g | 1019% |
| Vitamin C | 9.2mg | 85mg | 84% |
| Vitamin K | 126.3µg | 177µg | 42% |
| Vitamin A | 370µg | 38µg | 37% |
| Fiber | 1.3g | 3.8g | 10% |
| Vitamin B6 | 0.09mg | 0.219mg | 10% |
| Iron | 0.86mg | 1.4mg | 7% |
| Potassium | 194mg | 389mg | 6% |
| Phosphorus | 29mg | 69mg | 6% |
| Vitamin B1 | 0.07mg | 0.139mg | 6% |
| Folate | 38µg | 61µg | 6% |
| Copper | 0.029mg | 0.07mg | 5% |
| Protein | 1.36g | 3.38g | 4% |
| Vitamin E | 0.22mg | 0.88mg | 4% |
| Manganese | 0.25mg | 0.337mg | 4% |
| Vitamin B5 | 0.134mg | 0.309mg | 4% |
| Carbs | 2.87g | 8.95g | 2% |
| Magnesium | 13mg | 23mg | 2% |
| Zinc | 0.18mg | 0.42mg | 2% |
| Selenium | 0.6µg | 1.6µg | 2% |
| Vitamin B3 | 0.375mg | 0.745mg | 2% |
| Calories | 15kcal | 43kcal | 1% |
| Calcium | 36mg | 42mg | 1% |
| Vitamin B2 | 0.08mg | 0.09mg | 1% |
| Choline | 13.6mg | 19.1mg | 1% |
| Fructose | 0.43g | 0.93g | 1% |
| Fats | 0.15g | 0.3g | 0% |
| Net carbs | 1.57g | 5.15g | N/A |
| Sugar | 0.78g | 2.2g | N/A |
| Sodium | 28mg | 25mg | 0% |
| Saturated fat | 0.02g | 0.062g | 0% |
| Monounsaturated fat | 0.006g | 0.023g | 0% |
| Tryptophan | 0.009mg | 0.037mg | 0% |
| Threonine | 0.059mg | 0.12mg | 0% |
| Isoleucine | 0.084mg | 0.132mg | 0% |
| Leucine | 0.079mg | 0.152mg | 0% |
| Lysine | 0.084mg | 0.154mg | 0% |
| Methionine | 0.016mg | 0.032mg | 0% |
| Phenylalanine | 0.055mg | 0.098mg | 0% |
| Valine | 0.07mg | 0.155mg | 0% |
| Histidine | 0.022mg | 0.076mg | 0% |
Carbohydrate type comparison
| Contains more SucroseSucrose | +∞% |
| Contains more GlucoseGlucose | +125% |
| Contains more FructoseFructose | +116.3% |
People also compare
References
All the values for which the sources are not specified explicitly are taken from FDA’s Food Central. The exact link to the food presented on this page can be found below.
- Lettuce - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/169249/nutrients
- Brussels sprouts - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/170383/nutrients
All the Daily Values are presented for males aged 31-50, for 2000-calorie diets.






