Brussels sprouts vs. Broccoli — Health Impact and Nutrition Comparison


Summary
Brussels sprout provides more iron, potassium, Vitamin B1, Vitamin K, fiber, and copper than broccoli. It is also lower in sodium.
On the other hand, broccoli has more Vitamin B5 and calcium. Broccoli has lower sugars and saturated fats.
Introduction
In this article, you can find a detailed description of the differences between brussels sprouts and broccoli.
What's The Actual Difference?
Broccoli is dark green, with firm stalks and compact bud clusters, while brussels sprouts develop a thick stalk where the sprouts, which resemble miniature cabbage heads, form just above where the leaves attach. The flavor of raw broccoli is vegetal, slightly sweet, and slightly bitter. It tastes nothing like cooked broccoli, which is usually sweeter. Brussels sprouts have a sweet, nutty, and smoky flavor. They taste similar to cabbage but milder.
Nutrition
Below you can find the nutrition infographics that visually show the differences between broccoli and brussels sprouts. The nutritional information and infographics are for raw broccoli and raw brussels sprouts.
Calories
Both broccoli and brussels sprouts are low in calories and have almost equal numbers. Broccoli contains 34 calories per 100g, and brussels sprout contains 43 calories per 100g.
Fats
Both broccoli and brussels sprouts have fats of less than 1g.
Carbs
Broccoli contains 6.64g of carbs per 100g, whereas brussels sprout has 8.95g of carbs per 100g. Both are considered low-carb foods.
Fiber
Broccoli has 2.6g fiber and 4.04g net carbs. Brussels sprout provides 3.8g of and 5.15g of net carbs.
Cholesterol
Both foods have no cholesterol.
Vitamins
Brussels sprout contains more vitamins than broccoli. It has more Vitamin A, Vitamin B1, B3, B6, and Vitamin D.
Broccoli contains more Vitamin B2 and Vitamin B5.
Both broccoli and Brussels sprouts fall in the range of the top 10% of foods as a source of Vitamin C.
Both have an equal amount of folate.
Vitamin Comparison
| Contains more Vitamin AVitamin A | +22.6% |
| Contains more Vitamin EVitamin E | +12.8% |
| Contains more Vitamin B1Vitamin B1 | +95.8% |
| Contains more Vitamin B3Vitamin B3 | +16.6% |
| Contains more Vitamin B6Vitamin B6 | +25.1% |
| Contains more Vitamin KVitamin K | +74.2% |
| Contains more Vitamin B2Vitamin B2 | +30% |
| Contains more Vitamin B5Vitamin B5 | +85.4% |
Minerals
Brussels sprout has a relatively higher amount of minerals than broccoli. It contains more iron, potassium, copper, and less sodium than broccoli.
Broccoli contains more calcium.
Both have equal amounts of phosphorus, zinc, and magnesium.
Mineral Comparison
| Contains more PotassiumPotassium | +23.1% |
| Contains more IronIron | +91.8% |
| Contains more CopperCopper | +42.9% |
| Contains less SodiumSodium | -24.2% |
| Contains more ManganeseManganese | +60.5% |
| Contains more CalciumCalcium | +11.9% |
| Contains more SeleniumSelenium | +56.3% |
Glycemic Index
Although the exact number for the glycemic index of Brussels sprouts and broccoli is unknown, it is safe to assume that it is shallow due to their low sugar and high fiber content [1] [2].
Health Impact
According to studies, people who took a powdered broccoli sprout supplement had lower triglyceride and "bad" LDL cholesterol levels and higher "good" HDL cholesterol levels [3].
In some animal studies, treatment with broccoli extract reduced tumor growth and prevalence in mice with UV-induced skin cancer [4]. Small human studies have yielded similar results, revealing that broccoli extract significantly protects against skin damage and cancer after sun exposure.
Brussels sprouts are high in fiber. Studies show that a higher fiber intake is associated with lower blood sugar and better diabetic control [5].
Brussels sprouts are high in ALA omega-3 fatty acids, which may benefit the health of your brain, heart, immune system, and other organs [6].
Side Effects
Some people may experience gas as a result of eating Brussels sprouts. Also, those with hypothyroidism should avoid them in large quantities due to their potential iodine-inhibiting composition [7].
Broccoli can cause digestive problems, especially in people with irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) [8].
References
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S1751991815001825
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/23631497/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/20706790/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2737735/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8015811/
- https://ods.od.nih.gov/factsheets/Omega3FattyAcids-Consumer/#h7
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/23631258/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5467063/
Infographic
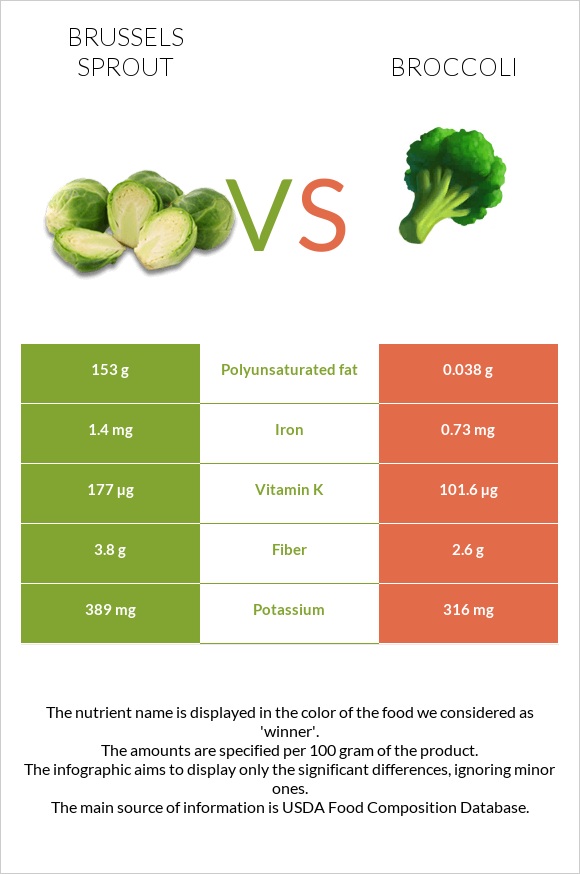
All nutrients comparison - raw data values
| Nutrient |  |
 |
DV% diff. |
| Polyunsaturated fat | 153g | 0.038g | 1020% |
| Vitamin K | 177µg | 101.6µg | 63% |
| Iron | 1.4mg | 0.73mg | 8% |
| Manganese | 0.337mg | 0.21mg | 6% |
| Vitamin B1 | 0.139mg | 0.071mg | 6% |
| Vitamin C | 85mg | 89.2mg | 5% |
| Fiber | 3.8g | 2.6g | 5% |
| Vitamin B5 | 0.309mg | 0.573mg | 5% |
| Vitamin B6 | 0.219mg | 0.175mg | 3% |
| Potassium | 389mg | 316mg | 2% |
| Copper | 0.07mg | 0.049mg | 2% |
| Selenium | 1.6µg | 2.5µg | 2% |
| Vitamin B2 | 0.09mg | 0.117mg | 2% |
| Protein | 3.38g | 2.82g | 1% |
| Carbs | 8.95g | 6.64g | 1% |
| Calcium | 42mg | 47mg | 1% |
| Vitamin A | 38µg | 31µg | 1% |
| Vitamin E | 0.88mg | 0.78mg | 1% |
| Vitamin B3 | 0.745mg | 0.639mg | 1% |
| Folate | 61µg | 63µg | 1% |
| Calories | 43kcal | 34kcal | 0% |
| Fats | 0.3g | 0.37g | 0% |
| Net carbs | 5.15g | 4.04g | N/A |
| Magnesium | 23mg | 21mg | 0% |
| Sugar | 2.2g | 1.7g | N/A |
| Zinc | 0.42mg | 0.41mg | 0% |
| Phosphorus | 69mg | 66mg | 0% |
| Sodium | 25mg | 33mg | 0% |
| Choline | 19.1mg | 18.7mg | 0% |
| Saturated fat | 0.062g | 0.039g | 0% |
| Monounsaturated fat | 0.023g | 0.011g | 0% |
| Tryptophan | 0.037mg | 0.033mg | 0% |
| Threonine | 0.12mg | 0.088mg | 0% |
| Isoleucine | 0.132mg | 0.079mg | 0% |
| Leucine | 0.152mg | 0.129mg | 0% |
| Lysine | 0.154mg | 0.135mg | 0% |
| Methionine | 0.032mg | 0.038mg | 0% |
| Phenylalanine | 0.098mg | 0.117mg | 0% |
| Valine | 0.155mg | 0.125mg | 0% |
| Histidine | 0.076mg | 0.059mg | 0% |
| Fructose | 0.93g | 0.68g | 0% |
Macronutrient Comparison
| Contains more ProteinProtein | +19.9% |
| Contains more CarbsCarbs | +34.8% |
| Contains more OtherOther | +57.5% |
| Contains more FatsFats | +23.3% |
Fat Type Comparison
| Contains more Mono. FatMonounsaturated fat | +109.1% |
| Contains more Poly. FatPolyunsaturated fat | +402531.6% |
| Contains less Sat. FatSaturated fat | -37.1% |
Carbohydrate type comparison
| Contains more SucroseSucrose | +360% |
| Contains more GlucoseGlucose | +65.3% |
| Contains more FructoseFructose | +36.8% |
| Contains more LactoseLactose | +∞% |
| Contains more MaltoseMaltose | +∞% |
People also compare
References
All the values for which the sources are not specified explicitly are taken from FDA’s Food Central. The exact link to the food presented on this page can be found below.
- Brussels sprouts - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/170383/nutrients
- Broccoli - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/170379/nutrients
All the Daily Values are presented for males aged 31-50, for 2000-calorie diets.





