Hazelnut vs. Macadamia — Health Impact and Nutrition Comparison


Summary
Hazelnuts contain more vitamins, minerals, and protein than macadamias. Hazelnuts contain 27 times more Vitamin E and two times more potassium than macadamias. On the other hand, macadamias are lower in glycemic index and have low levels of carbs.
Introduction
Hazelnut and Macadamia nuts are prevalent and used in daily life. They are used in baking and desserts and in combination with chocolate, but here their similarities end. In this article, you can find a detailed guide about the differences between macadamia nuts and hazelnuts.
Taste
Hazelnuts, known as filberts or cobnuts. Hazelnuts are nutty, with slight notes of musty and earthy.
Macadamia nuts taste like solid and creamy butter.
Uses
Hazelnuts are used in baking and desserts and used in combination with chocolate for chocolate truffles. The most popular products are chocolate bars, hazelnut cocoa spread such as Nutella, and Frangelico liqueur. The flavored hazelnut oil is used as a cooking oil. Macadamia nuts are also used in baking or breading for fish or chicken. The wood is used decoratively for small items (1) (2).
Nutrition
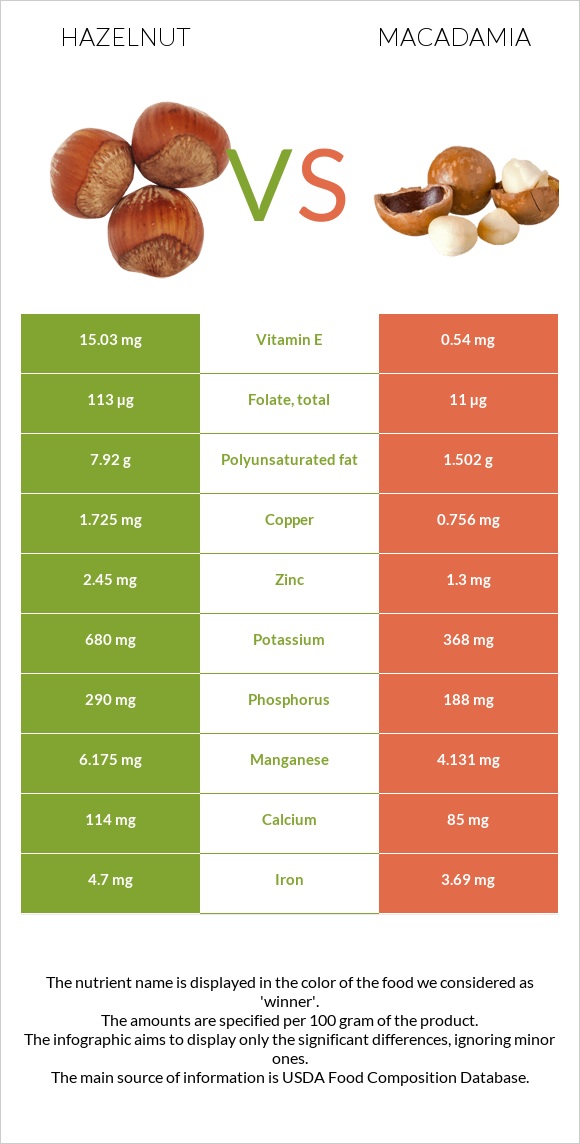
Although these nuts have a similar appearance, nutritionally, they are different. We created the nutrition infographic to understand the difference better and explore the nutritional aspects of these nuts. Have a look below.
Calories
Macadamia nuts contain more calories than hazelnuts. Each macadamia nut has about 718 calories per 100 g, while each hazelnut contains 628 calories per 100 g (3).
Vitamins
Hazelnuts significantly have a higher amount of vitamins than macadamia nuts. Hazelnuts are richer in Vitamin C, Vitamin B5, and Vitamin B6, and the amount of Vitamin E is 27 times higher than in macadamia nuts. Hazelnuts are also rich in Folate. Conversely, some vitamins in macadamia have a higher level than in hazelnuts: Vitamin B1, Vitamin B2, and Vitamin B3. Macadamia nuts lack Vitamin K and Vitamin A. Both of them contain no Vitamin B12 and Vitamin D (4).
Vitamin Comparison
Contains
more
Vitamin CVitamin C
+425%
Contains
more
Vitamin AVitamin A
+∞%
Contains
more
Vitamin EVitamin E
+2683.3%
Contains
more
Vitamin B5Vitamin B5
+21.1%
Contains
more
Vitamin B6Vitamin B6
+104.7%
Contains
more
Vitamin KVitamin K
+∞%
Contains
more
FolateFolate
+927.3%
Contains
more
Vitamin B1Vitamin B1
+85.8%
Contains
more
Vitamin B2Vitamin B2
+43.4%
Contains
more
Vitamin B3Vitamin B3
+37.4%
Potassium
Potassium is a mineral that has many functions in the human body. For example, it may help reduce the risk of kidney stones (8). Hazelnut contains two times more potassium than macadamia nuts. It contains 680 mg of potassium per 100 g, while macadamia nuts contain 368 mg per 100g (5).
Minerals
Overall, hazelnuts are richer in minerals than macadamia nuts. The copper, potassium, and phosphorus levels are almost three times higher in hazelnuts than in macadamia nuts. This nut also contains more iron, calcium, and magnesium. On the other hand, macadamia nuts contain more sodium than hazelnuts. People with high blood pressure should avoid macadamia nuts due to their high sodium content (6) (7).
Mineral Comparison
Contains
more
MagnesiumMagnesium
+25.4%
Contains
more
CalciumCalcium
+34.1%
Contains
more
PotassiumPotassium
+84.8%
Contains
more
IronIron
+27.4%
Contains
more
CopperCopper
+128.2%
Contains
more
ZincZinc
+88.5%
Contains
more
PhosphorusPhosphorus
+54.3%
Contains
less
SodiumSodium
-100%
Contains
more
ManganeseManganese
+49.5%
Contains
more
SeleniumSelenium
+50%
Glycemic Index
The relative ranking of carbohydrates in foods that affect blood sugar levels is called the Glycemic Index. The estimated glycemic index of hazelnuts is 15. Macadamia nuts have a low glycemic index – 10. According to studies, both nuts fall under the category of having a low GI value (6) (7).
HEALTH BENEFITS
Cardiovascular Health
Consuming hazelnuts may help in preventing the reduction of HDL (commonly known as "good" cholesterol) levels in the blood. Additionally, it can help prevent LDL (commonly known as "bad" cholesterol) oxidation and reduce inflammation, which is crucial in reducing the risk of atherosclerosis. Atherosclerosis is the main cause of coronary artery disease, which is the primary reason for heart attacks (9, 10, 11).
According to this study, consumption of 40–90 grams of macadamia nuts per day for 4 weeks resulted in a 3.0% decrease in plasma total cholesterol, a 5.3% decrease in LDL cholesterol, and a 7.9% increase in HDL cholesterol levels in hypercholesterolemic men. These cholesterol-lowering effects of macadamia nuts may help prevent coronary artery disease, making it a good idea to consume them regularly (12, 13).
It is important to note that the amount of nuts consumed is the key factor in lowering cholesterol rather than the type of nut. The research clearly indicates that nut dosage is the major determinant in reducing cholesterol (14, 15).
Choosing unsalted or unsweetened nuts is the best way to ensure that you get their full heart-healthy benefits. Adding salt or sugar to nuts may negate their positive impact on your health.
These findings suggest that eating nuts or related nutritional behaviors may reduce the risk of atrial fibrillation and heart failure (16).
Cancer
Hazelnuts are rich in tocopherols, especially Vitamin E, which are excellent dietary sources of natural antioxidants. In this case, antioxidants can help with fighting cancer. Similarly, hazelnuts contain Vitamin B6, which can also help fight several types of cancer (17). According to studies, some neolignans (Cedrusin and Balanophonin and gallic acid) can inhibit the growth of human cancer cells (18). Macadamia nuts also contain plant compounds called flavonoids, which can fight cancer (19).
Pregnancy
The essential fatty acid may help the body fight cellular inflammation. Macadamia nuts are a great source of omega-3s, which are essential during pregnancy. Overall, macadamia nuts have a high amount of monounsaturated fats and are low in carbs and sugar. These nuts have a moderate fiber content.
If you are not allergic to macadamia nuts, you can enjoy their many nutritional benefits, such as vitamins, minerals, and a low glycemic index. Macadamia oil is also an excellent oil for a baby massage (20).
Improving Hair Health
Hazelnut oil is an excellent product for maintaining good hair growth and is perfect for scalp massages to stimulate hair follicles and nourish them (21).
Calcium is also an element playing a significant role in keeping hair in the proper state, and women, in particular in the perimenopause period, are exposed to its deficiency (22).
Improving Skin Health
Overall, hazelnuts are a rich and inexpensive source of natural and effective phenolic antioxidants, decreasing oxidative stress and keeping skin healthy (23).
Besides, hazelnuts are a great source of Vitamin E, which can help to keep your skin looking young and vibrant.
Diabetes
Research shows that oleic acid in hazelnuts has beneficial effects on insulin sensitivity. Results show that incorporating hazelnuts into the diet can prevent the reduction of HDL-C concentrations in patients with type 2 diabetes (24).
On the other hand, macadamia nuts are a good source of dietary fiber and contain antioxidants and flavonoids. These nutritional components have beneficial effects on diabetes. Another study shows that macadamia nuts can help improve glycemic control in people with type 2 diabetes (25).
Brain Protection
According to the study, the tocotrienol-rich supplement may help to protect brain cells from conditions like Alzheimer's and Parkinson's. Research shows that macadamia nuts may increase neurotransmitter production, and the monounsaturated fats in these nuts can protect the brain from oxidative stress (26) (27).
DOWNSIDES AND RISKS
Although nuts have hugely beneficial effects on human health and can be a part of a healthful diet, they have some drawbacks.
Depending on the context, try to avoid macadamia nuts if you are on a low-fat diet (28).
Allergy
Allergy to hazelnuts is often found in patients with tree pollen allergies. The symptoms usually include itching, swelling, and burning in the mouth and throat after ingesting hazelnuts or hazelnut-containing products.
Allergy to macadamias is rare, estimated to cause less than 5% of all tree nut allergies. In severe cases, the allergic reaction can cause anaphylaxis (29).
Reference
- http://www.fao.org/3/x4484e/x4484e03.htm
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4125148/
- https://sci-hub.se/10.1017/S095442241100014X
- https://academic.oup.com/nutritionreviews/article-abstract/54/8/241/1818792
- https://sci-hub.se/10.1017/BJN20061862
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0048969702006113
- Chemical composition of Macadamia integrifolia (Maiden and Betche) nuts from Paraguay
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/27445166/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/23415431/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3793369/
- https://www.cdc.gov/heartdisease/heart_attack.htm
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/12672919/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/17437143/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4658458/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/24398275/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6161661/
- https://sci-hub.se/10.17660/ActaHortic.1997.445.39
- https://sci-hub.se/10.3390/ijms18020392
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4127821/
- https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jamainternalmedicine/article-abstract/415741
- A potential medicinal importance of zinc in human health and chronic disease
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4828511/
- https://sci-hub.se/10.1016/j.foodchem.2008.02.060
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3793377/
- https://sci-hub.se/10.1007/s11892-005-0097-x
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC1790869/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4333972
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S1051227619303565
- https://sci-hub.se/10.1017/BJN20061869
Infographic
All nutrients comparison - raw data values
| Nutrient |  |
 |
DV% diff. |
| Copper | 1.725mg | 0.756mg | 108% |
| Vitamin E | 15.03mg | 0.54mg | 97% |
| Manganese | 6.175mg | 4.131mg | 89% |
| Vitamin B1 | 0.643mg | 1.195mg | 46% |
| Polyunsaturated fat | 7.92g | 1.502g | 43% |
| Saturated fat | 4.464g | 12.061g | 35% |
| Monounsaturated fat | 45.652g | 58.877g | 33% |
| Folate | 113µg | 11µg | 26% |
| Fats | 60.75g | 75.77g | 23% |
| Vitamin B6 | 0.563mg | 0.275mg | 22% |
| Phosphorus | 290mg | 188mg | 15% |
| Protein | 14.95g | 7.91g | 14% |
| Iron | 4.7mg | 3.69mg | 13% |
| Vitamin K | 14.2µg | 12% | |
| Zinc | 2.45mg | 1.3mg | 10% |
| Potassium | 680mg | 368mg | 9% |
| Magnesium | 163mg | 130mg | 8% |
| Choline | 45.6mg | 8% | |
| Vitamin C | 6.3mg | 1.2mg | 6% |
| Calories | 628kcal | 718kcal | 5% |
| Fiber | 9.7g | 8.6g | 4% |
| Vitamin B2 | 0.113mg | 0.162mg | 4% |
| Vitamin B3 | 1.8mg | 2.473mg | 4% |
| Calcium | 114mg | 85mg | 3% |
| Vitamin B5 | 0.918mg | 0.758mg | 3% |
| Selenium | 2.4µg | 3.6µg | 2% |
| Carbs | 16.7g | 13.82g | 1% |
| Net carbs | 7g | 5.22g | N/A |
| Sugar | 4.34g | 4.57g | N/A |
| Starch | 0.48g | 1.05g | 0% |
| Sodium | 0mg | 5mg | 0% |
| Vitamin A | 1µg | 0µg | 0% |
| Tryptophan | 0.193mg | 0.067mg | 0% |
| Threonine | 0.497mg | 0.37mg | 0% |
| Isoleucine | 0.545mg | 0.314mg | 0% |
| Leucine | 1.063mg | 0.602mg | 0% |
| Lysine | 0.42mg | 0.018mg | 0% |
| Methionine | 0.221mg | 0.023mg | 0% |
| Phenylalanine | 0.663mg | 0.665mg | 0% |
| Valine | 0.701mg | 0.363mg | 0% |
| Histidine | 0.432mg | 0.195mg | 0% |
| Fructose | 0.07g | 0.07g | 0% |
Macronutrient Comparison
| Contains more ProteinProtein | +89% |
| Contains more CarbsCarbs | +20.8% |
| Contains more WaterWater | +290.4% |
| Contains more OtherOther | +100.9% |
| Contains more FatsFats | +24.7% |
Fat Type Comparison
| Contains less Sat. FatSaturated fat | -63% |
| Contains more Poly. FatPolyunsaturated fat | +427.3% |
| Contains more Mono. FatMonounsaturated fat | +29% |
Carbohydrate type comparison
| Contains more StarchStarch | +118.8% |
People also compare
References
All the values for which the sources are not specified explicitly are taken from FDA’s Food Central. The exact link to the food presented on this page can be found below.
- Hazelnut - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/170581/nutrients
- Macadamia - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/170178/nutrients
All the Daily Values are presented for males aged 31-50, for 2000-calorie diets.




