Pistachio vs. Walnut — Health Impact and Nutrition Comparison


Summary
Pistachios are richer in vitamins, iron, potassium, protein, fiber, carbs, have less saturated fats, less sodium, and are cheaper than walnuts. On the other hand, walnuts contain more magnesium, zinc, fewer sugars, and a lower glycemic index than pistachios.
Introduction
In general, nuts are healthy snack options. Each type of nut has different nutritional benefits. This article aims to compare two members of the culinary nut group: pistachio vs. walnut. Both nuts are natural sources of micronutrients, certain minerals, and vitamins. Nowadays, these nuts are prevalent in many dishes, including desserts.
Varieties
Pistachio belongs to the Anacardiaceae family. Pistachios are edible seeds of a small long-live tree that is probably originating from Central Asia. The most common pistachio types are the Noble pistachio, green almond, and the Levante, with a yellow edible part.
Nuts of any tree of the genus Juglans are called walnuts. Walnut is not a proper botanical nut; it is the edible seed of a drupe. There are two most common types of walnut: the Persian walnut and the black walnut.
Taste and Uses
Walnut itself is earthy and mild, but walnut skin might be slightly bitter. Pistachio has a smooth texture and a sweet, sometimes earthy flavor.
Pistachios are usually used as a snack, in salads, ground into sauces, or in desserts. Pistachio flavoring is also a common dessert ingredient; it's very versatile and mixed in any dessert.
Walnut and walnut oil are widely used worldwide. This nut is used in different dishes, salads, desserts such as brownies, ice creams, sauces, etc.
Nutrition
The nutritional values are presented for raw peanuts and raw walnuts. At the bottom of this page, you can find nutrition infographics of these nuts.
Minerals
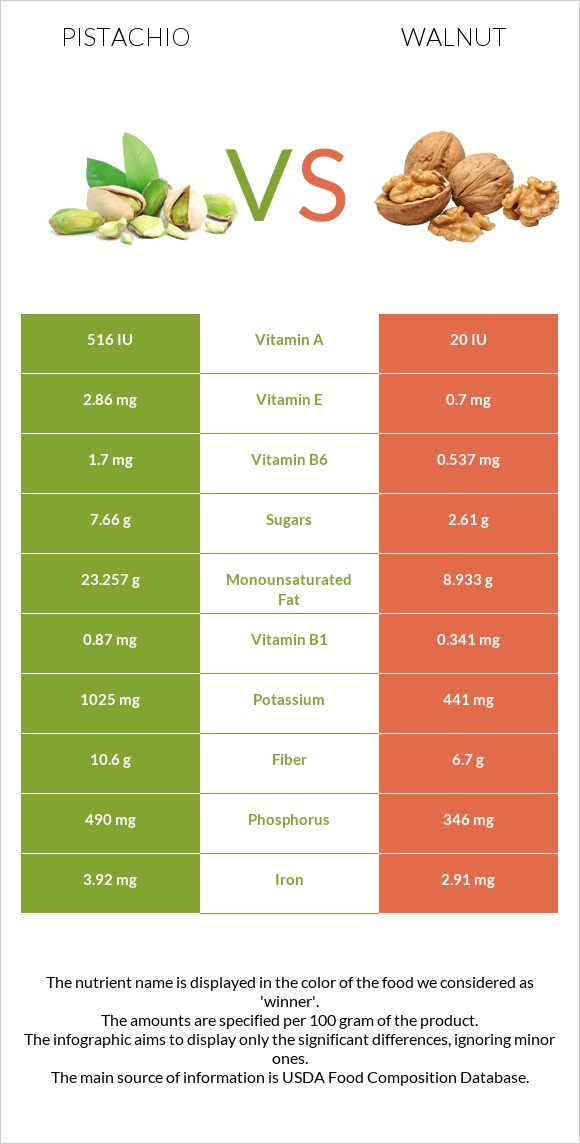
Pistachio contains more iron, potassium, phosphorus, and less sodium than a walnut. On the other hand, walnuts have more magnesium, copper, and zinc than pistachio. Both nuts have an equal level of calcium. It is essential to highlight that both nuts can be sources of minerals required for required daily consumption.
Mineral Comparison
Contains
more
PotassiumPotassium
+132.4%
Contains
more
IronIron
+34.7%
Contains
more
PhosphorusPhosphorus
+41.6%
Contains
less
SodiumSodium
-50%
Contains
more
SeleniumSelenium
+42.9%
Contains
more
MagnesiumMagnesium
+30.6%
Contains
more
CopperCopper
+22%
Contains
more
ZincZinc
+40.5%
Contains
more
ManganeseManganese
+184.5%
Vitamins
In comparison, pistachio has a higher amount of vitamins than walnuts. It has 24 times more Vitamin A, three times more Vitamin E and Vitamin C, two times more Vitamin B6, and more Vitamins B3 and B1.
Despite that, walnuts have more folate than pistachio. Both of these nuts contain equal levels of Vitamin B2 and Vitamin B5. Pistachio has no Vitamin K; both nuts lack Vitamin D and Vitamin B12.
Vitamin Comparison
Contains
more
Vitamin CVitamin C
+330.8%
Contains
more
Vitamin AVitamin A
+2500%
Contains
more
Vitamin EVitamin E
+308.6%
Contains
more
Vitamin B1Vitamin B1
+155.1%
Contains
more
Vitamin B3Vitamin B3
+15.6%
Contains
more
Vitamin B6Vitamin B6
+216.6%
Contains
more
FolateFolate
+92.2%
Micronutrients
Pistachios have higher protein content, while walnuts are rich in fats. However, both pistachio and walnut are rich in healthy fats. Pistachio contains more monounsaturated fat, whereas walnuts contain more polyunsaturated fats. Pistachio also has a higher amount of fiber and carbs. On the other hand, walnuts have less sugar content. Both nuts contain no cholesterol.
Glycemic Index
Overall, nuts are considered low glycemic index food. The glycemic index of pistachio is higher than that of walnut. It has a GI equal to 15, whereas the GI of walnuts is 0.
Calories
Both nuts are rich in calories; however, walnuts contain more calories than pistachios. It has 654 calories per 100 g, whereas pistachio has 560 calories per 100 g.
Health Impact
Weight Loss and Diet
Both nuts are high in calories, but healthy fats and fiber make them applicable for a healthy diet.
According to the study, the daily intake of these nuts does not significantly affect weight gain.
However, between these two nuts, pistachios are the better choice for low calories and low fats diets due to their low content of healthy fat. Walnuts are more suitable for a low-carb and a low glycemic index diet [1] [2].
Diabetes
Nuts are several foods that have beneficial effects for people with type 2 diabetes due to their unsaturated fats and fiber content.
Based on the study, 100 people with type 2 diabetes consuming one tablespoon of walnut oil a day for three months resulted in an 8% decrease in fasting blood sugar [3].
According to the study, individuals with type 2 diabetes showed a 9% reduction in fasting blood sugar after eating 25 grams of pistachios twice a day [4].
Cardiovascular Health
When comparing pistachios and walnuts in terms of cardiovascular health, both nuts offer significant benefits, although they differ slightly in their nutrient compositions and effects on heart health.
Pistachios are known for their unique combination of nutrients, including healthy fats, fiber, protein, antioxidants, and various vitamins and minerals. They are particularly rich in monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fats, which can help lower LDL (“bad” cholesterol) levels while increasing HDL (“good” cholesterol) levels, thus improving overall cholesterol profiles and reducing cardiovascular risk. Additionally, pistachios contain antioxidants such as lutein, zeaxanthin, and gamma-tocopherol, which have been associated with reduced inflammation and oxidative stress, contributing to cardiovascular health. The fiber content in pistachios also supports digestive health and helps regulate blood sugar levels, further benefiting heart health [5].
Walnuts, on the other hand, are renowned for their high content of alpha-linolenic acid (ALA), a plant-based omega-3 fatty acid. Omega-3 fatty acids are well-known for their anti-inflammatory properties and their ability to reduce the risk of heart disease by lowering blood pressure, improving blood vessel function, and reducing the risk of blood clot formation. Additionally, walnuts are rich in polyunsaturated fats, antioxidants such as ellagic acid and polyphenols, and plant sterols, all of which contribute to lower cholesterol levels and improved heart health. The combination of these nutrients makes walnuts a valuable addition to a heart-healthy diet [6, 7, 8].
Endothelial dysfunction is characterized by reduced vasodilation, which is the primary factor of heart disease. Pistachios are a great source of L-arginine, converted into nitric oxide in the body, a compound that plays an essential role in vasodilation. Nitric oxide causes blood vessels to dilate by signaling the smooth cells in the endothelium to relax. According to the study, 42 patients who daily consumed 40 grams of pistachio after three months showed improvements in markers of endothelial function and vascular stiffness [9].
In summary, both pistachios and walnuts offer unique nutritional profiles that can support cardiovascular health. Including a variety of nuts, including pistachios and walnuts, in your diet can provide a range of beneficial nutrients and help reduce the risk of heart disease. However, it's important to consume nuts in moderation due to their calorie density. Incorporating a handful of nuts into your daily diet as a snack or adding them to meals can be a flavorful and heart-healthy choice.
Cancer
Both pistachios and walnuts are rich in omega-3 fats and antioxidants, which help prevent several diseases, including cancer.
However, walnuts contain more antioxidants than most other nuts; therefore, they can prevent several types of cancer. Moreover, walnuts are a great source of 18-carbon α-linolenic acid, which may prevent or inhibit the growth of cancer cells [10].
Gut Health
Eating walnuts can be good for your gut microbiome and support health overall. According to a study, a daily intake of 43 grams of walnuts may increase beneficial bacteria, including those that have probiotic effects and produce butyrate, a gut health-promoting fatty acid. The study has also found a link between increased gut bacteria and a lower risk of heart disease after the walnut diet [11].
Pistachios may also change the microbiome composition, increasing beneficial bacteria, including butyrate-producing ones [12].
Brain Health
Walnuts contain amino-3 acids and potent antioxidants, which have anti-inflammatory effects. Based on several studies, adding walnuts to the diet may improve cognitive function and reduce the risk of progression of mild cognitive impairment and Alzheimer's disease [13].
Downsides and Risks
Allergy
Allergy to pistachios and walnuts is often found in patients with tree pollen allergies. The symptoms usually include itching, swelling, burning in the mouth and throat.
In this case, if you are allergic to nuts, try to avoid eating all tree nuts, even if a healthcare professional has only diagnosed you as being allergic to one type [14].
References
- https://www.mdpi.com/2072-6643/12/7/2155
- https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1111/jfbc.13235
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/28115966/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/25396407/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/27163889/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/35170723/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/24500935/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/21677123/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/25837212/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/25336096/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29470389/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC9370095/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32093220/
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/0091674976900865
Infographic
All nutrients comparison - raw data values
| Nutrient |  |
 |
DV% diff. |
| Polyunsaturated fat | 14.38g | 47.174g | 219% |
| Manganese | 1.2mg | 3.414mg | 96% |
| Vitamin B6 | 1.7mg | 0.537mg | 89% |
| Vitamin B1 | 0.87mg | 0.341mg | 44% |
| Monounsaturated fat | 23.257g | 8.933g | 36% |
| Copper | 1.3mg | 1.586mg | 32% |
| Fats | 45.32g | 65.21g | 31% |
| Phosphorus | 490mg | 346mg | 21% |
| Potassium | 1025mg | 441mg | 17% |
| Fiber | 10.6g | 6.7g | 16% |
| Vitamin E | 2.86mg | 0.7mg | 14% |
| Iron | 3.92mg | 2.91mg | 13% |
| Folate | 51µg | 98µg | 12% |
| Protein | 20.16g | 15.23g | 10% |
| Magnesium | 121mg | 158mg | 9% |
| Zinc | 2.2mg | 3.09mg | 8% |
| Choline | 39.2mg | 7% | |
| Calories | 560kcal | 654kcal | 5% |
| Vitamin C | 5.6mg | 1.3mg | 5% |
| Carbs | 27.17g | 13.71g | 4% |
| Selenium | 7µg | 4.9µg | 4% |
| Vitamin A | 26µg | 1µg | 3% |
| Vitamin K | 2.7µg | 2% | |
| Calcium | 105mg | 98mg | 1% |
| Starch | 1.67g | 0.06g | 1% |
| Vitamin B2 | 0.16mg | 0.15mg | 1% |
| Vitamin B3 | 1.3mg | 1.125mg | 1% |
| Vitamin B5 | 0.52mg | 0.57mg | 1% |
| Saturated fat | 5.907g | 6.126g | 1% |
| Protein per 100 calories | 3.6g | 2.3287461773700304g | N/A |
| Calories per 10 g protein | 277.77777777777777kcal | 429.4156270518713kcal | N/A |
| Net carbs | 16.57g | 7.01g | N/A |
| Sugar | 7.66g | 2.61g | N/A |
| Sodium | 1mg | 2mg | 0% |
| Tryptophan | 0.251mg | 0.17mg | 0% |
| Threonine | 0.684mg | 0.596mg | 0% |
| Isoleucine | 0.917mg | 0.625mg | 0% |
| Leucine | 1.604mg | 1.17mg | 0% |
| Lysine | 1.138mg | 0.424mg | 0% |
| Methionine | 0.36mg | 0.236mg | 0% |
| Phenylalanine | 1.092mg | 0.711mg | 0% |
| Valine | 1.249mg | 0.753mg | 0% |
| Histidine | 0.512mg | 0.391mg | 0% |
| Fructose | 0.24g | 0.09g | 0% |
| Omega-6 - Linoleic acid | 14.091g | N/A |
Macronutrient Comparison
| Contains more ProteinProtein | +32.4% |
| Contains more CarbsCarbs | +98.2% |
| Contains more OtherOther | +67.4% |
| Contains more FatsFats | +43.9% |
Fat Type Comparison
| Contains more Mono. FatMonounsaturated fat | +160.3% |
| Contains more Poly. FatPolyunsaturated fat | +228.1% |
Carbohydrate type comparison
| Contains more StarchStarch | +2683.3% |
| Contains more SucroseSucrose | +182.7% |
| Contains more GlucoseGlucose | +300% |
| Contains more FructoseFructose | +166.7% |
| Contains more MaltoseMaltose | +∞% |
People also compare
References
All the values for which the sources are not specified explicitly are taken from FDA’s Food Central. The exact link to the food presented on this page can be found below.
- Pistachio - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/170184/nutrients
- Walnut - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/170187/nutrients
All the Daily Values are presented for males aged 31-50, for 2000-calorie diets.





