Parsnip vs. Potato — Health Impact and Nutrition Comparison


Summary
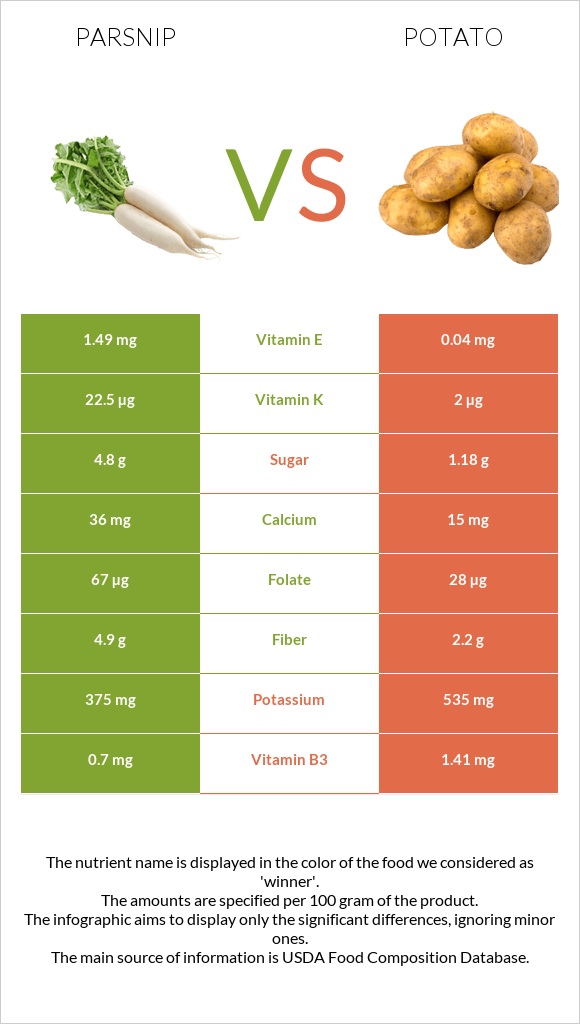
Parsnips are richer in fiber, calcium, selenium, vitamin C, vitamin B3, vitamin K, folate, and vitamin E.
On the other hand, potatoes provide more potassium, iron, protein, and vitamin B3. Potatoes also have a lower glycemic index.
Table of contents
Introduction
Parsnip is a taproot vegetable that is native to the Eurasian plateau. Parsnip was cultivated by the Romans and was used as a natural sweetener in their diets before using cane sugar. It is a taproot vegetable that resembles carrots and is creamy white. This vegetable was introduced to the North Americas by the French settlers.
Potato is a root vegetable, similar to parsnip. It is native to the American continent. The potato plant was domesticated between 10000 and 7000 BC as they tried to make the potato plant into an edible version of its wild type. This highlights its integration into the human diet for nearly 12000 years. Nowadays, potatoes are one of the most consumed vegetables worldwide. They are one of the most versatile foods in every household, and without potatoes, we would have never enjoyed fries.
This article will discuss the difference between parsnips and potatoes according to general differences, nutritional content differences, diet and weight loss impacts, and health impacts.
What Are The Actual Differences?
There are some general differences when it comes to comparing these foods. The price, shelf life, culinary world usage, and taste are from those.
Shelf life
They both have long shelf lives when stored properly. Potatoes can have a longer shelf life lasting for a few months when stored properly.
Culinary world usage
Parsnip is a versatile food that can be cooked and added to stews and soups; some even bake parsnips and season them with herbs and spices. On the other hand, potatoes are more versatile and can be used in numerous ways. They can be boiled, fried, baked, or grilled. Potatoes are also associated with stews and soups. Even potatoes can be used in alcoholic beverage preparations.
Taste
Parsnips look like carrots since they are taproot vegetables and have a sweet earthy flavor with a solid texture before cooking. After cooking, the flavors are enriched, but it becomes softer.
On the other hand, potatoes have a starchy flavor (depending on the type of potatoes). They have different tastes when fried, boiled, or grilled. Both are white to white-yellow.
Nutrition
Note that the default serving size in this part is considered 100g unless written otherwise.
Macronutrients
As the chart below shows, parsnip contains slightly more water than potatoes. Instead, potato is more affluent in carbohydrates and protein. Please, check the corresponding paragraphs for more detailed information.
Macronutrient Comparison
Contains
more
FatsFats
+130.8%
Contains
more
ProteinProtein
+108.3%
Contains
more
CarbsCarbs
+17.6%
Contains
more
OtherOther
+35.7%
Carbs
Per 100g of each, potatoes contain more carbs compared to parsnips. While potatoes have 21g of carbohydrates, parsnips contain only 18g.
Potatoes are extremely rich in starch. Parsnips contain 4 times more sugar. Hence they may seem sweeter.
Fiber
Parsnips contain more fiber than potatoes, and the amount is double for parsnips. Parsnips are rich in both soluble and insoluble fiber.
Parsnips have 4.9g of fiber per 100g, while potatoes have 2.2g of fiber.
Although it is essential to mention that part of the fibers is lost during the boiling process or exposing the foods to high temperatures, this is mostly the case for potatoes.
Fats
Both foods contain negligible amounts of fats.
Cholesterol
Since they are plants, they are devoid of cholesterol.
Proteins
Potatoes are richer in proteins; however, these amounts are meager to consider. They are classified as low-protein foods.
Calories
Parsnips are lower in calories than potatoes. Parsnips contain 75 calories, whereas potatoes have 77 calories per 100g. They are within low-caloric foods.
Glycemic Index
Parsnip has a higher glycemic index than potatoes. Parsnip has a glycemic index equal to 97, which is very high compared to potato, which has a glycemic index 86. Both these foods have high glycemic indices.
Minerals
Parsnip is more affluent in calcium, zinc, copper, and selenium.
In comparison, potatoes are richer in potassium. Noting that they are both deficient in sodium.
Below is the comparative diagram that highlights their mineral distributions.
Mineral Comparison
Contains
more
CalciumCalcium
+140%
Contains
more
ZincZinc
+63.9%
Contains
more
ManganeseManganese
+155.7%
Contains
more
SeleniumSelenium
+350%
Contains
more
PotassiumPotassium
+42.7%
Contains
more
IronIron
+83.1%
Vitamins
Parsnip is richer in vitamins C, B1, B5, K, folate, and E. On the other hand, potato is richer in vitamins B3 and B6.
Since most eating methods involve a cooking process that exposes the potato to high temperatures, it is, to some extent, unavailable once it is ready to eat.
Below is the comparative diagram of their vitamin profiles.
Vitamin Comparison
Contains
more
Vitamin CVitamin C
+77.1%
Contains
more
Vitamin EVitamin E
+3625%
Contains
more
Vitamin B1Vitamin B1
+40.6%
Contains
more
Vitamin B5Vitamin B5
+59.6%
Contains
more
Vitamin KVitamin K
+1025%
Contains
more
FolateFolate
+139.3%
Contains
more
Vitamin AVitamin A
+∞%
Contains
more
Vitamin B3Vitamin B3
+101.4%
Contains
more
Vitamin B6Vitamin B6
+245.6%
Diets and Weight Loss
Vegan
Parsnips and potatoes are vegetables and part of the vegan diet. It is also important to mention that some plant-based burgers use potatoes as an alternative to meat. This can also be applied to other foods where meat has to be replaced with a plant-based alternative.
Keto
Since they are high in carbs and have a high glycemic index, they are not part of the keto diet.
Bodybuilding
Bodybuilders consume boiled potatoes as a carb in association with their protein intake. Potatoes' high carb and high glycemic index can be used in this manner beneficially as it provides a surge of glucose and a quick boost of energy. However, some bodybuilders prefer consuming carbs with a lower glycemic index.
Health Impact
Cardiovascular Health
When comparing parsnips and potatoes in terms of their impact on cardiovascular disease (CVD) risk, several factors come into play:
Nutritional composition: Parsnips are slightly lower in calories and carbohydrates compared to potatoes. They are also higher in fiber, which can help lower cholesterol levels and improve heart health. Potatoes, on the other hand, are higher in carbohydrates and lower in fiber but are a good source of potassium, which can help lower blood pressure.
Glycemic index: Potatoes generally have a higher glycemic index (GI) compared to parsnips. Foods with a high GI can cause a rapid increase in blood sugar levels, which may contribute to insulin resistance and increase the risk of CVD. Choosing foods with a lower GI, like parsnips, may help regulate blood sugar levels and reduce the risk of CVD.
Preparation methods: How parsnips and potatoes are prepared can significantly impact their CVD risk. Frying or preparing them with high-fat ingredients can increase their calorie and fat content, which may contribute to weight gain and increase the risk of CVD. Healthier cooking methods, such as baking, roasting, or steaming with minimal added fat, are preferable (1).
Sodium content: Both parsnips and potatoes are naturally low in sodium. However, the sodium content can increase depending on how they are prepared and seasoned. High sodium intake is associated with high blood pressure and an increased risk of CVD, so it's essential to monitor sodium intake, especially if adding salt during cooking or consuming processed potato products like chips (2).
In summary, while both parsnips and potatoes can be part of a healthy diet, parsnips may have a slight edge when it comes to reducing CVD risk due to their lower glycemic index and higher fiber content. However, the overall impact on CVD risk depends on various factors, including portion sizes, preparation methods, and overall dietary patterns. Incorporating a variety of vegetables, including parsnips and potatoes, into a balanced diet is key to promoting heart health.
Diabetes
Foods high in carbs and a higher glycemic index are associated with uncontrolled glucose concentrations in the blood. The most important feature is glucose control in type 2 diabetic patients. Thus it is essential to avoid foods with a high glycemic index in prediabetes or type 2 diabetes. (3)
Consumption of potatoes in boiled or fried states increases the risk of developing type 2 diabetes. When it comes to boiled potatoes, the risks are null to very low in moderation. (1)
Cancer
According to the study, parsnip compounds may have apoptotic and neutralizing roles over cancer cells, such as leukemic cell lines, lungs, prostate, etc. (4)
There is no association between potato consumption and the risk of cancer. Although some preparation methods might differ, the case of fried potatoes with various oils can increase the risk of developing different types of cancer. In those cases, it is essential to consider all the variables. (5)
Antioxidants
Research shows that parsnips' antioxidants and anti-inflammatory compounds may help to reduce oxidative stress and local or system inflammation. This, in turn, decreases many primarily chronic diseases, like arthritis, diabetes, and cardiovascular diseases. (6)
Potatoes have the property of decreasing biomarkers of inflammation which in turn provides anti-inflammatory characteristics. (7)
Miscellaneous
Parsnips decrease spasms of smooth muscles in the overall human body. It has antispasmodic properties. It reduces the spasm of the intestines, urogenital tract, and, most importantly, bronchospasm, which is important in asthma. (8)
Phytophotodermatitis is a condition that comes after touching wild parsnip leaves and being exposed to the sun. The UV and the compounds in the plant irritate and burn the skin, causing phytophotodermatitis. (9)
References
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29987352/
- https://www.fda.gov/food/nutrition-education-resources-materials/sodium-your-diet
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/12081851/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/16520011/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/33861304/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4469963/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/23855880/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8010426/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29630166/
Infographic
All nutrients comparison - raw data values
| Nutrient |  |
 |
DV% diff. |
| Vitamin B6 | 0.09mg | 0.311mg | 17% |
| Vitamin K | 22.5µg | 2µg | 17% |
| Manganese | 0.56mg | 0.219mg | 15% |
| Fiber | 4.9g | 2.2g | 11% |
| Vitamin E | 1.49mg | 0.04mg | 10% |
| Folate | 67µg | 28µg | 10% |
| Vitamin C | 17mg | 9.6mg | 8% |
| Starch | 17.27g | 7% | |
| Iron | 0.59mg | 1.08mg | 6% |
| Potassium | 375mg | 535mg | 5% |
| Vitamin B3 | 0.7mg | 1.41mg | 4% |
| Vitamin B5 | 0.6mg | 0.376mg | 4% |
| Protein | 1.2g | 2.5g | 3% |
| Selenium | 1.8µg | 0.4µg | 3% |
| Choline | 14.8mg | 3% | |
| Calcium | 36mg | 15mg | 2% |
| Zinc | 0.59mg | 0.36mg | 2% |
| Vitamin B1 | 0.09mg | 0.064mg | 2% |
| Calories | 75kcal | 93kcal | 1% |
| Carbs | 17.99g | 21.15g | 1% |
| Protein per 100 calories | 1.6g | 2.6881720430107525g | N/A |
| Calories per 10 g protein | 625kcal | 372kcal | N/A |
| Fats | 0.3g | 0.13g | 0% |
| Net carbs | 13.09g | 18.95g | N/A |
| Magnesium | 29mg | 28mg | 0% |
| Sugar | 4.8g | 1.18g | N/A |
| Copper | 0.12mg | 0.118mg | 0% |
| Phosphorus | 71mg | 70mg | 0% |
| Sodium | 10mg | 10mg | 0% |
| Vitamin A | 0µg | 1µg | 0% |
| Vitamin B2 | 0.05mg | 0.048mg | 0% |
| Saturated fat | 0.05g | 0.034g | 0% |
| Monounsaturated fat | 0.112g | 0.003g | 0% |
| Polyunsaturated fat | 0.047g | 0.057g | 0% |
| Tryptophan | 0.025mg | 0% | |
| Threonine | 0.081mg | 0% | |
| Isoleucine | 0.08mg | 0% | |
| Leucine | 0.119mg | 0% | |
| Lysine | 0.13mg | 0% | |
| Methionine | 0.038mg | 0% | |
| Phenylalanine | 0.099mg | 0% | |
| Valine | 0.125mg | 0% | |
| Histidine | 0.042mg | 0% | |
| Fructose | 0.34g | 0% |
Fat Type Comparison
| Contains more Mono. FatMonounsaturated fat | +3633.3% |
| Contains less Sat. FatSaturated fat | -32% |
| Contains more Poly. FatPolyunsaturated fat | +21.3% |
People also compare
References
All the values for which the sources are not specified explicitly are taken from FDA’s Food Central. The exact link to the food presented on this page can be found below.
- Parsnip - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/170417/nutrients
- Potato - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/170093/nutrients
All the Daily Values are presented for males aged 31-50, for 2000-calorie diets.






