Poppy seed vs. Sesame — Health Impact and Nutrition Comparison


Summary
Poppy seeds are high in calcium, phosphorus, potassium, manganese, polyunsaturated fats, total carbs, dietary fiber, and vitamins C, E, and B5. Moreover, poppy seeds contain fewer calories and saturated fats, whereas sesame seeds have less sodium.
On the other hand, sesame seeds are high in iron, choline, selenium, copper, net carbs, monounsaturated fats, and vitamins B3, B6, A, and folate.
Table of contents
Introduction
Sesame seeds, originating from the Sesamum indicum plant, are tiny, oil-rich seeds with a long history of use in folk medicine. They can be found in both unhulled and hulled forms, with the hull giving them a golden-brown appearance. Hulled sesame seeds are off-white but turn brown when roasted. In contrast, poppy seeds, derived from the Papaver somniferum plant native to the Eastern Mediterranean, are small and round and come in shades of bluish-black to light gray. Poppy seeds have been utilized in baked goods and traditional dishes globally and have a historical reputation for potential health benefits ranging from alleviating headaches and coughs to addressing conditions like asthma and insomnia. Both seeds offer unique qualities and flavors, making them versatile additions to various culinary creations.
Classification
Sesame seeds (Sesamum indicum) belong to the family Pedaliaceae and the genus Sesamum. Poppy seeds (Papaver somniferum) belong to the family Papaveraceae and the genus Papaver.
Poppy seeds come from Greece. Sesame seeds, on the other hand, are native to Asia or East Africa.
Appearance
Poppy seeds are kidney-shaped and small in size. Sesame seeds are small, thick, and elongated like a pear. Poppy seeds are about 1mm, whereas sesame seeds are 3mm.
Taste
Poppy seeds have a delicate, nutty flavor with a trace of sweetness. Sesame seeds have a mild and nut-like flavor.
Nutrition
In this part of the article, we will compare the nutritional values of poppy seed and sesame, concentrating on differences. The information below is for a hundred grams of each food.
The average serving size of poppy seed is 0.25 tsp or 0.5 grams. The serving size of sesame seed is 1 tbsp or 9 grams. Because the serving size for each is small, the macronutrients, vitamins, and minerals are presented in minimal quantities.
Macronutrients and Calories
Poppy and sesame seeds have almost identical protein content, with poppy seeds containing 17.73 g and sesame seeds 17.99 g per 100 g. However, they differ in fat and carbohydrate content, with sesame seeds having slightly more fat (49.67 g) and lower carbohydrates (23.45 g) compared to poppy seeds, which have slightly lower fat (41.56 g) and higher carbohydrates (28.13 g). Regarding sugar, sesame seeds contain only 0.3 g, while poppy seeds contain 2.99 g. Both seeds are fiber-rich, but poppy seeds have slightly less (11.8 g) per 100 g than sesame seeds (19.5 g). Because poppy and sesame seeds are typically used in small serving sizes, the absolute amount of macronutrients such as calories, fats, proteins, and carbohydrates per serving size remains relatively low.
Macronutrient Comparison
Contains
more
CarbsCarbs
+20%
Contains
more
WaterWater
+26.9%
Contains
more
OtherOther
+42.8%
Contains
more
FatsFats
+19.5%
Calories
Compared to poppy seeds, sesame provides more calories. A hundred grams of poppy seeds contain 525 calories, whereas sesame contains 573 calories per hundred grams.
One serving of poppy seeds provides 46 calories, while one serving of sesame seeds contains 52 calories.
Fats
100g of poppy seeds provide 41.56g of total fat, whereas the same amount of sesame provides 49.67g. Sesame contains over three times more monounsaturated fats. A hundred grams provides 6g of monounsaturated fats, whereas sesame has 18.8g. On the other hand, poppy seed is high in polyunsaturated fats. Poppy seed contains 28.6g of polyunsaturated fats, whereas sesame has 21.8g. Compared to sesame, poppy seed has fewer saturated fats.
Fat Type Comparison
Contains
less
Sat. FatSaturated fat
-35.1%
Contains
more
Poly. FatPolyunsaturated fat
+31.2%
Contains
more
Mono. FatMonounsaturated fat
+213.6%
Carbohydrates
Poppy seed is high in total carb content. A hundred grams of poppy seeds contain 28.13g of carbs, whereas sesame seeds provide 23.45g.
Poppy seeds contain 8.63g of net carbs and 19.5g of dietary fiber. Sesame seeds contain 11.65g of net carbs and 11.8g of dietary fiber.
Cholesterol
Poppy seeds and sesame seeds do not contain cholesterol.
Vitamins
Sesame seeds contain 9 IU of vitamin A, while poppy seeds do not contain this vitamin. Poppy seeds provide higher levels of vitamin E at 1,77 mg compared to 0.25 mg in sesame seeds. B vitamins contain almost equal amounts of vitamin B1: 0.854 mg and 0.791 mg; vitamin B2: 0.247 mg and 0.1 mg; and vitamin B6: 0.79 mg and 0.247. But sesame seeds have more B3 vitamins (4.515) than poppy seeds (0.896). Sesame seeds provide slightly more folate at 97 mcg, while poppy seeds provide 82 mcg. But the absolute amount of vitamins in each serving will also be lower.
Vitamin Comparison
Contains
more
Vitamin CVitamin C
+∞%
Contains
more
Vitamin EVitamin E
+608%
Contains
more
Vitamin B5Vitamin B5
+548%
Contains
more
Vitamin B2Vitamin B2
+147%
Contains
more
Vitamin B3Vitamin B3
+403.9%
Contains
more
Vitamin B6Vitamin B6
+219.8%
Contains
more
FolateFolate
+18.3%
Minerals
Poppy seeds are notably rich in calcium, with a significant content of 1438mg and potassium at 719mg.
However, sesame seeds take the lead in several crucial minerals: they are significantly richer in iron at 14.55mg and copper at 4.082mg. Both seeds offer comparable levels of zinc and magnesium. Regarding trace elements, poppy seeds are higher in manganese, boasting 6.707mg, while sesame seeds provide substantially more selenium at 34.4 g.In the case of minerals, the corresponding serving size will also be smaller.
Mineral Comparison
Contains
more
CalciumCalcium
+47.5%
Contains
more
PotassiumPotassium
+53.6%
Contains
more
PhosphorusPhosphorus
+38.3%
Contains
more
ManganeseManganese
+172.6%
Contains
more
IronIron
+49.1%
Contains
more
CopperCopper
+150.9%
Contains
less
SodiumSodium
-57.7%
Contains
more
SeleniumSelenium
+154.8%
Acidity
The quantity of acid or base created by foods inside the body is known as the PRAL or potential renal acid load. The PRAL level of poppy seeds is -1.8. Sesame seeds have a PRAL level of 0.3. Poppy seed is alkaline, whereas sesame is acidic.
Glycemic Index
The glycemic index value of poppy seed is 5, indicating minimal impact on blood sugar levels. There is not enough data to determine the glycemic index value of sesame seeds.
Visit our Glycemic Index Chart: Complete (350+) List from the All Sources page to discover more about the glycemic index ratings of various foods.
Weight Loss & Diets
Poppy seeds and sesame seeds are vegan. They are good options for people who follow the Mediterranean diet. Sesame seeds and poppy seeds can be part of the paleo diet. Both are allowed in the DASH diet.
Health Impact
Cardiovascular Health
Sesame is rich in bioactive phenolic compounds lignans, such as sesamin, sesamol, and sesamolin. Sesamin has anti-hypertensive, anti-atherogenic, and anti-thrombotic effects through multiple pathways. According to the study, sesame consumption may reduce the risk of cardiovascular diseases(CVD) (1).
Poppy seeds, on the other hand, contain opiates such as morphine (2-251 micro g/g) and codeine (0.4-57.1 micro g/g) (2).
According to one study, opium users had much higher rates of hypertension than non-users. The majority of research found no link between opium addiction and the prevalence of hypertension(3).
Diabetes
Sesamin also has antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties. Sesamin substantially reduces fasting plasma glucose, insulin, and glycosylated plasma proteins. Sesamin can help slow the progression of type II diabetes by protecting pancreatic β-cells(1).
While opium may lower blood lipids in some situations, the majority of human investigations have shown that opium ingestion is either ineffective or has a negative influence on serum lipids. Furthermore, long-term usage of opium has detrimental consequences on diabetes and dyslipidemia (3)(4).
Analgesic properties and anti-inflammatory effects
Sesamin, a substance found in sesame seeds, can reduce joint discomfort and increase mobility in people with knee arthritis (5,6). Additionally, early research suggests that sesame oil and seeds have anti-inflammatory qualities (7). However, considerable caution must be used when handling unwashed poppy seeds because they may contain opioids, including morphine, codeine, and thebaine. Although eating unwashed poppy seeds involves significant health hazards and should only be explored under appropriate medical supervision, these substances can reduce pain (8,9).
Downsides and Risks
Allergy
Seed consumption may cause allergic reactions. Sesame seed consumption may induce severe allergic responses such as pruritus, widespread erythema, uvula angioedema, clinical shock, and wheezing (10).
Poppy seed hypersensitivity can result from IgE-dependent or non-immune pathways(6). Immediate-type allergic responses can affect the digestive, respiratory, or cutaneous systems (11). According to other studies, urticaria, vomiting, oral mucosal edema, and respiratory discomfort are the main clinical signs (12).
Sources
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/8871378/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5061814/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/25140211/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/25871017/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/22704650/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/24824289/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6513924/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6513924/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/2622878
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/16425801/
- https://www.thermofisher.com/
Infographic
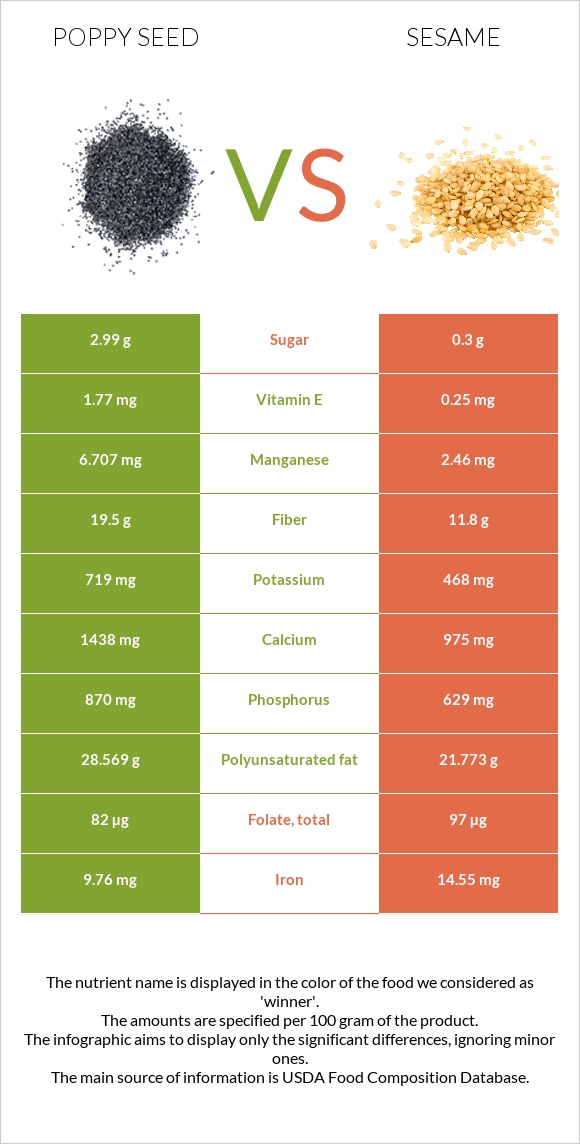
All nutrients comparison - raw data values
| Nutrient |  |
 |
DV% diff. |
| Copper | 1.627mg | 4.082mg | 273% |
| Manganese | 6.707mg | 2.46mg | 185% |
| Iron | 9.76mg | 14.55mg | 60% |
| Calcium | 1438mg | 975mg | 46% |
| Polyunsaturated fat | 28.569g | 21.773g | 45% |
| Vitamin B6 | 0.247mg | 0.79mg | 42% |
| Selenium | 13.5µg | 34.4µg | 38% |
| Phosphorus | 870mg | 629mg | 34% |
| Monounsaturated fat | 5.982g | 18.759g | 32% |
| Fiber | 19.5g | 11.8g | 31% |
| Vitamin B3 | 0.896mg | 4.515mg | 23% |
| Fats | 41.56g | 49.67g | 12% |
| Vitamin B2 | 0.1mg | 0.247mg | 11% |
| Saturated fat | 4.517g | 6.957g | 11% |
| Vitamin E | 1.77mg | 0.25mg | 10% |
| Potassium | 719mg | 468mg | 7% |
| Vitamin B1 | 0.854mg | 0.791mg | 5% |
| Vitamin B5 | 0.324mg | 0.05mg | 5% |
| Folate | 82µg | 97µg | 4% |
| Choline | 8.8mg | 25.6mg | 3% |
| Calories | 525kcal | 573kcal | 2% |
| Carbs | 28.13g | 23.45g | 2% |
| Protein | 17.99g | 17.73g | 1% |
| Vitamin C | 1mg | 0mg | 1% |
| Magnesium | 347mg | 351mg | 1% |
| Zinc | 7.9mg | 7.75mg | 1% |
| Sodium | 26mg | 11mg | 1% |
| Net carbs | 8.63g | 11.65g | N/A |
| Sugar | 2.99g | 0.3g | N/A |
| Tryptophan | 0.184mg | 0.388mg | 0% |
| Threonine | 0.686mg | 0.736mg | 0% |
| Isoleucine | 0.819mg | 0.763mg | 0% |
| Leucine | 1.321mg | 1.358mg | 0% |
| Lysine | 0.952mg | 0.569mg | 0% |
| Methionine | 0.502mg | 0.586mg | 0% |
| Phenylalanine | 0.758mg | 0.94mg | 0% |
| Valine | 1.095mg | 0.99mg | 0% |
| Histidine | 0.471mg | 0.522mg | 0% |
| Fructose | 0.29g | 0% | |
| Omega-3 - ALA | 0.273g | N/A |
People also compare
References
All the values for which the sources are not specified explicitly are taken from FDA’s Food Central. The exact link to the food presented on this page can be found below.
- Poppy seed - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/171330/nutrients
- Sesame - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/170150/nutrients
All the Daily Values are presented for males aged 31-50, for 2000-calorie diets.