Pomelo vs. Grapefruit — Health Impact and Nutrition Comparison


Summary
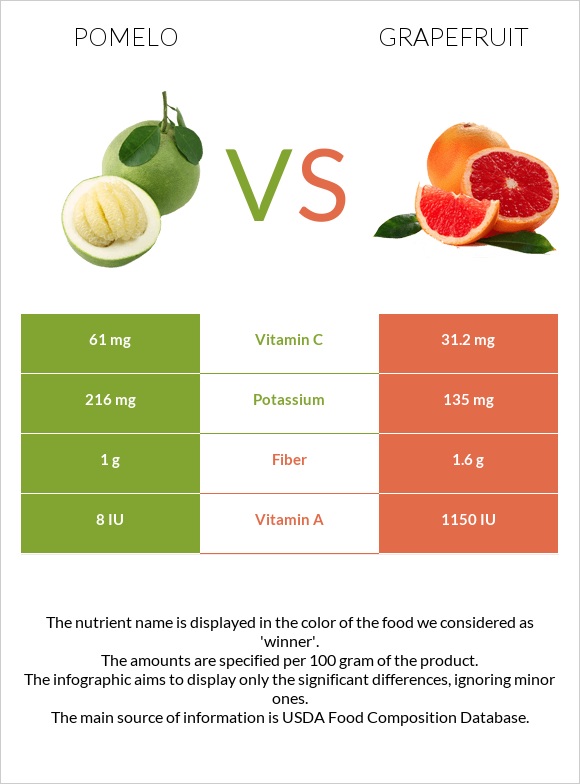
Grapefruits are higher in calories and carbs, while pomelos are richer in iron and vitamin C. Pomelos provide 2 times more vitamin C than grapefruits.
Introduction
This article discusses the main differences in nutritional composition and health impacts of pomelo (1) and grapefruit (2). You can check the daily coverages of some essential nutrients these fruits provide in the corresponding charts.
Appearance and taste
Grapefruit is round in shape and has pale yellow or reddish skin, which can be rough or smooth. Pomelo's shape looks like a teardrop. It has a yellow or green flash. Usually, pomelo is larger than grapefruit. Pomelo has a more delicate and flowery taste than grapefruit. Grapefruits have a semisweet, usually bitter flavor.
Pomelo is native to southern Asia and Malaysia, while grapefruit originates from Barbados.
Nutrition
Both pomelo and grapefruit are citrus fruits with many similarities, yet there are differences in how each nutrient is distributed.
Calories
Pomelo and grapefruit are plant food products. So, these two are considered low-calorie foods. Grapefruit, on the other hand, contains more calories than grapefruit. A 100g of grapefruit contains 42 kcal (176 kJ); a 100g of pomelo contains 38 kcal (159 kJ) (1.2).
Carbs
Grapefruit is higher in carbs compared to pomelo. A 100g of grapefruit contains 1.6g of dietary fiber, while the same amount of pomelo contains only 1g (1.2).
Protein
These two fruits are supposed to contain little protein. They both have less than 1g of protein per 100g. We can neglect that amount.
Fats
It is not necessary to pay attention to the fat content of these fruits, as they have less than 1g of fat per 100g. Pomelo and grapefruit do not contain any amount of cholesterol.
Vitamins
Pomelo and grapefruit are rich in different vitamins. Pomelos are an excellent source of vitamin C: they are two times higher in vitamin C than grapefruits. Grapefruit is richer in vitamin A and B-complex vitamins. Pomelo contains no vitamin A, while grapefruit provides 69% of the DV.
Minerals
Grapefruit is higher in calcium and magnesium. Pomelo is richer in iron, potassium, zinc, and copper. You can compare the mineral composition of these two fruits in the chart below.
Glycemic index
Grapefruit and pomelo have a low glycemic index. According to the glycemic index food guide, grapefruit has a glycemic index of 55 or less (3). The glycemic index for pomelo isn’t applicable.
Acidity
Both of these products are acidic foods. Grapefruit has a 3.00-3.75 pH level (4). Too much exposure to this juice can damage teeth and cause enamel erosion. In grapefruit juice, citric acid is a major component of carbon-based acids. The exact amount of pomelo’s acidity is unknown.
Weight loss and diets
Pomelo and grapefruit are low-calorie fruits, but they are rich in fiber and water. The fiber content helps you feel full and reduce calorie intake (5) (6). Even a study shows that those who consumed grapefruit in a certain period had a reduced waist size (7).
- Because the Atkins diet is low in carbohydrates, you should avoid eating most fruits. However, pomelo and grapefruit are allowed in moderation.
- Similarly to the Atkins diet, the Dukan diet follows a four-phase plan with very low carbs and a high protein intake. Fruits, including these, are off the menu until the third (consolidation) phase.
- The Mediterranean diet promotes the use of fruits and vegetables in your diet. The Mediterranean diet profile emphasizes whole grains, useful fats (fish, olive oil, nuts, and so on), vegetables, fruits, fish, and very little non-fish meat consumption, therefore pomelo and grapefruit are advised during this diet.
- A paleo diet often consists of lean meats, fish, fruits, vegetables, nuts, and seeds — items that could have been obtained through hunting and gathering in the past, so these fruits are recommended during this diet.
- Because it regulates when you eat rather than what you eat, intermittent fasting is more like an eating habit than a diet. During this diet, grapefruit and pomelo are advised.
- They can also be consumed as part of the DASH (Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension) diet.
Health impact
Health Benefits
Cardiovascular health
Pomelo promotes heart health by reducing blood cholesterol and triglycerides, while grapefruit also reduces blood pressure.
Pomelo contains antioxidants that prevent consumed cholesterol from being fully absorbed into the bloodstream, which is important for people with coronary heart disease and for people who have had a myocardial infarction (8).
According to this study, at the doses tested, grapefruit juice prolongs the QT interval in the ECG (electrocardiogram). The effect is significant in healthy volunteers, stronger in female patients, and even stronger in LQTS (long QT syndrome) patients. LQTS can increase the risk of torsade de pointes (a type of arrhythmia) and mortality (9).
Grapefruit is high in potassium, maintaining healthy blood pressure (10). Besides, the consumption of grapefruit shows protection from heart disease and stroke (11).
However, many clinicians advise against eating grapefruit and drinking grapefruit juice while taking statins (Atorvastatin, Rosuvastatin, Fluvastatin, and Lovastatin), which are used to lower cholesterol levels in the blood.
Diabetes
Grapefruit juice's hypoglycemic effects are well known, however, the processes by which grapefruit juice decreases blood glucose levels have not been studied (12). Pomelo is a low glycemic index fruit that can be supplied to diabetic people if consumed in moderation (13).
According to this study, people with type 1, type 2, or pre-diabetes should pick foods with a lower glycemic index (including these products) to help control blood sugar (14).
Pomelo and grapefruit are rich in dietary fiber. A high intake of dietary fiber, particularly soluble fiber, over the level suggested by the American Diabetes Association, improves glycemic control, decreases hyperinsulinemia, and lowers plasma lipid contents in type 2 diabetes patients (15).
Digestive Health
Pomelo and grapefruit are good sources of dietary fiber. According to this study, inadequate amounts of dietary fiber can result in a variety of diseases. To gain the benefits of dietary fiber's beneficial health impacts, adults should consume 25-29 g per day. Dietary fiber may help to lower appetite, food intake, the risk of obesity, blood glucose levels, and cholesterol (16.17).
In addition, consuming dietary fiber may obviously increase stool frequency in patients with constipation (18).
Pomelo and grapefruit consumption (especially grapefruit) may inhibit pancreatic lipase. Total cholesterol levels in the body are lowered when the lipase enzyme is inhibited. This is one of the potential methods for treating obesity (19).
Cancer
Because they contain flavonoids, grapefruit, and pomelo have the potential to be anticancer plants. This review indicated that the flavonoid naringenin (found in these fruits) is a natural substance with the potential to treat different types of cancer (20).
According to this study, several flavonoids in pomelo could be candidates for natural breast cancer treatments (21).
According to the findings of this study, combining grapefruit extract with radiation therapy reduces cell proliferation in PC-3 prostate cancer cells, suggesting that grapefruit may have a role as a radiosensitizer for prostate cancer (22).
Hydration
Adequate fluid intake is essential for maintaining homeostasis, which includes regulating body temperature, preventing infections, delivering nutrients to cells, and keeping organs functioning properly (23).
Experts recommend that women drink 11 cups of water daily, while men should drink 16 cups. And not all of those drinks have to be ordinary water; some can be replaced with fruit (including pomelo and grapefruit), vegetables, coffee, or tea (23).
Despite this, it should be emphasized that water consumption should be restricted in the case of heart valve disease.
Downsides and Risks
Citrus food allergies are unusual. There is a scarcity of clinical and biochemical evidence on this allergy in the literature. Mild symptoms, such as an oral allergy syndrome, are commonly observed; anaphylaxis is uncommon (24).
References
- https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/174673/nutrients
- https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/167754/nutrients
- https://guidelines.diabetes.ca/docs/patient-resources/glycemic-index-food-guide.pdf
- https://www.clemson.edu/extension/food/food2market/documents/ph_of_common_foods.pdf
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4757923/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/33096647/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/21288350/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31281355/
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S1547527119303686
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/23558164/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5490577/
- https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s00394-015-0883-4
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29058284/
- https://www.diabetes.ca/resources/tools---resources/the-glycemic-index-(gi)
- https://www.nejm.org/doi/full/10.1056/NEJM200005113421903
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S014486172031359X
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S2212619817300098
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3544045/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/35779626/
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2590157522001663
- https://www.researchgate.net/publication/359174895_Inhibition_of_Human_Epidermal_Growth_Factor_Receptor-2_HER-2_from_Pomelo_Citrus_maxima_Flavonoid_Compounds_an_In_Silico_Approach
- https://www.researchgate.net/publication/333118548_Grapefruit_extract_as_a_potential_radiosensitizer_of_prostate_cancer_cells
- https://www.hsph.harvard.edu/news/hsph-in-the-news/the-importance-of-hydration/#:~:text=Drinking%20enough%20water%20each%20day,quality%2C%20cognition%2C%20and%20mood.
- https://ctajournal.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/2045-7022-3-S3-P153
Infographic
Mineral Comparison
| Contains more PotassiumPotassium | +60% |
| Contains more IronIron | +37.5% |
| Contains more CopperCopper | +50% |
| Contains more ZincZinc | +14.3% |
| Contains more MagnesiumMagnesium | +50% |
| Contains more CalciumCalcium | +450% |
| Contains less SodiumSodium | -100% |
| Contains more ManganeseManganese | +29.4% |
Vitamin Comparison
| Contains more Vitamin CVitamin C | +95.5% |
| Contains more Vitamin AVitamin A | +∞% |
| Contains more Vitamin B1Vitamin B1 | +26.5% |
| Contains more Vitamin B2Vitamin B2 | +14.8% |
| Contains more Vitamin B6Vitamin B6 | +47.2% |
All nutrients comparison - raw data values
| Nutrient |  |
 |
DV% diff. |
| Vitamin C | 61mg | 31.2mg | 33% |
| Vitamin A | 0µg | 58µg | 6% |
| Vitamin B5 | 0.262mg | 5% | |
| Folate | 13µg | 3% | |
| Calcium | 4mg | 22mg | 2% |
| Potassium | 216mg | 135mg | 2% |
| Fiber | 1g | 1.6g | 2% |
| Copper | 0.048mg | 0.032mg | 2% |
| Fructose | 1.77g | 2% | |
| Magnesium | 6mg | 9mg | 1% |
| Vitamin E | 0.13mg | 1% | |
| Vitamin B1 | 0.034mg | 0.043mg | 1% |
| Vitamin B6 | 0.036mg | 0.053mg | 1% |
| Choline | 7.7mg | 1% | |
| Calories | 38kcal | 42kcal | 0% |
| Protein | 0.76g | 0.77g | 0% |
| Fats | 0.04g | 0.14g | 0% |
| Net carbs | 8.62g | 9.06g | N/A |
| Carbs | 9.62g | 10.66g | 0% |
| Iron | 0.11mg | 0.08mg | 0% |
| Sugar | 6.89g | N/A | |
| Zinc | 0.08mg | 0.07mg | 0% |
| Phosphorus | 17mg | 18mg | 0% |
| Sodium | 1mg | 0mg | 0% |
| Manganese | 0.017mg | 0.022mg | 0% |
| Selenium | 0.1µg | 0% | |
| Vitamin B2 | 0.027mg | 0.031mg | 0% |
| Vitamin B3 | 0.22mg | 0.204mg | 0% |
| Saturated fat | 0.021g | 0% | |
| Monounsaturated fat | 0.02g | 0% | |
| Polyunsaturated fat | 0.036g | 0% | |
| Tryptophan | 0.008mg | 0% | |
| Threonine | 0.013mg | 0% | |
| Isoleucine | 0.008mg | 0% | |
| Leucine | 0.015mg | 0% | |
| Lysine | 0.019mg | 0% | |
| Methionine | 0.007mg | 0% | |
| Phenylalanine | 0.013mg | 0% | |
| Valine | 0.015mg | 0% | |
| Histidine | 0.008mg | 0% |
Macronutrient Comparison
| Contains more OtherOther | +29.7% |
| Contains more FatsFats | +250% |
| Contains more CarbsCarbs | +10.8% |
People also compare
References
All the values for which the sources are not specified explicitly are taken from FDA’s Food Central. The exact link to the food presented on this page can be found below.
- Pomelo - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/167754/nutrients
- Grapefruit - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/174673/nutrients
All the Daily Values are presented for males aged 31-50, for 2000-calorie diets.



