Spelt vs. Oat — Nutrition and Health Differences


Summary
Spelt is higher in carbs, oxalate, glycemic index, selenium, vitamins B3, B6, and E. It contains gluten and FODMAPs. Oats are richer in protein, manganese, copper, zinc, potassium, phosphorus, magnesium, iron, calcium, vitamins B1, B2, B5, and folate. They are safe to eat for IBS and Celiac.
Introduction
Grains and cereals are among the most consumed foods in different cuisines and cultures worldwide. There is much controversy around their health effects, which are scientifically inaccurate. We will debunk the most common misconceptions about these cereals.
In this article, we will compare two types of grains: spelt and oats.
We will dive deep into their general differences, nutritional differences, and health impacts.
This article compares oat and spelt in uncooked forms.
Nutrition
This section will compare 100g of each in uncooked forms.
Calories
Oats contain 390 calories, whereas spelt contains 340 calories. In uncooked forms, oats are higher in calories.
Carbs
Their carb profile is significantly different. Uncooked spelt is higher in carbs compared to uncooked oats.
Spelt contains 70g of carbs, whereas oats contain 66g.
Fiber
Even though oats are lower in carbs, their fiber content is the same.
They both contain a decent amount of fiber, about 10.6g.
Glycemic Index
Since they are grains, their glycemic index is considered important.
Spelt has a higher glycemic index of 63 than oats, with a glycemic index of 59.
Oxalate
Spelt contains a higher amount of oxalates than oats. Oats contain 16mg of oxalate, which is considered low. Spelt contains 36mg of oxalate.
Protein
Oats contain higher amounts of protein compared to spelt. In oats, 17g of proteins, whereas spelt contains 14.5g of protein.
Fat
In cooked form, this would be negligible; however, in uncooked forms, oats contain about three times more fat (7g) compared to spelt (2.4g)
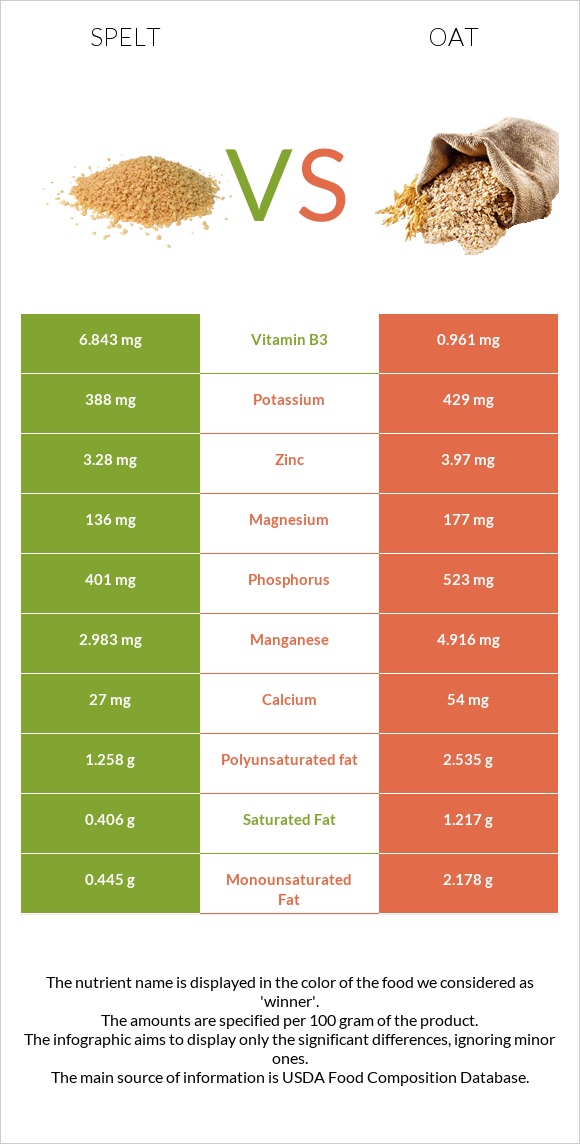
Minerals
Oat is richer in manganese, copper, zinc, potassium, phosphorus, magnesium, iron, and calcium. In comparison, spelt is richer in selenium.
Note that spelt contains a decent amount of all the minerals in oats aswell.
Mineral Comparison
Contains
more
SeleniumSelenium
+∞%
Contains
more
MagnesiumMagnesium
+261.2%
Contains
more
CalciumCalcium
+440%
Contains
more
PotassiumPotassium
+200%
Contains
more
IronIron
+182.6%
Contains
more
CopperCopper
+191.2%
Contains
more
ZincZinc
+217.6%
Contains
more
PhosphorusPhosphorus
+248.7%
Contains
less
SodiumSodium
-60%
Contains
more
ManganeseManganese
+350.6%
Vitamins
Spelt is richer in vitamins B3 (niacin), B6, and E. In comparison, oat is richer in vitamins B1 (thiamine), B2, B5, and folate.
Vitamin Comparison
Contains
more
Vitamin EVitamin E
+∞%
Contains
more
Vitamin B3Vitamin B3
+167.4%
Contains
more
Vitamin B1Vitamin B1
+640.8%
Contains
more
Vitamin B2Vitamin B2
+363.3%
Contains
more
Vitamin B6Vitamin B6
+48.8%
Contains
more
FolateFolate
+330.8%
Health Impacts
If you scroll through social media's nutrition and health section, maybe one out of four posts talks about the bad impacts of grains such as oats. However, are these claims evidence-based or just personal opinions?
In short, these are personal opinions that are wrong. They are not evidence-based, and even if they are in a way brought from scientific papers, they are manipulated with different biases. But let's dig in and discuss them.
Cardiovascular Health and Diabetes
Spelt has antioxidative properties from damage caused by prolonged hyperglycemia. It reduces the risks of cardiovascular diseases and diabetes complications (1).
Oats are one of the top foods you can consider consuming for a balanced diet. Compared to spelt, they are a highly researched food. Oats have been shown to have antidiabetogenic and lipid-lowering properties, which decrease the risk of heart disease and diabetes overall. Oats are associated with decreased cholesterol levels.
Oats are associated with decreased HbA1c levels in people with diabetes (2).
In addition, insulin control was observed when oats and oatmeal were included in a diet specifically designed for type 2 diabetics (3).
Phytic Acid
We often hear that whole grains such as oats and spelt contain phytic acid, which prevents nutrient absorption. However, when we cook and process these oats and spelt, this phytic acid gets neutralized and won't affect our dietary needs. In addition, we consume more nutrients and calories than we need most of the time, and the tiny amount of phytic acid, if consumed, will not show any significant decrease in nutrient absorption (4).
Obesity
What is the relation of grains with obesity?
Well, oats are associated with decreased body waist circumference and visceral fat. Overall, there are decreased risks of obesity, reduced weight, and improved metabolic indicators associated with oat consumption (5).
IBS and Gluten Intolerance
Oats naturally do not contain gluten and are safe to consume for IBS, gluten intolerance, or Celiac (6).
Oats are gluten-free.
Spelt contains gluten and FODMAPs, which should not be consumed in both IBS and gluten intolerance or celiac diets (7).
It is important to consider sources of oats. Sometimes, oats are processed in areas where wheat is also kept, which might mix small amounts of gluten in the oats and trigger symptoms of Celiac. However, it's not due to the oats itself.
Beta-Glucans and Overall Health
Oats are the highest-containing cereals for beta-glucans, and spelt is the lowest.
Thus, beta-glucan has numerous health benefits for our overall health. Beta-glucans in oats are anti-diabetogenic, lower cholesterol, and antioxidative, and they are associated with a healthier cardiovascular and immune system (8)(9).
You can also read about spelt vs. teff.
General Differences
The general differences between oats and spelt are based on their culinary usage, taste, and texture.
Culinary Usage
Since oats and spelt are considered whole grains, they have multipurpose uses. Oats are mostly processed into oatmeal for breakfast. They are also made into granola, porridge, and even plant-based milk.
On a personal note, oat milk is the best-tasting plant-based milk. It is sweeter and milder than most of the rest.
In comparison, spelt has different uses in the culinary world. Spelt can be used to make bread, pasta, risotto, pilaf, porridge. Spelt flour can also be used as an alternative to wheat flour for different recipes.
Taste and Texture
Since they are both whole-grain cereals, they have an earthy and nutty taste. However, considering the comparison, spelt has a bolder, nutty flavor and earthier taste than oats.
Oats are milder in taste and on the sweeter side. When cooked, they are more chewy and easier to consume.
Oat and spelt contain their bran, part of the grain, considering they are wholegrain.
References
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29068605/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4690088/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30157531/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8746346/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/23371785/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC9661369/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/35889757/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC10001039/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31960663/
Infographic
All nutrients comparison - raw data values
| Nutrient |  |
 |
DV% diff. |
| Manganese | 1.091mg | 4.916mg | 166% |
| Vitamin B1 | 0.103mg | 0.763mg | 55% |
| Phosphorus | 150mg | 523mg | 53% |
| Copper | 0.215mg | 0.626mg | 46% |
| Iron | 1.67mg | 4.72mg | 38% |
| Magnesium | 49mg | 177mg | 30% |
| Fiber | 3.9g | 10.6g | 27% |
| Vitamin B5 | 1.349mg | 27% | |
| Zinc | 1.25mg | 3.97mg | 25% |
| Protein | 5.5g | 16.89g | 23% |
| Polyunsaturated fat | 2.535g | 17% | |
| Calories | 127kcal | 389kcal | 13% |
| Carbs | 26.44g | 66.27g | 13% |
| Folate | 13µg | 56µg | 11% |
| Vitamin B3 | 2.57mg | 0.961mg | 10% |
| Fats | 0.85g | 6.9g | 9% |
| Potassium | 143mg | 429mg | 8% |
| Starch | 19.57g | 8% | |
| Vitamin B2 | 0.03mg | 0.139mg | 8% |
| Selenium | 4µg | 7% | |
| Saturated fat | 1.217g | 6% | |
| Monounsaturated fat | 2.178g | 5% | |
| Calcium | 10mg | 54mg | 4% |
| Vitamin B6 | 0.08mg | 0.119mg | 3% |
| Vitamin E | 0.26mg | 2% | |
| Net carbs | 22.54g | 55.67g | N/A |
| Sodium | 5mg | 2mg | 0% |
| Tryptophan | 0.234mg | 0% | |
| Threonine | 0.575mg | 0% | |
| Isoleucine | 0.694mg | 0% | |
| Leucine | 1.284mg | 0% | |
| Lysine | 0.701mg | 0% | |
| Methionine | 0.312mg | 0% | |
| Phenylalanine | 0.895mg | 0% | |
| Valine | 0.937mg | 0% | |
| Histidine | 0.405mg | 0% |
Macronutrient Comparison
| Contains more WaterWater | +709.7% |
| Contains more ProteinProtein | +207.1% |
| Contains more FatsFats | +711.8% |
| Contains more CarbsCarbs | +150.6% |
| Contains more OtherOther | +164.6% |
People also compare
References
All the values for which the sources are not specified explicitly are taken from FDA’s Food Central. The exact link to the food presented on this page can be found below.
- Spelt - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/169746/nutrients
- Oats - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/169705/nutrients
All the Daily Values are presented for males aged 31-50, for 2000-calorie diets.






