Vegetable oil vs. Butter — Health Impact and Nutrition Comparison


Summary
Butter contains more minerals and is richer in vitamins B12 and A. butter is higher in saturated fats; however, it has a shorter shelf life. On the other hand, Vegetable oil is higher in fats and unsaturated fats and is richer in vitamins K and E.
Introduction
This article will discuss the difference between butter and vegetable oil, considering their general differences, nutritional content, and health impacts.
General differences
Butter is obtained from churning milk or cream. Butter has been part of the human diet since the agricultural ages after the domestication of mammals. It could be that the first butter was prepared from sheep’s milk; however, nowadays, the most common source of butter is cow’s milk.
Vegetable oils are extracted from vegetables which is the main difference between butter. Some various seeds and vegetables yield vegetable oil. This article will discuss corn oil, peanut oil, and olive oil.
Similar to butter, vegetable oils have been used since the agricultural ages.
The general differences between butter and vegetable oil are based on shelf life and culinary usage.
Shelf life
Butter has a shorter shelf life compared to vegetable oil.
Also, there is no requirement for refrigeration.
Culinary usage
They both have versatile usages. Vegetable oil can be used for salads, frying, and cooking. Butter can be used in cooking, frying, and spread for breakfast. Vegetable oil is more widely used in non-frying recipes such as making marinades.
Can you substitute butter for vegetable oil?
Definitely yes. You should substitute butter and vegetable oil with a 1:1 ratio. The butter should be melted before the substitution for a more accurate measurement.
Nutritional content comparison
Macronutrients
In contrast to vegetable oil, butter contains some amounts of water and protein. Vegetable oil is 100% fat. Check the infographic below to visualize the macronutrient distribution.
Macronutrient Comparison
Contains
more
FatsFats
+23.3%
Contains
more
ProteinProtein
+∞%
Contains
more
CarbsCarbs
+∞%
Contains
more
WaterWater
+∞%
Contains
more
OtherOther
+∞%
Calories
Vegetable oil contains higher calories than butter. They are both high in calories.
Carbs
They contain negligible amounts of carbs.
Glycemic index
The glycemic index of both is equal to 0.
Proteins
They contain negligible amounts of proteins.
Fats
Vegetable oil is 100% made of fats as a macronutrient. On the other hand, butter contains less fat, nearly 81g per 100g.
Vegetable oil contains mostly unsaturated fats, whereas butter contains mostly saturated fats.
Fat Type Comparison
Contains
less
Sat. FatSaturated fat
-71.5%
Contains
more
Mono. FatMonounsaturated fat
+105%
Contains
more
Poly. FatPolyunsaturated fat
+997.4%
Minerals
Vegetable oil is nearly devoid of minerals.
On the other hand, Butter contains more phosphorus and calcium; however, they are in very low amounts.
Below is the chart that displays the mineral distribution.
Mineral Comparison
Contains
more
IronIron
+550%
Contains
less
SodiumSodium
-100%
Contains
more
MagnesiumMagnesium
+∞%
Contains
more
CalciumCalcium
+∞%
Contains
more
PotassiumPotassium
+∞%
Contains
more
CopperCopper
+∞%
Contains
more
ZincZinc
+350%
Contains
more
PhosphorusPhosphorus
+∞%
Contains
more
ManganeseManganese
+∞%
Contains
more
SeleniumSelenium
+∞%
Vitamins
Vegetable oil is richer in vitamins K and E. Whereas butter is richer in vitamins B12 and A.
The vitamin distribution chart displays the vitamin profiles for each food.
Vitamin Comparison
Contains
more
Vitamin EVitamin E
+537.1%
Contains
more
Vitamin KVitamin K
+200%
Contains
more
Vitamin AVitamin A
+∞%
Contains
more
Vitamin B1Vitamin B1
+∞%
Contains
more
Vitamin B2Vitamin B2
+∞%
Contains
more
Vitamin B3Vitamin B3
+∞%
Contains
more
Vitamin B5Vitamin B5
+∞%
Contains
more
Vitamin B6Vitamin B6
+∞%
Contains
more
Vitamin B12Vitamin B12
+∞%
Contains
more
FolateFolate
+∞%
Health impacts
Keto diet
Both these foods can be used in the keto diet.
Vegan diet
Butter is a dairy product that cannot be consumed in the vegan diet. However, vegetable oil can be consumed.
Does butter have positive and negative effects on health?
Positive effects of butter
Conjugated linoleic acid in butter decreases body weight and reduces pro-inflammatory proteins and cytokines in the body (1) (2) (3).
Butyrate, which is found in butter, is also useful to the digestive tract, lowering symptoms and regulating IBS (irritable bowel syndrome) and Crohn's disease. Butyrate in butter has also been proven to reduce blood glucose levels and insulin intolerance positively (4) (5) (6).
Butter consumption in small to moderate amounts has beneficial effects. When consumed in small to moderate amounts, butter lowers the risk of obesity, cardiovascular disease, and stroke. When we ingest large amounts of butter, the same effects are reversed. We talk about excessive consumption in the section below (7) (8) (9).
Negative effects of butter
Daily use of butter has been associated with higher LDL levels, which raises the risk of cardiovascular disease (10). Because butter is abundant in calories, it will cause weight gain and other metabolic issues if consumed in an unregulated and unmoderated manner. As a result, it is critical to maintain your calorie consumption.
Does vegetable oil have positive and negative effects on health?
Positive effects of vegetable oil
Olive oil
Olive oil, used as an alternative to other vegetable oils, reduces cardiovascular disease risks. Even in the section below, we discuss other oils having negative effects on cardiovascular diseases (11).
Corn oil
Corn oil consumption is a good alternative to vegetable oils since it is a good source of polyunsaturated fatty acids (12).
Even so, corn oil decreases LDL levels more than olive oil (13).
Peanut oil
There is a slow increase in triglyceride levels and LDL levels with peanut oil consumption as there are lower risks of developing atherosclerosis than in seed oils (14).
Negative effects of vegetable oil
Most vegetable oils, specifically the ones derived from seeds, increase LDL levels in the blood, a marker for increased risks of atherosclerosis (15).
Overall, heating and frying with vegetable oils increase fat oxidation, and these oxidized fats can have adverse effects as it increases metabolic disorders (16).
Peanut oil
Peanut allergy can induce allergic and anaphylactic shocks.
Corn oil
High consumption of corn oil increases breast cancer cell proliferation (17).
Health impact summary
We can see that low to moderate butter consumption is beneficial for overall health. High consumption of butter is causing most problems. However, vegetable oil has its pros and cons, and it is versatile. It is essential to know which cooking process oil is better. In oils, we must keep LDL and triglyceride levels in control.
References
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/15795434/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/15674307/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/26968277/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4027835/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/16225487/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/19366864/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/22810464/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/16267503/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/19457271/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29511019/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/26148920/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/2258533/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/27677368/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/20546405/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6196963/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/26148922/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/26091908/
Infographic
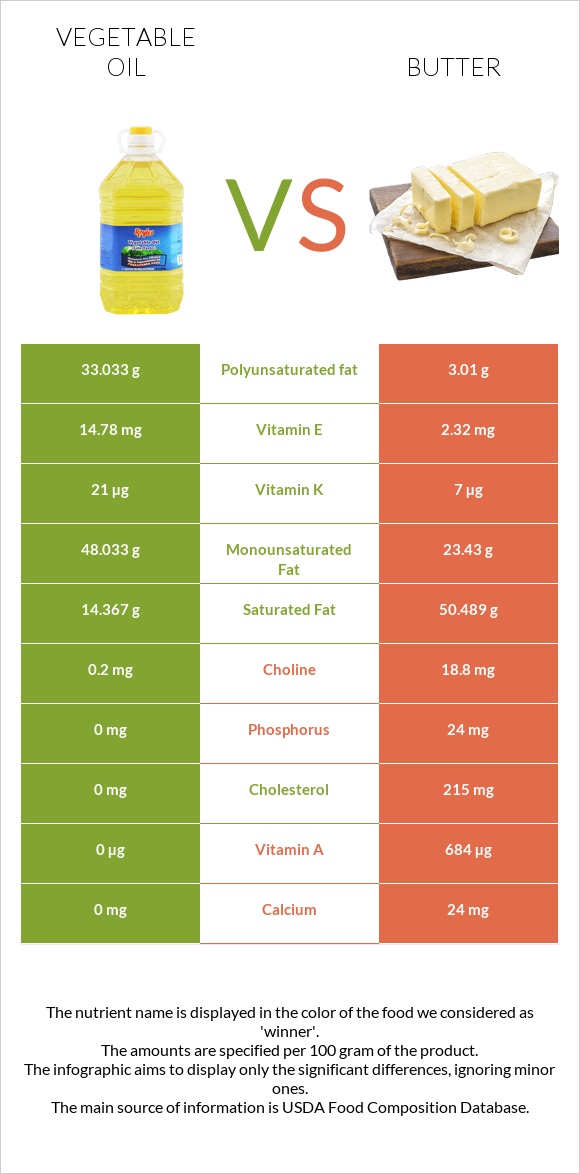
All nutrients comparison - raw data values
| Nutrient |  |
 |
DV% diff. |
| Polyunsaturated fat | 33.033g | 3.01g | 200% |
| Saturated fat | 14.367g | 50.489g | 164% |
| Vitamin E | 14.78mg | 2.32mg | 83% |
| Vitamin A | 0µg | 684µg | 76% |
| Cholesterol | 0mg | 215mg | 72% |
| Monounsaturated fat | 48.033g | 23.43g | 62% |
| Fats | 100g | 81.11g | 29% |
| Vitamin K | 21µg | 7µg | 12% |
| Calories | 884kcal | 717kcal | 8% |
| Vitamin B12 | 0µg | 0.17µg | 7% |
| Phosphorus | 0mg | 24mg | 3% |
| Vitamin B2 | 0mg | 0.034mg | 3% |
| Choline | 0.2mg | 18.8mg | 3% |
| Protein | 0g | 0.85g | 2% |
| Calcium | 0mg | 24mg | 2% |
| Copper | 0mg | 0.016mg | 2% |
| Selenium | 0µg | 1µg | 2% |
| Vitamin B5 | 0mg | 0.11mg | 2% |
| Potassium | 0mg | 24mg | 1% |
| Iron | 0.13mg | 0.02mg | 1% |
| Zinc | 0.02mg | 0.09mg | 1% |
| Folate | 0µg | 3µg | 1% |
| Net carbs | 0g | 0.06g | N/A |
| Carbs | 0g | 0.06g | 0% |
| Magnesium | 0mg | 2mg | 0% |
| Sugar | 0g | 0.06g | N/A |
| Sodium | 0mg | 11mg | 0% |
| Manganese | 0mg | 0.004mg | 0% |
| Vitamin B1 | 0mg | 0.005mg | 0% |
| Vitamin B3 | 0mg | 0.042mg | 0% |
| Vitamin B6 | 0mg | 0.003mg | 0% |
| Tryptophan | 0.012mg | 0% | |
| Threonine | 0.038mg | 0% | |
| Isoleucine | 0.051mg | 0% | |
| Leucine | 0.083mg | 0% | |
| Lysine | 0.067mg | 0% | |
| Methionine | 0.021mg | 0% | |
| Phenylalanine | 0.041mg | 0% | |
| Valine | 0.057mg | 0% | |
| Histidine | 0.023mg | 0% | |
| Omega-3 - ALA | 0.315g | N/A | |
| Omega-6 - Linoleic acid | 2.166g | N/A |
People also compare
References
All the values for which the sources are not specified explicitly are taken from FDA’s Food Central. The exact link to the food presented on this page can be found below.
- Vegetable oil - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/167737/nutrients
- Butter - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/173430/nutrients
All the Daily Values are presented for males aged 31-50, for 2000-calorie diets.






