Barley vs Oats - Health impact and Nutrition Comparison


Summary
Barley has a lower glycemic index and is lower in calories. It is richer in fibers, and vitamins B2, B3, and B6. On the other hand, oats are richer in phosphorus, zinc, copper, magnesium, iron, potassium, vitamins B1, B5, and folate. Oats are gluten-free.
Introduction
Barley is a grain that was first grown and harvested in Eurasia 10,000 years ago. Since people established and developed agricultural societies, it has become a component of their food cycle.
In this article, we are discussing barley which is hulled, also known as hulled barley. Hulled barley is a complete grain. It goes through a procedure of removing its inedible coating without removing the bran. There are several forms of barley, such as pearly barley, which is less nutritious since it has lost its bran. As a result, it is preferable to ingest hulled barley. The disadvantage of hulled barley is that it takes longer to cook.
The oat grain is a cereal grain that originated in the Near East and expanded to the Middle East and Europe. Oatmeal and rolled oats are the most common forms of processed oats. Oats grow best in temperate climates, and the nations with the most oat farming include Russia and Canada.
Oats are the source of many different meals, including rolled oats, oatmeal, oat flour, oat milk, and others. In addition to human use, oats are utilized in cattle feed.
Oats may also be used to make beverages. One of the most prominent uses for oats is to make oatmeal stout, a dark brew. Oats are used in the production of other alcoholic drinks, including whiskey.
In this article, we will discuss the difference between their general differences, nutritional content, weight loss and diet, and health impacts.
What are the actual differences?
Both these foods have general differences based on taste, shelf life, price, and culinary world usage.
Taste
Barley has a relatively sweeter taste than other cereal grains; in addition to that, it has a nutty flavor. It takes about 30 min to cook barley. On the other hand, oats are relatively bitter and earthy in flavor. They are also associated with fruits or chocolate that come in ready-made packages. Similarly to barley, it takes around 30 min to cook oats. It is important to note that crushed or other oats like oatmeal are quicker to prepare and don't require 30 minutes.
Shelf life
Both are cereal that, if properly kept in a dry and dark area within proper containers, can last for one year, even more.
Price
They have similar prices; in general, barley might be cheaper than oats; however, the difference is irrelevant.
Culinary world
Barley is a cereal grain like oats with a wide range of usages in the culinary world. Barley can be used in cooking, alcohol making. It can be used in stews, porridges, and even bread making. Oats have some common preparations, but one additional importance is that oats are gluten-free and can be used as an alternative to baking and cooking for people who suffer from gluten intolerance.
Nutritional content comparison
In this content comparison, we will discuss the difference between the nutritional content of both these foods according to 100g of each. It is also important that these amounts are for uncooked oats and barley.
Glycemic index
Barley has a lower glycemic index than oats. Barley is categorized as low glycemic index food, whereas oat is categorized as medium glycemic index food. Oat has double the glycemic index of barley.
Calories
Oats are higher in calories than barley, although it is important to mention that both are high calories.
Fibers
Both foods are rich in fibers. However, barley is richer in fibers and contains nearly 1.7 times more fibers than oats.
Protein
Oats contain more proteins than barley. The protein distribution is also high in both these foods. In the case of barley, gluten is the highest protein available, and in the case of oats, it is avenalin.
Fats
Oats contain higher amounts of fats than barley. They are nearly equally distributed among saturated, monounsaturated, and polyunsaturated fats. Nearly three times more fat is available in oats compared to barley.
Minerals
In this part, we are going to take into consideration 300g of each food when we are giving the % of each mineral concerning the recommended daily value.
Oats are richer in all types of minerals in comparison to barley, and oats satisfy more than 100% of the recommended daily value of the following minerals phosphorus, zinc, copper, magnesium, and iron. Oats are also richer in potassium. However, it is important to mention that barley also satisfies more than 100% of the recommended daily values of the following minerals, phosphorus, copper, and iron.
Below is a diagram that displays the comparative mineral profiles of both foods.
Mineral Comparison
Contains
more
PotassiumPotassium
+52.5%
Contains
more
CopperCopper
+59.1%
Contains
more
ZincZinc
+32.3%
Contains
less
SodiumSodium
-93.9%
Contains
more
SeleniumSelenium
+72%
Contains
more
MagnesiumMagnesium
+18.2%
Contains
more
CalciumCalcium
+627.3%
Contains
more
IronIron
+348.1%
Contains
more
PhosphorusPhosphorus
+42.6%
Contains
more
ManganeseManganese
+115.4%
Vitamins
Barley is richer in vitamins B2, B3, and B6. On the other hand, oats are richer in vitamins B1, B5, and folate.
Below is a diagram that displays the comparative vitamin profiles of both foods.
Vitamin Comparison
Contains
more
Vitamin KVitamin K
+100%
Contains
more
Vitamin AVitamin A
+∞%
Contains
more
Vitamin EVitamin E
+600%
Contains
more
Vitamin B1Vitamin B1
+213.3%
Contains
more
Vitamin B2Vitamin B2
+246.8%
Contains
more
Vitamin B3Vitamin B3
+46.6%
Contains
more
Vitamin B5Vitamin B5
+134.8%
Contains
more
Vitamin B6Vitamin B6
+152.2%
Contains
more
FolateFolate
+175%
Weight loss and diets
Barley provides a sensation of fullness due to its high fiber content. This means you may eat less and feel fuller, which might help you lose weight.
Gluten intolerance
The presence of gluten is one of the most significant distinctions between oat and barley. Barley's main protein composition is gluten, which gives it its adhesive and sticky properties during cooking processes. On the other hand, because oat does not contain gluten, it is a gluten-free alternative to barley. Because oat flour does not contain gluten, it is an excellent substitute for any flour which contains gluten. However, the gluten-free trait has an impact on the breadmaking process, for example, because gluten is one of the ingredients that hold the bread together and keeps it from crumbling and drying out.
Thus for gluten-free diets, oats labeled as “gluten-free” can be consumed, whereas barley cannot be consumed.
Vegan
Vegans are not restricted from eating oats or barley.
Vegans can use barley and oat milk as a substitute for dairy milk. Barely milk, like other non-dairy milk, is sweeter and often supplemented with vitamins and minerals.
Barley and oat milk are held alternative milk for vegans since it minimizes bloating, indigestion, and gas, except in the case of gluten intolerance, barley milk causes bloating and gas.
Keto
Barley and oats are high in carbs; thus, they are not part of the keto diet. However, oats can be used in making cookies which is a better alternative to wheat flour.
Barley diet
Some people have tried the barley diet, which mostly consists of barley porridges, and claims to have lost up to 4 kg in 7 days.
However, these diets are restricted and may result in malnutrition.
Lactose intolerance
Lactose-intolerant people can consume as an alternative to dairy milk which contains lactose, barley milk, or oat milk.
Baby food
Because it is high in fibers, minerals, and vitamins, it is advised for newborns. It is extremely versatile and may be made into a stew or consistently blended food with other nutritious foods like fruits.
In addition to that, oats are also recommended for babies as soon as they can eat solid foods.
Bodybuilding
Barley carbs are slowly absorbed in the body and do not cause a spike in insulin levels, and these are beneficial for the long release of carbohydrates. In addition to that, barley is richer in fibers which provide better gastrointestinal tract health and digestion. On the other hand, oats are also perfect to be consumed in bodybuilders' diets, and they are advised to be added into blends which are proteins and fruits, to make a well-balanced shake with a fluid consistency.
Health impacts
Cardiovascular health
To maintain a healthy diet, including whole-grain foods high in soluble or insoluble fibers is important. These foods can effectively lower blood pressure and aid in weight control (1.2).
Studies have shown that moderate and consistent consumption of barley can help lower LDL (bad cholesterol) levels in men and women with mild hypercholesterolemia, reducing the risk of cardiovascular disease (3).
Similarly, consuming oats has been linked to reduced serum cholesterol and blood sugar levels, which can help lower cardiovascular risk (4).
Diabetes
Long-term barley eating has resulted in lower blood glucose levels. This is mostly explained by the high fiber content of barley, which reduces glucose absorption. (5)
Consuming whole-grain cereals like oats and barley lowers the risk of developing type 2 diabetes. Furthermore, it regulates blood glucose and lipid levels. When compared to other cereal grains, oat-based diets have lower fatty acid absorption. (6)
Digestive tract
Barley consumption improves intestinal microbiota, which provides a wide range of benefits for overall well-being. (7)
Oat consumption has been associated with improved gut microbiota. (8)
Fiber-rich foods like barley and oats may be beneficial for constipation and colon diverticulosis treatment. (9)
Cancer
Barley grass extract has apoptotic functions on cancer cells. Although the grass is not part of the grain, it is important to mention such a feature. (10)
Oats include beta-glucans, which have anti-cancer capabilities against lung cancer cells. (11)
Celiac disease
Barley protein is mostly composed of gluten, which causes inflammation in celiac disease. As a result, it is critical for celiac disease patients not to ingest gluten. Barley should not be eaten by celiac disease patients. (12)
References
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/16963350/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/36435335/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/15531664/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/7840076/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4311281/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32641435/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4616929/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31638148/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/15471177/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5449973/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/28756506/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6647104/
Infographic
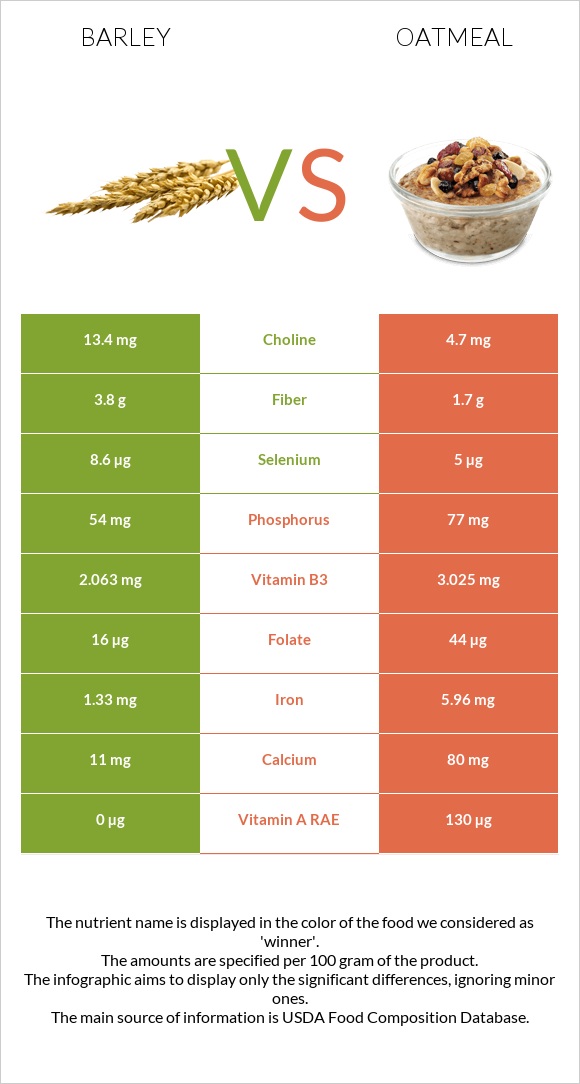
All nutrients comparison - raw data values
| Nutrient |  |
 |
DV% diff. |
| Iron | 1.33mg | 5.96mg | 58% |
| Vitamin B1 | 0.083mg | 0.26mg | 15% |
| Vitamin A | 0µg | 130µg | 14% |
| Manganese | 0.259mg | 0.558mg | 13% |
| Vitamin B6 | 0.115mg | 0.29mg | 13% |
| Vitamin B2 | 0.062mg | 0.215mg | 12% |
| Fiber | 3.8g | 1.7g | 8% |
| Calcium | 11mg | 80mg | 7% |
| Selenium | 8.6µg | 5µg | 7% |
| Folate | 16µg | 44µg | 7% |
| Carbs | 28.22g | 11.67g | 6% |
| Vitamin B3 | 2.063mg | 3.025mg | 6% |
| Copper | 0.105mg | 0.066mg | 4% |
| Starch | 10.37g | 4% | |
| Vitamin B5 | 0.135mg | 0.317mg | 4% |
| Calories | 123kcal | 68kcal | 3% |
| Phosphorus | 54mg | 77mg | 3% |
| Zinc | 0.82mg | 0.62mg | 2% |
| Sodium | 3mg | 49mg | 2% |
| Choline | 13.4mg | 4.7mg | 2% |
| Fats | 0.44g | 1.36g | 1% |
| Magnesium | 22mg | 26mg | 1% |
| Potassium | 93mg | 61mg | 1% |
| Saturated fat | 0.093g | 0.226g | 1% |
| Monounsaturated fat | 0.057g | 0.391g | 1% |
| Polyunsaturated fat | 0.214g | 0.426g | 1% |
| Protein | 2.26g | 2.37g | 0% |
| Net carbs | 24.42g | 9.97g | N/A |
| Sugar | 0.28g | 0.46g | N/A |
| Vitamin E | 0.01mg | 0.07mg | 0% |
| Vitamin K | 0.8µg | 0.4µg | 0% |
| Trans fat | 0.003g | N/A | |
| Tryptophan | 0.038mg | 0.04mg | 0% |
| Threonine | 0.077mg | 0.083mg | 0% |
| Isoleucine | 0.083mg | 0.105mg | 0% |
| Leucine | 0.154mg | 0.2mg | 0% |
| Lysine | 0.084mg | 0.135mg | 0% |
| Methionine | 0.043mg | 0.04mg | 0% |
| Phenylalanine | 0.127mg | 0.13mg | 0% |
| Valine | 0.111mg | 0.151mg | 0% |
| Histidine | 0.051mg | 0.057mg | 0% |
Macronutrient Comparison
| Contains more CarbsCarbs | +141.8% |
| Contains more FatsFats | +209.1% |
| Contains more WaterWater | +22.1% |
| Contains more OtherOther | +103.6% |
Fat Type Comparison
| Contains less Sat. FatSaturated fat | -58.8% |
| Contains more Mono. FatMonounsaturated fat | +586% |
| Contains more Poly. FatPolyunsaturated fat | +99.1% |
People also compare
References
All the values for which the sources are not specified explicitly are taken from FDA’s Food Central. The exact link to the food presented on this page can be found below.
- Barley - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/170285/nutrients
- Oatmeal - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/171662/nutrients
All the Daily Values are presented for males aged 31-50, for 2000-calorie diets.






