Bratwurst vs. Italian sausage — Health Impact and Nutrition Comparison


Summary
Bratwursts contain more Vitamin B12, Vitamin B5 and B2, potassium, zinc, and lower saturated fats. On the other hand, Italian sausages have more Vitamin C, Vitamin B1, and B6, iron, and calcium; they are also lower in cholesterol and sugar.
Table of contents
Introduction
The reality is that we all love sausage. All sausages are from the same family, so how can we prefer one? This article compares Italian sausage and bratwurst, their nutritional values, and their impact on our health.
What’s The Actual Difference?
All sausages are meat products from beef, pork, or chicken mixed with spices and salt. It is also essential to distinguish between cured sausage, smoked sausage, and fresh sausage.
Bratwursts are a type of German sausage which are made with pork or beef. Italian sausages are a type of pork sausage.
The most significant difference between Italian sausages and bratwursts is that Italian sausages are commonly referred to as a style of pork sausage. Besides, they also differ from each other in spices. Particularly, Italian sausages are often noted for flavoring with fennel seed.
Production
Weighing the meat and spice ingredients is one of the essential steps in preparing good sausages. The meat of Italian sausage is mixed with a curing solution to improve the taste and increase the shelf life. Salt is essential for making the meat easier to handle and for making it taste good.
Usually, the bratwurst meat is crushed, salted, seasoned with spices, and pressed into the intestines as a shell; then, they hang it in a meat cellar to keep it cool.
Nutrition
At the bottom of this page, you can find a nutritional table that visually shows the differences between bratwurst and Italian sausages. The food varieties used in this article are bratwurst, beef, pork, smoked and Sausage, Italian, and raw.
Macronutrients
Italian sausages contain more fats, more protein, and less cholesterol. On the other hand, bratwursts contain more water. Both products have no fiber and sugars.
Macronutrient Comparison
Contains
more
WaterWater
+20.2%
Contains
more
OtherOther
+29.5%
Contains
more
ProteinProtein
+56.7%
Contains
more
CarbsCarbs
+113.5%
Fats
Italian sausages contain three times more polyunsaturated fat than bratwurst. They contain 3.6g of polyunsaturated fat, while bratwursts contain 1.58g. On the other hand, bratwursts are 4g lower in saturated fats.
Fat Type Comparison
Contains
less
Sat. FatSaturated fat
-40.4%
Contains
more
Mono. FatMonounsaturated fat
+113.9%
Contains
more
Poly. FatPolyunsaturated fat
+122.7%
Calories
The number of calories in Italian sausages is slightly higher than in bratwurst. They contain 344 calories per 100g, whereas bratwursts contain 297 calories per 100g.
It is important to note that both products are considered high-calorie food.
Minerals
Let’s have a look at the mineral content of these products.
Italian sausages have more iron and calcium than brats.
The level of sodium is 13.8% less in Italian sausages. Bratwursts and Italian sausages are equal in potassium, copper, and zinc.
Mineral Comparison
Contains
more
ManganeseManganese
+∞%
Contains
more
MagnesiumMagnesium
+20%
Contains
more
CalciumCalcium
+200%
Contains
more
IronIron
+43%
Contains
more
PhosphorusPhosphorus
+30.8%
Contains
less
SodiumSodium
-12.4%
Contains
more
SeleniumSelenium
+56%
Vitamins
Generally, bratwursts contain significantly higher concentrations of Vitamin B12. Moreover, bratwurst covers your daily need for Vitamin B12.
On the other hand, Italian sausages are higher in Folate, Vitamin C, Vitamin B6, and Vitamin B1.
These products have an equal level of Vitamin B2.
Bratwursts and Italian sausages lack Vitamin E, Vitamin A, Vitamin K, and Vitamin D.
Vitamin Comparison
Contains
more
Vitamin B5Vitamin B5
+∞%
Contains
more
Vitamin B12Vitamin B12
+105.4%
Contains
more
Vitamin CVitamin C
+∞%
Contains
more
Vitamin AVitamin A
+∞%
Contains
more
Vitamin B1Vitamin B1
+63.9%
Contains
more
Vitamin B3Vitamin B3
+33.9%
Contains
more
Vitamin B6Vitamin B6
+65%
Contains
more
FolateFolate
+25%
Glycemic Index
The glycemic index of a food is a value based on how quickly a food can cause an increase in blood glucose levels. The glycemic index of bratwursts and sausages is equal; it is 28. Both are considered low glycemic index foods.
Acidity
The acidity level of bratwursts is about 4.4, while Italian sausages have an acidity level equal to 6.3. Both are acidic.
Health Benefits
Benefits of Eating Red Meat
Red meat is rich in iron and easily absorbed by our bodies. Besides, red meat provides protein that can help build bones and muscles. Red meat is also a good source of Vitamin B12, which helps to keep nerve and red blood cells healthy, and zinc, which keeps the immune system working correctly. In addition, bratwurst may cover the daily intake of Vitamin B12. For adults it is 2.4 micrograms, and bratwurst contains 2.67 mg of Vitamin B12 per 100 g (1).
Other Health Benefits
Italian sausages and bratwursts offer several essential nutrients beneficial for the body. They both are good sources of protein. 100 g of each of these products contains 12-14 g protein, 12% of the daily recommended intake for adults. Protein is a critical nutrient that helps to develop and repair strong muscles. Also, it helps reduce muscle mass loss that often occurs with age (2).
Ketogenic (Keto) Diet
The ketogenic diet is a high-fat and low-carb diet. This diet includes foods with high protein. Eating meat during this diet, including fatty meats such as pork and beef, is recommended. Bratwursts contain fewer carbs than Italian sausages and are a good source of protein. Italian sausages are more affluent in fats. If you’re on this diet, combine these products with a natural source of healthy fats (3).
Side Effects
Italian sausages and bratwursts are rich in several vitamins and minerals but are also rich in sodium and saturated fats. That means daily consumption of these products can harm your health. This section of the article will discuss the side effects of Italian sausages and bratwursts.
Cardiovascular Health
Both Italian sausage and bratwurst are generally not considered heart-healthy choices due to their high saturated fat and sodium content. However, comparing the two, bratwurst tends to have a slightly lower saturated fat content compared to Italian sausage, but the difference may not be significant enough to make one markedly better than the other in terms of cardiovascular health (4).
It should be noted that the daily recommended intake of sodium is 2.3 g. In particular, too much sodium can be bad for your health. Studies show that sodium intake can increase the risk of high blood pressure, a significant cause of heart disease (5).
For a heart-healthy diet, it's generally recommended to choose leaner protein sources such as skinless poultry, fish, legumes, and tofu. If you're craving sausage, consider looking for lower-fat varieties or consuming them in moderation as part of a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and healthy fats. Additionally, preparing them by grilling, baking, or broiling instead of frying can help reduce their overall fat content.
Diabetes
Research shows a link between eating red meat, mainly processed meats, and type 2 diabetes due to its high heme iron content.
One study shows that women who often eat red meat have an almost one-third higher risk of developing type 2 diabetes than women who eat less red meat (6).
Red Meat Allergy
Red meat allergy is a common allergy type, including any age group and race. People can have an allergic reaction to red meat if they are sensitive to cat serum albumin that cross-reacts with albumin in pork. Also, those who are allergic to alpha-gal should avoid all meat types.
Symptoms of red meat allergy include urticaria, vomiting, stomach cramps, and, in rare cases, anaphylaxis. Usually, these symptoms last three to six hours after eating red meat (8).
Herb Allergy
Allergies to spices and herbs usually include:
- Local reactions in the mouth.
- Causing itchy mucous membranes.
- Swelling of the lips and tongue.
Italian sausages are flavored with fennel seed, which can cause an allergic reaction. Common symptoms include dizziness, hives, and throat swelling (8).
References
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/20374748/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/26643369/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31805451/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/20089734/
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0033062006000831
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30229313/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6488443/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/18873139/
Infographic
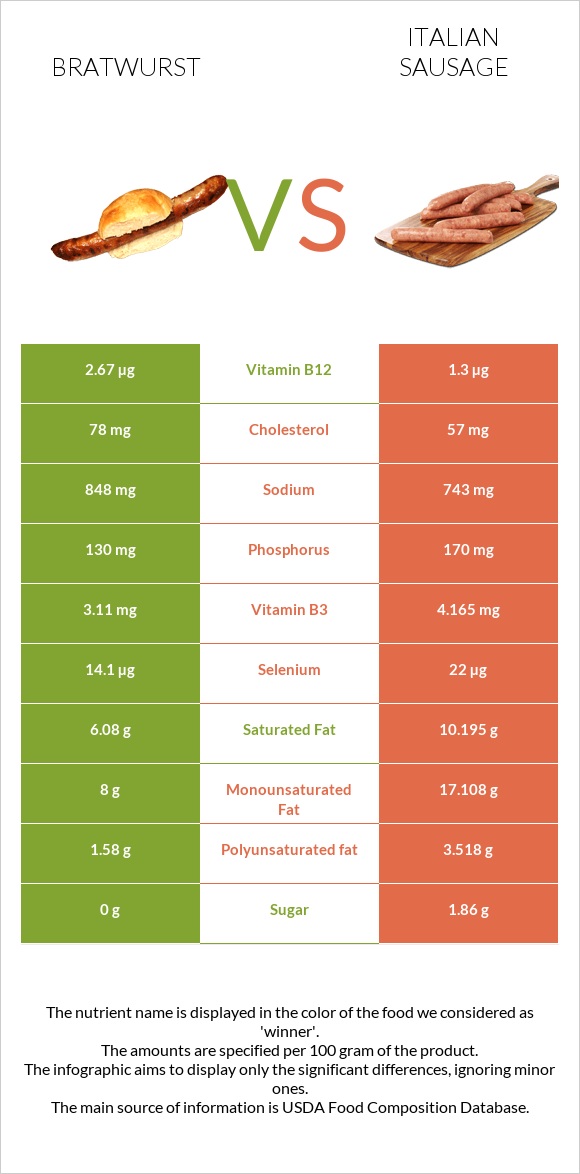
All nutrients comparison - raw data values
| Nutrient |  |
 |
DV% diff. |
| Vitamin B12 | 2.67µg | 1.3µg | 57% |
| Monounsaturated fat | 8g | 17.108g | 23% |
| Vitamin B1 | 0.38mg | 0.623mg | 20% |
| Saturated fat | 6.08g | 10.195g | 19% |
| Protein | 12.2g | 19.12g | 14% |
| Selenium | 14.1µg | 22µg | 14% |
| Vitamin B5 | 0.69mg | 14% | |
| Choline | 78.2mg | 14% | |
| Polyunsaturated fat | 1.58g | 3.518g | 13% |
| Vitamin B6 | 0.2mg | 0.33mg | 10% |
| Cholesterol | 78mg | 57mg | 7% |
| Vitamin B3 | 3.11mg | 4.165mg | 7% |
| Phosphorus | 130mg | 170mg | 6% |
| Vitamin D | 41 IU | 5% | |
| Iron | 1mg | 1.43mg | 5% |
| Sodium | 848mg | 743mg | 5% |
| Vitamin D | 1µg | 5% | |
| Vitamin K | 3.4µg | 3% | |
| Calories | 297kcal | 344kcal | 2% |
| Vitamin E | 0.25mg | 2% | |
| Manganese | 0.041mg | 2% | |
| Vitamin B2 | 0.213mg | 0.233mg | 2% |
| Fats | 26.34g | 27.31g | 1% |
| Carbs | 2g | 4.27g | 1% |
| Magnesium | 15mg | 18mg | 1% |
| Calcium | 7mg | 21mg | 1% |
| Potassium | 283mg | 304mg | 1% |
| Zinc | 2.47mg | 2.39mg | 1% |
| Vitamin A | 0µg | 10µg | 1% |
| Vitamin C | 0mg | 0.1mg | 0% |
| Net carbs | 2g | 4.17g | N/A |
| Sugar | 0g | 1.86g | N/A |
| Fiber | 0g | 0.1g | 0% |
| Copper | 0.08mg | 0.08mg | 0% |
| Folate | 4µg | 5µg | 0% |
| Tryptophan | 0.107mg | 0.161mg | 0% |
| Threonine | 0.465mg | 0.792mg | 0% |
| Isoleucine | 0.485mg | 0.731mg | 0% |
| Leucine | 0.81mg | 1.343mg | 0% |
| Lysine | 0.903mg | 1.522mg | 0% |
| Methionine | 0.364mg | 0.486mg | 0% |
| Phenylalanine | 0.405mg | 0.67mg | 0% |
| Valine | 0.464mg | 0.804mg | 0% |
| Histidine | 0.395mg | 0.577mg | 0% |
People also compare
References
All the values for which the sources are not specified explicitly are taken from FDA’s Food Central. The exact link to the food presented on this page can be found below.
- Bratwurst - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/172956/nutrients
- Italian sausage - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/174586/nutrients
All the Daily Values are presented for males aged 31-50, for 2000-calorie diets.




