Buckwheat vs. Bulgur - Health Impact and Nutrition Comparison


Summary
Buckwheat is richer in copper, phosphorus, and magnesium. In comparison, bulgur is lower in carbs and richer in fiber, vitamin B1, manganese, and iron. Bulgur has a lower glycemic index. Since buckwheat is a whole grain compared to bulgur, it has more health benefits.
Introduction
This text compares two types of cereal grains, buckwheat and bulgur. We will dive deep into their nutritional content and health impacts.
It is important to know which type of cereal grain is healthier and most beneficial when it comes to comparing buckwheat and bulgur.
We will get an answer by going through their nutritional content and checking health impacts.
Nutrition
This section will compare 100g of buckwheat and bulgur in cooked forms.
Calories
The amount of calories is similar for both. Buckwheat has slightly higher calories.
Carbohydrates
Buckwheat is higher in net carbs compared to bulgur. Buckwheat contains 17.2g of net carbs, whereas bulgur contains 14g of net carbs.
However, their total carb content is similar.
Fiber
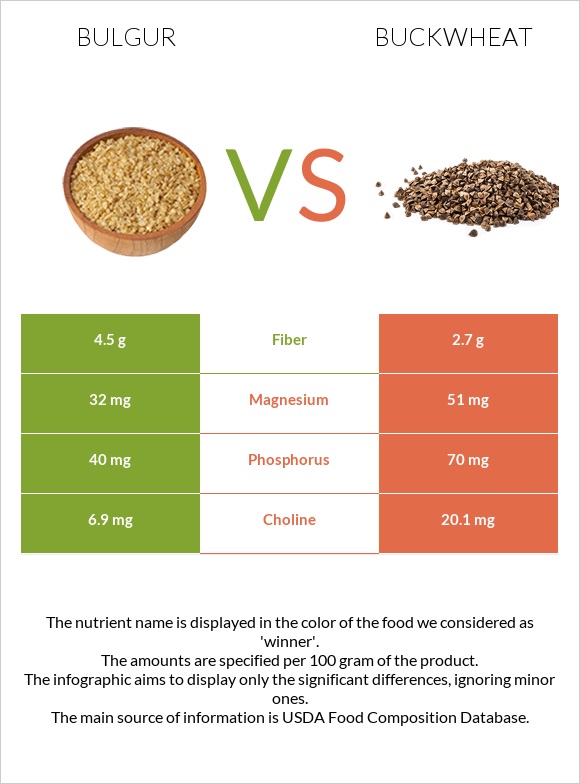
Bulgur is richer in fiber than buckwheat. The difference is quite significant when it comes to fiber.
Bulgur contains 4.5g of fiber, whereas buckwheat contains 2.7g.
This will show a positive impact on the health section for bulgur.
Glycemic Index
Bulgur has a lower glycemic index than buckwheat.
For the glycemic index of buckwheat and bulgur, you can check these links.
Bulgur has a glycemic index 47, and buckwheat has a glycemic index 51.
Fat
The amount of fat in both is insignificant.
Protein
The amount of protein is similar in both.
Macronutrient Comparison
Contains
more
FatsFats
+158.3%
Contains
more
OtherOther
+26.5%
Minerals
Buckwheat is richer in copper, phosphorus, and magnesium. In comparison, bulgur is richer in manganese and iron.
Mineral Comparison
Contains
more
CalciumCalcium
+42.9%
Contains
more
IronIron
+20%
Contains
more
ManganeseManganese
+51.1%
Contains
more
MagnesiumMagnesium
+59.4%
Contains
more
PotassiumPotassium
+29.4%
Contains
more
CopperCopper
+94.7%
Contains
more
PhosphorusPhosphorus
+75%
Contains
less
SodiumSodium
-20%
Contains
more
SeleniumSelenium
+266.7%
Vitamins
Their vitamin profiles are not that significant. They have similar amounts of the vitamin B complex. A slight difference is seen in vitamin B1 thiamine, which is higher in bulgur. Buckwheat is also slightly higher in vitamin K.
Vitamin Comparison
Contains
more
Vitamin B1Vitamin B1
+42.5%
Contains
more
FolateFolate
+28.6%
Contains
more
Vitamin EVitamin E
+800%
Contains
more
Vitamin B2Vitamin B2
+39.3%
Contains
more
Vitamin KVitamin K
+280%
You can also read about rice vs. buckwheat.
Health Impacts
Bulgur is more commonly consumed than buckwheat, but it's important to understand the health impacts of each since they are one of the most commonly used cereal grains out there.
Here, we will get an answer to which one is healthier: bulgur or buckwheat. That answer can be relative aswell, depending on the variables we are considering.
Is Bulgur or Buckwheat Healthier for Diabetes?
The lower the glycemic index of a certain food, the better it is for glycemic control and diabetes. In this case, bulgur has a lower glycemic index than buckwheat. However, it is important to remember that the more you process wheat and bulgur, the higher the glycemic index it can get.
Low glycemic index foods are best for blood sugar level control.
However, there is also an association between the consumption of unprocessed whole grains and a lower risk of diabetes aswell. In this case, buckwheat is a good option to include in diabetes or prediabetes.
Overall, whole grain is associated with lower HbA1c, HOMA-IR, and fasting blood glucose levels (1)(2)(3).
In moderation, both can be consumed. It is preferable to go for buckwheat since it is a whole grain, even though bulgur has a lower glycemic index, but that difference is very narrow.
Digestive Health
One of the most beneficial impacts on healthy digestive health is dietary fiber.
In this case, Bulgur is richer in fiber and can reduce risks of colorectal cancer, diverticular disease, and constipation (4).
Adding bulgur to a salad, such as tabbouleh, is a healthy choice.
Cardiovascular Health
Buckwheat contains polyphenols, quercetin, and rutin, which have been found to lower total cholesterol and triglyceride levels in the blood. However, further research is required to validate this claim conclusively. Generally, buckwheat is considered to have a neutral or positive impact on cardiovascular health (5, 6).
Elevate your heart health by incorporating bulgur into your diet. Studies show that consuming high-fiber foods like bulgur can significantly reduce the risk of cardiovascular disease. Make a positive impact on your well-being by choosing the right foods (7, 8).
You can also read about buckwheat vs. quinoa.
Gluten
Gluten is negatively spoken about in mainstream social media; however, that’s an exaggeration. You should avoid gluten if you have celiac disease and gluten intolerance. Both these should be medically diagnosed.
If you have celiac disease, buckwheat is considered safe since it is gluten-free. However, bulgur contains gluten.
The concept of grains being inflammatory, especially when it comes to buckwheat as a whole grain, we can say that it is misleading. Buckwheat is not an inflammatory food. The same goes for bulgur.
For individuals without celiac disease, bulgur is not inflammatory.
General Differences
Classification and Consumption
Buckwheat is considered a pseudocereal, and bulgur is a grain since it's derived from wheat.
Bulgur is commonly consumed in Mediterranean and Middle Eastern cuisine and used in salads and soups.
In comparison, buckwheat is commonly used in eastern Europe and western Asia.
Bulgur is often used instead of rice in stuffing. In comparison, buckwheat is often used as a side dish instead of rice in eastern Europe and western Asia.
Buckwheat flour is also used instead of wheat flour.
You can read about bulgur vs. bran.
Taste and Texture
Buckwheat groats have a nutty flavor, whereas bulgur has a wheat-like taste and not a nutty taste. Their texture, when cooked, is somehow similar.
You can also read about bulgur vs. couscous.
References
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7341349/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC1952203/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31374573/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/19335713/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5986499/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8747956/
- https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/pdf/10.1080/10408399009527518
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29237548/
Infographic
All nutrients comparison - raw data values
| Nutrient |  |
 |
DV% diff. |
| Manganese | 0.609mg | 0.403mg | 9% |
| Copper | 0.075mg | 0.146mg | 8% |
| Fiber | 4.5g | 2.7g | 7% |
| Magnesium | 32mg | 51mg | 5% |
| Phosphorus | 40mg | 70mg | 4% |
| Selenium | 0.6µg | 2.2µg | 3% |
| Iron | 0.96mg | 0.8mg | 2% |
| Choline | 6.9mg | 20.1mg | 2% |
| Protein | 3.08g | 3.38g | 1% |
| Fats | 0.24g | 0.62g | 1% |
| Potassium | 68mg | 88mg | 1% |
| Vitamin E | 0.01mg | 0.09mg | 1% |
| Vitamin B1 | 0.057mg | 0.04mg | 1% |
| Vitamin B2 | 0.028mg | 0.039mg | 1% |
| Vitamin K | 0.5µg | 1.9µg | 1% |
| Folate | 18µg | 14µg | 1% |
| Polyunsaturated fat | 0.098g | 0.188g | 1% |
| Calories | 83kcal | 92kcal | 0% |
| Net carbs | 14.08g | 17.24g | N/A |
| Carbs | 18.58g | 19.94g | 0% |
| Calcium | 10mg | 7mg | 0% |
| Sugar | 0.1g | 0.9g | N/A |
| Zinc | 0.57mg | 0.61mg | 0% |
| Sodium | 5mg | 4mg | 0% |
| Vitamin B3 | 1mg | 0.94mg | 0% |
| Vitamin B5 | 0.344mg | 0.359mg | 0% |
| Vitamin B6 | 0.083mg | 0.077mg | 0% |
| Saturated fat | 0.042g | 0.134g | 0% |
| Monounsaturated fat | 0.031g | 0.188g | 0% |
| Tryptophan | 0.048mg | 0.049mg | 0% |
| Threonine | 0.089mg | 0.129mg | 0% |
| Isoleucine | 0.114mg | 0.127mg | 0% |
| Leucine | 0.208mg | 0.212mg | 0% |
| Lysine | 0.085mg | 0.172mg | 0% |
| Methionine | 0.048mg | 0.044mg | 0% |
| Phenylalanine | 0.145mg | 0.133mg | 0% |
| Valine | 0.139mg | 0.173mg | 0% |
| Histidine | 0.071mg | 0.079mg | 0% |
| Fructose | 0.1g | 0% |
Fat Type Comparison
| Contains less Sat. FatSaturated fat | -68.7% |
| Contains more Mono. FatMonounsaturated fat | +506.5% |
| Contains more Poly. FatPolyunsaturated fat | +91.8% |
People also compare
References
All the values for which the sources are not specified explicitly are taken from FDA’s Food Central. The exact link to the food presented on this page can be found below.
- Bulgur - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/170287/nutrients
- Buckwheat - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/170686/nutrients
All the Daily Values are presented for males aged 31-50, for 2000-calorie diets.






