Butter vs. Coconut milk — Health Impact and Nutrition Comparison


Summary
Coconut milk surpasses butter in essential minerals such as manganese, copper, iron, phosphorus, selenium, and fiber. It offers a nutrient-rich alternative with notable amounts of these minerals and dietary fiber. Conversely, butter provides higher levels of vitamins A and E. However, it's crucial to note that while butter excels in these vitamins, it covers the daily need for saturated fat by 147% more than coconut milk. In terms of saturated fat content, coconut milk proves to be a lower-fat option.
Introduction
Coconut milk is made from the shredded flesh of mature coconuts, while butter is a dairy product made from churning cream or milk. This article will compare the two, focusing on nutrition and its influence on health.
Nutrition
The infographics below are presented for 100g servings of butter without salt and raw coconut milk, expressed from grated meat and water. However, the average serving size of these foods per person is one tablespoon, or 15g, for coconut milk and one tablespoon, or 14.2 g, for butter.
Macronutrients and Calories
Butter and coconut milk significantly differ in their macronutrient contents. Butter is much denser in nutrients, consisting of 18% water and 82% nutrients, while coconut milk comprises 68% water and 32% nutrients.
The primary macronutrient of both foods is fat, making up 81% of the total mass in butter and 24% in coconut milk.
Macronutrient Comparison
Contains
more
FatsFats
+240.2%
Contains
more
ProteinProtein
+169.4%
Contains
more
CarbsCarbs
+9133.3%
Contains
more
WaterWater
+276.9%
Contains
more
OtherOther
+1675%
Calories
While both are high-calorie foods, butter is considerably higher in calories, containing 484 more calories in a 100-gram serving.
A 100-gram serving of butter provides 717 calories, while this number for coconut milk is 230.
Protein
Coconut milk is about 2.6 times richer in protein. Protein content in coconut milk is 2.29 grams per 100 grams, while it is only 0.85 grams in butter. Both foods contain some levels of essential amino acids; however, coconut milk is richer.
Fats
Conversely, butter is 3.4 times higher in fat than coconut milk.
The fat content of coconut milk consists almost entirely of saturated fats, whereas butter fat content comprises 66% saturated, 30% monounsaturated, and 4% polyunsaturated.
Thus, both are higher in saturated fats but lower in unsaturated fats.
Compared to coconut milk, butter contains more omega-6 (linoleic acid) and omega-3 (ALA) fatty acids per serving (2.166g and 0.320g, respectively). In contrast, coconut milk has a lower omega-6 content of 0.261g; no omega-3 content is specified (1).
Fat Type Comparison
Contains
more
Mono. FatMonounsaturated fat
+2210.7%
Contains
more
Poly. FatPolyunsaturated fat
+1053.3%
Contains
less
Sat. FatSaturated fat
-58.1%
Carbohydrates
A 100-gram serving of butter provides 0.06g of carbohydrates, while the same serving size of coconut milk has 5.54g.
While butter lacks dietary fiber, coconut milk provides 2.2g of fiber per 100g serving. However, while 100% of the carbs in butter are net carbs, this number is only 60% for coconut milk. The other 40% of coconut milk carbohydrates are dietary fiber.
Vitamins
Coconut milk and butter are good sources of various vitamins. Coconut is 18 times more decadent in vitamin B3, 11 times richer in vitamin B6, five times richer in vitamin B1 and folate, and almost richer in vitamin C (2.8 mg) and vitamin B5.
Butter contains vitamins in which coconut milk is absent, such as vitamins A, B2, and B12.
That said, butter contains nearly 15 times more vitamin E and vitamin K.
Vitamin Comparison
Contains
more
Vitamin AVitamin A
+∞%
Contains
more
Vitamin EVitamin E
+1446.7%
Contains
more
Vitamin B2Vitamin B2
+∞%
Contains
more
Vitamin B12Vitamin B12
+∞%
Contains
more
Vitamin KVitamin K
+6900%
Contains
more
Vitamin CVitamin C
+∞%
Contains
more
Vitamin B1Vitamin B1
+420%
Contains
more
Vitamin B3Vitamin B3
+1709.5%
Contains
more
Vitamin B5Vitamin B5
+66.4%
Contains
more
Vitamin B6Vitamin B6
+1000%
Contains
more
FolateFolate
+433.3%
Minerals
Coconut milk is richer in minerals than butter. Coconut milk is 229 times richer in manganese, 82 times richer in iron, 16 times richer in copper, 18 times richer in magnesium, 10 times richer in potassium, seven times richer in zinc, six times richer in selenium, and almost four times richer in phosphorus. At the same time, butter provides 1.5 times more calcium. Coconut milk also contains more sodium.
Mineral Comparison
Contains
more
CalciumCalcium
+50%
Contains
less
SodiumSodium
-26.7%
Contains
more
MagnesiumMagnesium
+1750%
Contains
more
PotassiumPotassium
+995.8%
Contains
more
IronIron
+8100%
Contains
more
CopperCopper
+1562.5%
Contains
more
ZincZinc
+644.4%
Contains
more
PhosphorusPhosphorus
+316.7%
Contains
more
ManganeseManganese
+22800%
Contains
more
SeleniumSelenium
+520%
Glycemic Index
Butter has a low glycemic index of 0. Coconut milk has a glycemic index of 97, which is significantly higher than predicted.
The glycemic load of coconut milk is rated at 5, meaning one serving raises glucose levels slowly. Visit our website to learn more about coconut milk's glycemic impact.
Acidity
The comparison of acidity levels based on potential renal acid load (PRAL) reveals that coconut milk is slightly alkaline, with a value of -1.9. At the same time, butter has a slightly acidic nature with a PRAL value of 0.4.
Weight Loss & Diets
Butter stands as a preferred choice in ketogenic diets due to its high fat content and low carbohydrates, aligning well with the macronutrient profile required for inducing ketosis. However, moderation is vital, as excessive saturated fat intake may pose potential health risks. On the contrary, butter may not be suitable for low-fat diets, given its concentrated fat content. For individuals seeking plant-based or vegan alternatives, butter is not ideal, as it is an animal-derived product. In contrast, coconut milk is a favorable option for low-carb and low-calorie diets, providing a lighter alternative with a distinct flavor profile. While not a strict fit for ketogenic diets due to its moderate carbohydrate content, coconut milk excels in vegan and plant-based diets.
Health Benefits
Cardiovascular Health
Coconut milk, known for its high saturated fat content, has been studied for cholesterol levels. Some research suggests potential benefits, indicating that coconut milk may lower "bad" LDL cholesterol and increase "good" HDL cholesterol. Lauric acid, a primary fatty acid in coconut fat, has shown mixed effects on LDL cholesterol levels in different studies, and its impact may vary among individuals.
On the other hand, butter, a high-fat dairy product, has also been scrutinized in the context of saturated fat and heart health (2, 3). There's a link between saturated fat intake and high LDL cholesterol levels, a risk factor for heart disease (4). However, controversies persist, with some studies failing to establish a clear connection between saturated fat intake and heart disease (5, 6, 7). Some observational studies even suggest potential benefits for heart health associated with high-fat dairy product consumption (8, 9).
Diabetes
Butter has been associated with increased insulin response and elevated concentrations of fatty acids and triacylglycerols (10). In contrast, virgin and filtered coconut oils, coconut water, and coconut milk have significantly reversed these parameters in diabetic rats. Additionally, consuming these coconut products demonstrated a preventive effect on diabetes-induced histopathological changes in kidney tissue (11). This suggests that while butter may potentially exacerbate certain aspects of diabetes, coconut products, including coconut milk, seem to exhibit positive effects, potentially mitigating diabetes-related markers and providing protective effects on organ tissues.
Inflammation
The saturated fats in butter contain approximately 11% short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs), with butyric acid being the most common. Butyric acid is a distinctive component found in the milk fat of ruminant animals like cattle, sheep, and goats. In contrast, coconut milk, derived from coconuts, has been studied for its potential anti-inflammatory effects (12, 13). In animal studies, coconut oil and extract reduce inflammation and swelling in injured rats and mice (14).
The contrasting sources of these saturated fats highlight the unique butter and coconut milk components. While butter's SCFAs, particularly butyric acid, have been associated with certain benefits, such as butyrate's potential to reduce inflammation in the digestive system, coconut milk, with its distinct composition, showcases anti-inflammatory properties in animal studies (15, 16).
Cancer
There is conjugated linoleic acid (CLA) in butter and coconut milk, a fatty acid associated with anti-cancer properties and the potential to lower body fat percentage (17, 18, 19). Studies suggest that lauric acid in butter and coconut milk may induce apoptosis in breast and endometrial cancer cells (20).
Downsides and Risks
Though low in lactose, butter contains enough allergenic whey proteins to trigger reactions in individuals with milk allergies (21). On the other hand, coconut milk is generally safe for those without coconut allergies, but experts advise individuals with FODMAP intolerance to limit their intake (22). In addition, some canned coconut milk varieties may contain bisphenol A (BPA), a cancer-causing chemical (23, 24, 25). To mitigate risks, BPA-free packaging is recommended when consuming canned coconut milk.
Production
Butter production traditionally involves separating cream from milk, with cream rising to the surface due to the lighter nature of fat. Centrifugation, a modern and efficient method, is commonly employed for cream separation. The ensuing step is churning, where the cream is vigorously shaken until the milk fat coalesces into butter and separates from the buttermilk. The final product undergoes further churning before packaging.
On the other hand, coconut milk is derived from grated coconut flesh and is categorized as either thick or thin based on consistency. Thick coconut milk is created by boiling or simmering finely grated coconut flesh in water, followed by straining through cheesecloth. Thin coconut milk is produced by simmering the remaining grated coconut in water and repeating the straining process.
Taste and Use
With its rich and creamy flavor, butter imparts a classic, savory richness to various dishes. Its versatility shines through in baking, sautéing, frying, and as a finishing touch, enhancing sweet and savory creations. On the other hand, coconut milk introduces a tropical and slightly sweet coconut essence, contributing a creamy texture to various recipes. Widely used in Asian and tropical cuisines, coconut milk serves as a dairy-free alternative in vegan and lactose-free diets. Thick coconut milk finds its place in desserts and robust sauces, while the thinner variant elevates the flavors of soups and lighter dishes.
Sources
- https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/19259609/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/12716665/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/22208554/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/22208554/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/20071648/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/19259609/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/19457271/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/20372173/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/8561067/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/34354403/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/23680079/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/22527352/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/20645831/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/1612357/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/11989838/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/11110851/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/19266226/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/16475675/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5601385/
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2987573/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/21038926/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/23012422/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2531072/
Infographic
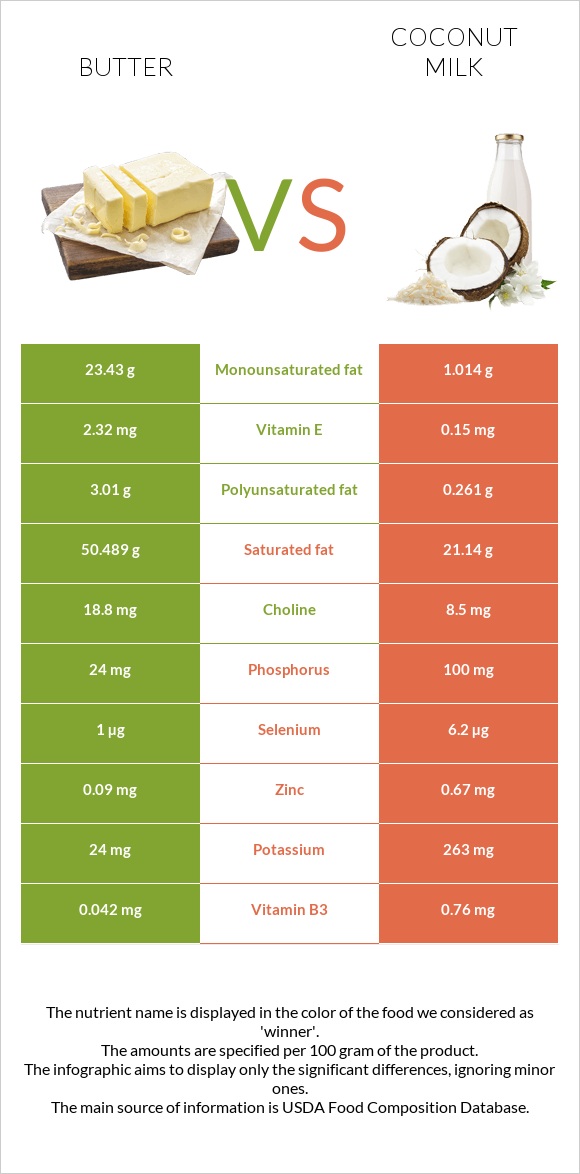
All nutrients comparison - raw data values
| Nutrient |  |
 |
DV% diff. |
| Saturated fat | 50.489g | 21.14g | 133% |
| Fats | 81.11g | 23.84g | 88% |
| Vitamin A | 684µg | 0µg | 76% |
| Cholesterol | 215mg | 0mg | 72% |
| Monounsaturated fat | 23.43g | 1.014g | 56% |
| Manganese | 0.004mg | 0.916mg | 40% |
| Copper | 0.016mg | 0.266mg | 28% |
| Calories | 717kcal | 230kcal | 24% |
| Iron | 0.02mg | 1.64mg | 20% |
| Polyunsaturated fat | 3.01g | 0.261g | 18% |
| Vitamin E | 2.32mg | 0.15mg | 14% |
| Phosphorus | 24mg | 100mg | 11% |
| Fiber | 0g | 2.2g | 9% |
| Selenium | 1µg | 6.2µg | 9% |
| Magnesium | 2mg | 37mg | 8% |
| Potassium | 24mg | 263mg | 7% |
| Vitamin B12 | 0.17µg | 0µg | 7% |
| Vitamin K | 7µg | 0.1µg | 6% |
| Zinc | 0.09mg | 0.67mg | 5% |
| Vitamin B3 | 0.042mg | 0.76mg | 4% |
| Protein | 0.85g | 2.29g | 3% |
| Vitamin C | 0mg | 2.8mg | 3% |
| Vitamin B2 | 0.034mg | 0mg | 3% |
| Folate | 3µg | 16µg | 3% |
| Carbs | 0.06g | 5.54g | 2% |
| Vitamin B1 | 0.005mg | 0.026mg | 2% |
| Vitamin B6 | 0.003mg | 0.033mg | 2% |
| Choline | 18.8mg | 8.5mg | 2% |
| Calcium | 24mg | 16mg | 1% |
| Vitamin B5 | 0.11mg | 0.183mg | 1% |
| Net carbs | 0.06g | 3.34g | N/A |
| Sugar | 0.06g | 3.34g | N/A |
| Sodium | 11mg | 15mg | 0% |
| Tryptophan | 0.012mg | 0.027mg | 0% |
| Threonine | 0.038mg | 0.083mg | 0% |
| Isoleucine | 0.051mg | 0.09mg | 0% |
| Leucine | 0.083mg | 0.17mg | 0% |
| Lysine | 0.067mg | 0.101mg | 0% |
| Methionine | 0.021mg | 0.043mg | 0% |
| Phenylalanine | 0.041mg | 0.116mg | 0% |
| Valine | 0.057mg | 0.139mg | 0% |
| Histidine | 0.023mg | 0.053mg | 0% |
| Omega-3 - ALA | 0.315g | N/A | |
| Omega-6 - Linoleic acid | 2.166g | N/A |
People also compare
References
All the values for which the sources are not specified explicitly are taken from FDA’s Food Central. The exact link to the food presented on this page can be found below.
- Butter - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/173430/nutrients
- Coconut milk - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/170172/nutrients
All the Daily Values are presented for males aged 31-50, for 2000-calorie diets.





