Canola oil vs. Peanut oil — Health Impact and Nutrition Comparison


Summary
Canola oil is a cheaper and more neutral-tasting oil richer in monounsaturated fats, vitamins E and K. in comparison, peanut oil has a stronger flavor and a higher smoke point and is richer in polyunsaturated fats. They are hydrogenated oils that are linked with inflammation.
Introduction
This article compares two types of oils; canola oil and peanut oil. These oils are vegetable seed oils, canola oil is derived from rapeseeds, and peanut oil is derived from the peanut nut itself.
We will compare general aspects of these oils, such as their taste and smoke point. In addition, we will compare their nutritional content and health impacts.
General aspects
Taste
Peanut oil has a stronger flavor and is "nuttier," while canola oil has a more neutral flavor.
When used in cooking and frying, peanut oils' nutty flavor can be overwhelming.
Price
Canola oil is a cheaper oil in comparison to peanut oil.
Smoke point
They are high smoke-point oils; however, peanut oil has a higher smoke point.
Canola oil has a smoke point of 204°C. In comparison, peanut oil has a higher smoke point that is 232°C.
Both these oils can be used in high-temperature cooking and frying.
Nutritional content comparison
In this section, we will compare 100g of each oil.
Calories
Their caloric content is 884 calories. They are high in calories.
Carbs and proteins
Their carb and protein contents are negligible.
Fats
They are made of 100% fat. However, there is a difference between their fat compositions. Below we can visualize their fat distributions.
Their fat composition is mostly monounsaturated fats.
Canola oil is richer in monounsaturated fats, whereas peanut oil is richer in polyunsaturated fats.
Fat Type Comparison
Contains
less
Sat. FatSaturated fat
-56.4%
Contains
more
Mono. FatMonounsaturated fat
+37%
Contains
more
Poly. FatPolyunsaturated fat
+13.7%
Minerals
Their mineral profile is negligible.
Vitamins
Canola oil is richer in vitamins E and K. Although it is important to mention that peanut oil is also a rich source of vitamin E.
Vitamin Comparison
Contains
more
Vitamin EVitamin E
+11.3%
Contains
more
Vitamin KVitamin K
+10085.7%
Health impacts
Vitamin E
Canola oil is a good source of vitamin E. Vitamin E has positive health impacts. (1)
Vitamin E has antioxidative and anticarcinogenic properties. In addition, vitamin E has immune-boosting functions.
Another great source of vitamin E is sunflower oil. You can read in detail about sunflower oil vs. canola oil in this article.
Cardiovascular health
Atherosclerosis is one of the most important factors that contribute to cardiovascular mortality. High levels of lipids in the blood are one of several risk factors for atherosclerosis. These oils primarily comprise polyunsaturated and monounsaturated fats, which relatively reduce the risk of atherosclerosis. Thus, incorporating canola or peanut oil in moderation does not increase the risk of atherosclerosis when compared to saturated fat-rich oils. (2)(3)
Metabolic health
An increased risk of metabolic diseases and obesity are linked with the consumption of canola oil and especially high-temperature fried canola oil. Although we mentioned above that there is less risk of cardiovascular diseases in comparison to saturated fats, however, overall, it does not decrease the risks of cardiovascular diseases. On the contrary, it increases risks, specifically when fried at higher temperatures. (4)
Infographic
Mineral Comparison
All nutrients comparison - raw data values
| Nutrient |  |
 |
DV% diff. |
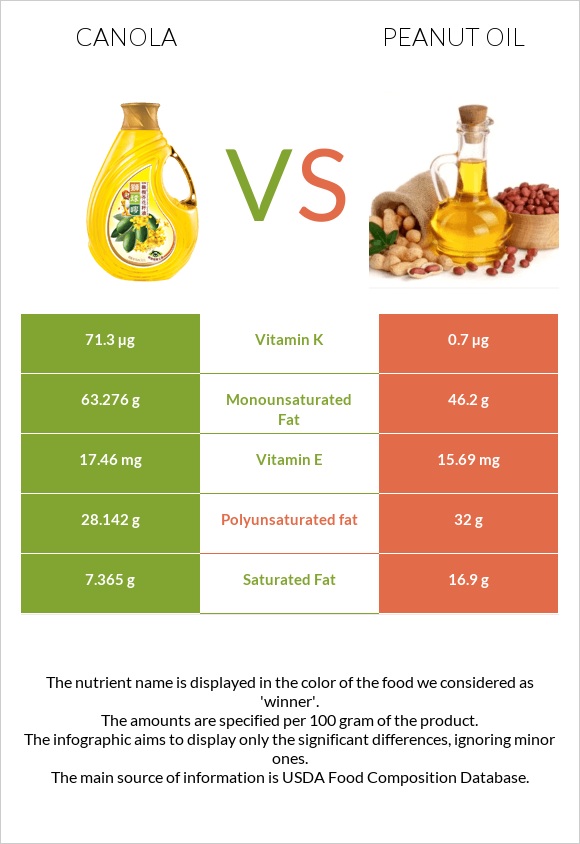
| Vitamin K | 71.3µg | 0.7µg | 59% |
| Saturated fat | 7.365g | 16.9g | 43% |
| Monounsaturated fat | 63.276g | 46.2g | 43% |
| Polyunsaturated fat | 28.142g | 32g | 26% |
| Vitamin E | 17.46mg | 15.69mg | 12% |
| Calories | 884kcal | 884kcal | 0% |
| Fats | 100g | 100g | 0% |
| Iron | 0mg | 0.03mg | 0% |
| Zinc | 0mg | 0.01mg | 0% |
| Trans fat | 0.395g | N/A | |
| Choline | 0.2mg | 0.1mg | 0% |
| Omega-3 - ALA | 9.137g | N/A | |
| Omega-6 - Linoleic acid | 18.64g | N/A |
Macronutrient Comparison
People also compare
References
All the values for which the sources are not specified explicitly are taken from FDA’s Food Central. The exact link to the food presented on this page can be found below.
- Canola oil - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/172336/nutrients
- Peanut oil - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/171410/nutrients
All the Daily Values are presented for males aged 31-50, for 2000-calorie diets.





