Cream cheese vs. Butter — Health Impact and Nutrition Comparison


Summary
Butter is higher in calories, fats, and specifically saturated fats. It is richer in vitamins A, E, and K and lower in sodium. On the other hand, cream cheese is richer in protein, phosphorus, calcium, zinc, and B complex vitamins.
Introduction
Butter is made by churning milk or cream. It is semisolid at room temperature and may be used as a spread. In refrigerated forms, it is solid.
Since the agricultural ages, butter has been a part of the human diet with the domestication of animals. It is possible that butter was made from sheep's milk; nonetheless, cow's milk is today the most prevalent source of butter.
Cream cheese is a processed cheese obtained from processing milk with fermenting bacteria that coagulates milk. Cream cheese relatively retains water which gives it a creamy, spreadable texture.
On the other hand, cream cheese is a relatively more recent dairy food than butter. It was mainly popularized in the 19th century. Again it is nowadays mostly done with cow’s milk.
This article will discuss the difference between butter and cream cheese-based on their general differences, nutritional content comparison, and health impacts.
General differences
The general differences between butter and cream cheese are shelf life, texture, and flavor.
Shelf life
Butter has a longer shelf life than cream cheese, noting that both require refrigeration.
Texture and flavor
Butter has a flavor that is richer and fattier than cream cheese. They are both spreadable, but butter at refrigerated temperature is more solid.
Cream cheese has a lighter flavor.
Nutritional content comparison
Calories
Butter is twice as higher in calories as compared to cream cheese. The difference is very significant as 100g of butter contains 717 calories, whereas, in cream cheese, it is 350 calories.
Carbs
Butter contains negligible amounts of carbs. It is mostly fat. Cream cheese contains 5.5g of carbs per 100g. Butter contains fewer carbs than cream cheese; it has negligible carbs.
Glycemic index
They both contain glycemic indices equal to 0.
Proteins
Cream cheese contains higher amounts of protein than butter. The protein content of butter is almost negligible.
Fats
Butter is mainly composed of fats. 81g out of 100g of butter is fat. 34g out of 100g of cream cheese is fat. The difference between the fat distribution is of great importance.
Saturated fats are among the highest components of both these foods.
However, butter contains much higher amounts of saturated fats than cream cheese. Nearly 51% of butter is saturated fats.
In addition to that, butter is richer in monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fats.
Minerals
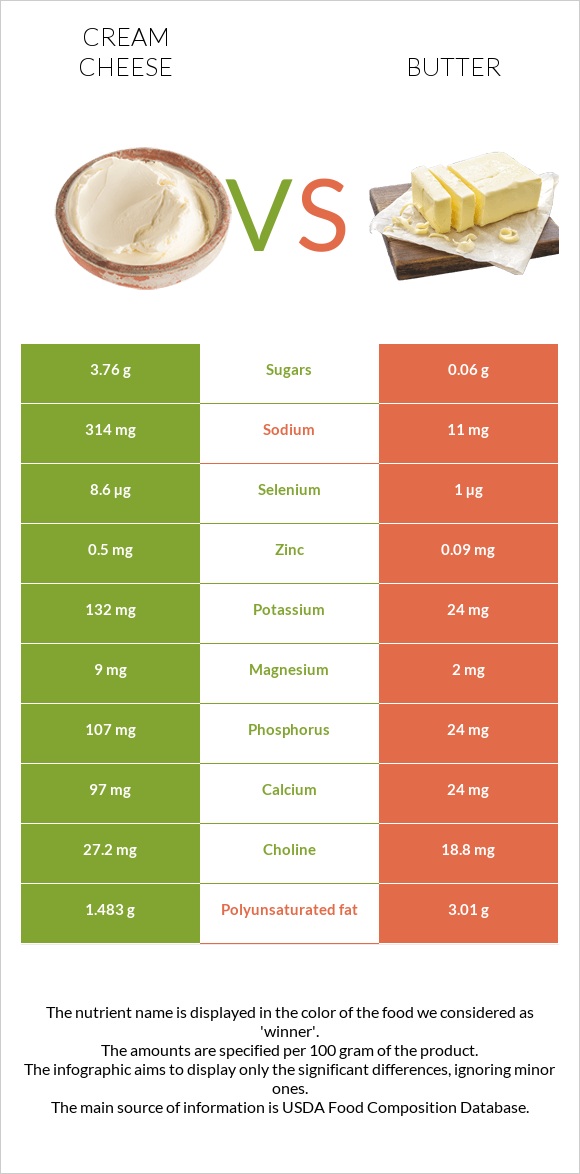
The mineral profile of cream cheese is richer and more versatile than butter.
Cream cheese is richer in all minerals; however, the remarkable minerals are phosphorus, calcium, and zinc.
Important to note that butter is lower in sodium.
Below is the mineral distribution chart that displays the mineral distributions.
Mineral Comparison
Contains
more
MagnesiumMagnesium
+350%
Contains
more
CalciumCalcium
+304.2%
Contains
more
PotassiumPotassium
+450%
Contains
more
IronIron
+450%
Contains
more
CopperCopper
+12.5%
Contains
more
ZincZinc
+455.6%
Contains
more
PhosphorusPhosphorus
+345.8%
Contains
more
ManganeseManganese
+175%
Contains
more
SeleniumSelenium
+760%
Contains
less
SodiumSodium
-96.5%
Vitamins
Butter is richer in vitamins A, E, and K, whereas cream cheese is richer in the most vitamin B complex.
In the following chart, we can see the vitamin distribution.
Vitamin Comparison
Contains
more
Vitamin B1Vitamin B1
+360%
Contains
more
Vitamin B2Vitamin B2
+576.5%
Contains
more
Vitamin B3Vitamin B3
+116.7%
Contains
more
Vitamin B5Vitamin B5
+370%
Contains
more
Vitamin B6Vitamin B6
+1766.7%
Contains
more
Vitamin B12Vitamin B12
+29.4%
Contains
more
FolateFolate
+200%
Contains
more
Vitamin AVitamin A
+122.1%
Contains
more
Vitamin EVitamin E
+169.8%
Contains
more
Vitamin KVitamin K
+233.3%
Health impacts
Keto diet
Butter and cream cheese are suitable for the keto diet. However, butter is ideal because it contains negligible carbs and a glycemic index of 0.
Vegan diet
Butter and cream cheese are dairy products that cannot be consumed in the vegan diet.
What are the positive and negative effects of butter on overall health?
Butter has its negative and positive points on health.
Positive effects of butter
Butter contains conjugated linoleic acid, which reduces weight and pro-inflammatory proteins and cytokines in the body. (1) (2) (3)
Butter also contains butyrate, which has beneficial effects on the digestive system, reducing the symptoms of IBS (irritable bowel syndrome). Butyrate in butter has also been shown to control blood glucose levels and insulin intolerance positively. (4) (5)
Consumption of butter in low to moderate amounts has positive effects. The same effects become inverted if we consume butter in high amounts. Butter reduces the risks of obesity, cardiovascular diseases, and strokes when consumed in low to moderate amounts. About high amount of consumption, we discuss it in the below section. (6) (7) (8)
Negative effects of butter
Frequent and high consumption of butter daily is linked with increased LDL levels, which increases the risks of cardiovascular diseases. (9)
Since butter is high in calories, it will lead to weight gain and other metabolic problems if eaten at uncontrolled and unmoderated levels. Thus it is crucial to keep track of the intake of calories.
What are the effects of cream cheese on overall health?
Positive effects
Cream cheese has positive effects on the digestive tract. It contains probiotic lactobacilli that help improve gut microbiota. In turn, there are positive effects on overall health. (10)
Cream cheese is low in lactose and thus can be consumed in minimal amounts by lactose-intolerant individuals. (11)
Negative effects
Lactose-intolerant people who consume too much cream cheese will have bloating and diarrhea. (12)
Cream cheese is processed cheese, and most cream cheese available in the markets is processed and has preservatives added to them. Consuming these cheese might have adverse side effects on overall health. In addition, cream cheese is packed with saturated fats, relatively lower than butter. Still, if not monitored, it will cause adverse effects on the health like obesity and cardiovascular diseases. (13)
Conclusion on health impacts
Overall, butter and cream cheese have positive and negative impacts.
Research mostly shows that butter or cream cheese consumption in low to moderate amounts has mostly positive effects on overall health.
The adverse effects are when unmonitored and high amounts of these foods are consumed.
References
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/15795434/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/15674307/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/26968277/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4027835/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/19366864/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/22810464/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/16267503/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/19457271/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29511019/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/23126664/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4586575/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/12018807/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5577766/
Infographic
All nutrients comparison - raw data values
| Nutrient |  |
 |
DV% diff. |
| Saturated fat | 20.213g | 50.489g | 138% |
| Fats | 34.44g | 81.11g | 72% |
| Vitamin A | 308µg | 684µg | 42% |
| Cholesterol | 101mg | 215mg | 38% |
| Monounsaturated fat | 8.907g | 23.43g | 36% |
| Calories | 350kcal | 717kcal | 18% |
| Vitamin B2 | 0.23mg | 0.034mg | 15% |
| Selenium | 8.6µg | 1µg | 14% |
| Sodium | 314mg | 11mg | 13% |
| Phosphorus | 107mg | 24mg | 12% |
| Protein | 6.15g | 0.85g | 11% |
| Vitamin E | 0.86mg | 2.32mg | 10% |
| Polyunsaturated fat | 1.483g | 3.01g | 10% |
| Vitamin B5 | 0.517mg | 0.11mg | 8% |
| Calcium | 97mg | 24mg | 7% |
| Zinc | 0.5mg | 0.09mg | 4% |
| Vitamin B6 | 0.056mg | 0.003mg | 4% |
| Vitamin K | 2.1µg | 7µg | 4% |
| Potassium | 132mg | 24mg | 3% |
| Carbs | 5.52g | 0.06g | 2% |
| Magnesium | 9mg | 2mg | 2% |
| Vitamin B1 | 0.023mg | 0.005mg | 2% |
| Vitamin B12 | 0.22µg | 0.17µg | 2% |
| Folate | 9µg | 3µg | 2% |
| Choline | 27.2mg | 18.8mg | 2% |
| Iron | 0.11mg | 0.02mg | 1% |
| Net carbs | 5.52g | 0.06g | N/A |
| Sugar | 3.76g | 0.06g | N/A |
| Copper | 0.018mg | 0.016mg | 0% |
| Starch | 0.35g | 0% | |
| Manganese | 0.011mg | 0.004mg | 0% |
| Vitamin B3 | 0.091mg | 0.042mg | 0% |
| Tryptophan | 0.069mg | 0.012mg | 0% |
| Threonine | 0.233mg | 0.038mg | 0% |
| Isoleucine | 0.324mg | 0.051mg | 0% |
| Leucine | 0.657mg | 0.083mg | 0% |
| Lysine | 0.567mg | 0.067mg | 0% |
| Methionine | 0.191mg | 0.021mg | 0% |
| Phenylalanine | 0.291mg | 0.041mg | 0% |
| Valine | 0.395mg | 0.057mg | 0% |
| Histidine | 0.175mg | 0.023mg | 0% |
| Omega-3 - EPA | 0.01g | 0g | N/A |
| Omega-3 - ALA | 0.125g | 0.315g | N/A |
| Omega-3 - DPA | 0.02g | 0g | N/A |
| Omega-3 - Eicosatrienoic acid | 0.002g | N/A | |
| Omega-6 - Gamma-linoleic acid | 0.002g | N/A | |
| Omega-6 - Dihomo-gamma-linoleic acid | 0.036g | N/A | |
| Omega-6 - Eicosadienoic acid | 0.007g | N/A | |
| Omega-6 - Linoleic acid | 0.807g | 2.166g | N/A |
Macronutrient Comparison
| Contains more ProteinProtein | +623.5% |
| Contains more CarbsCarbs | +9100% |
| Contains more WaterWater | +193.3% |
| Contains more OtherOther | +3075% |
| Contains more FatsFats | +135.5% |
Fat Type Comparison
| Contains less Sat. FatSaturated fat | -60% |
| Contains more Mono. FatMonounsaturated fat | +163.1% |
| Contains more Poly. FatPolyunsaturated fat | +103% |
People also compare
References
All the values for which the sources are not specified explicitly are taken from FDA’s Food Central. The exact link to the food presented on this page can be found below.
- Cream cheese - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/173418/nutrients
- Butter - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/173430/nutrients
All the Daily Values are presented for males aged 31-50, for 2000-calorie diets.






