Cream cheese vs. Ricotta — Health Impact and Nutrition Comparison


Summary
Ricotta is richer in proteins, selenium, calcium, zinc, phosphorus, and vitamin B12. Cream cheese is higher in calories, fat, saturated fats, and sodium. Cream cheese is richer in vitamins B2, B5, A, and E.
Introduction
This article compares two types of dairy products: ricotta and cream cheese. We will discuss their differences according to their general aspects, nutritional content, and health impacts.
General aspects
Ricotta is prepared from leftovers of cheese making by reheating and acidifying the whey product. In comparison, cream cheese is directly prepared from milk.
Ricotta is less creamy and has a granular texture compared to cream cheese; however, it has a slightly sweeter taste. On the other hand, cream cheese has a creamier texture than ricotta and has a saltier taste.
Nutritional content comparison
In this section, we are taking into consideration 100g of each.
Calories
Cream cheese contains double the number of calories compared to ricotta. There are 350 calories in 100g of cream cheese.
Carbs
Cream cheese is higher in carbohydrates than ricotta.
Fats
Cream cheese contains higher amounts of fats compared to ricotta. There is nearly 35g of fat in cream cheese compared to 13g in ricotta.
Saturated fats
Cream cheese contains 2.5 times more saturated fats than ricotta. This difference is significant. Cream cheese contains 20g of saturated fats.
Fat Type Comparison
Contains
more
Mono. FatMonounsaturated fat
+145.6%
Contains
more
Poly. FatPolyunsaturated fat
+285.2%
Contains
less
Sat. FatSaturated fat
-59%
Proteins
Ricotta contains double the amount of protein compared to cream cheese. There are nearly 12g of protein per 100g of ricotta.
Macronutrient Comparison
Contains
more
FatsFats
+165.3%
Contains
more
CarbsCarbs
+81.6%
Contains
more
OtherOther
+24.5%
Contains
more
ProteinProtein
+83.1%
Contains
more
WaterWater
+36.3%
Minerals
Ricotta is richer in selenium, calcium, zinc, and phosphorus. In comparison, cream cheese is high in sodium.
In the visual diagram below, we can visualize the difference in their mineral distributions.
Mineral Comparison
Contains
more
PotassiumPotassium
+25.7%
Contains
more
ManganeseManganese
+83.3%
Contains
more
MagnesiumMagnesium
+22.2%
Contains
more
CalciumCalcium
+113.4%
Contains
more
IronIron
+245.5%
Contains
more
CopperCopper
+16.7%
Contains
more
ZincZinc
+132%
Contains
more
PhosphorusPhosphorus
+47.7%
Contains
less
SodiumSodium
-73.2%
Contains
more
SeleniumSelenium
+68.6%
Vitamins
Ricotta is richer in vitamin B12. Cream cheese is richer in vitamins B2, B5, A, and E.
In the visual diagram below, we can visualize the difference in their vitamin distributions.
Vitamin Comparison
Contains
more
Vitamin AVitamin A
+156.7%
Contains
more
Vitamin EVitamin E
+681.8%
Contains
more
Vitamin B1Vitamin B1
+76.9%
Contains
more
Vitamin B2Vitamin B2
+17.9%
Contains
more
Vitamin B5Vitamin B5
+142.7%
Contains
more
Vitamin B6Vitamin B6
+30.2%
Contains
more
Vitamin KVitamin K
+90.9%
Contains
more
Vitamin DVitamin D
+∞%
Contains
more
Vitamin B3Vitamin B3
+14.3%
Contains
more
Vitamin B12Vitamin B12
+54.5%
Contains
more
FolateFolate
+33.3%
Health impacts
Both dairy products share common health impacts; however, this section will focus on the different health impacts
Cardiovascular health
Cream cheese is high in saturated fats and cholesterol, which have been linked to an increased risk of cardiovascular disease. Excessive consumption of saturated fats, like those found in cream cheese, can elevate LDL (bad cholesterol) levels, a key contributor to atherosclerosis and heart disease. In contrast, ricotta cheese, especially the low-fat variety, contains less saturated fat than cream cheese (1).
Both the Heart Association and the European Society of Cardiology recommend limiting saturated fat intake and opting for low-fat dairy products (2).
Additionally, cheese has a high level of conjugated linoleic acid, which has been associated with lower blood pressure in rats and may influence the progression of atherosclerosis in rabbits. However, more research is needed to better understand these effects in humans (2).
In summary, studies suggest that ricotta, particularly the low-fat version, is a healthier choice than cream cheese for reducing the risk of cardiovascular disease.
Antioxidant
Ricotta is richer in selenium, which has anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties. Selenium maintains a healthy immune system. (3)
Cream cheese is richer in vitamin E, which also provides antioxidant properties. (4)
Cancer
Calcium-rich foods, in this case, ricotta, are associated with increased risks of prostate cancer in males. It is essential to keep dairy consumption to moderate amounts. (5)
Infographic
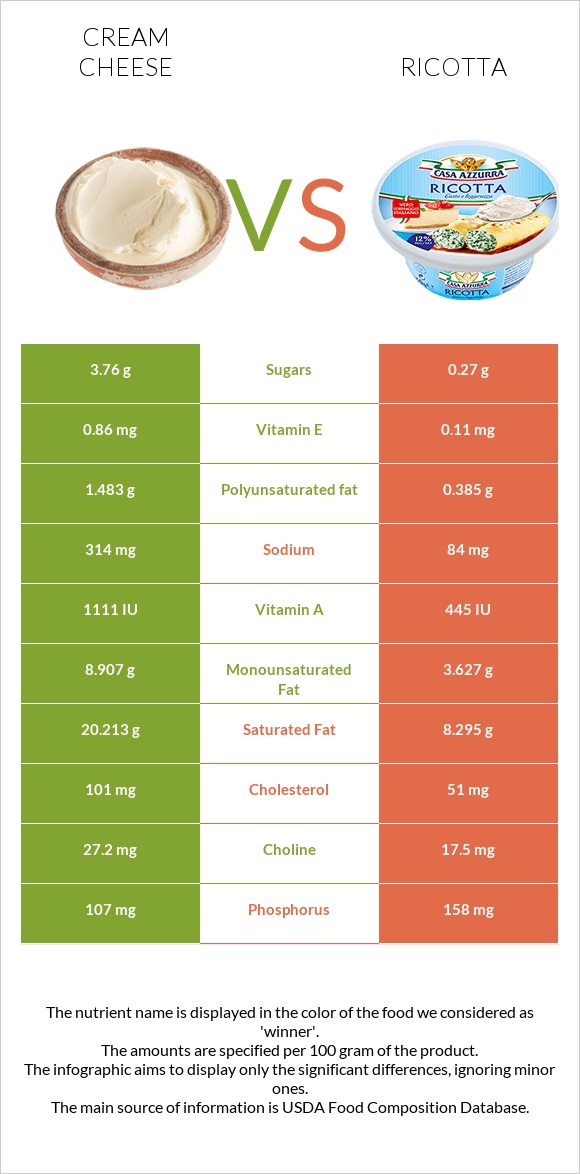
All nutrients comparison - raw data values
| Nutrient |  |
 |
DV% diff. |
| Saturated fat | 20.213g | 8.295g | 54% |
| Fats | 34.44g | 12.98g | 33% |
| Vitamin A | 308µg | 120µg | 21% |
| Cholesterol | 101mg | 51mg | 17% |
| Monounsaturated fat | 8.907g | 3.627g | 13% |
| Calcium | 97mg | 207mg | 11% |
| Selenium | 8.6µg | 14.5µg | 11% |
| Protein | 6.15g | 11.26g | 10% |
| Sodium | 314mg | 84mg | 10% |
| Calories | 350kcal | 174kcal | 9% |
| Phosphorus | 107mg | 158mg | 7% |
| Polyunsaturated fat | 1.483g | 0.385g | 7% |
| Zinc | 0.5mg | 1.16mg | 6% |
| Vitamin B5 | 0.517mg | 0.213mg | 6% |
| Vitamin E | 0.86mg | 0.11mg | 5% |
| Vitamin B12 | 0.22µg | 0.34µg | 5% |
| Iron | 0.11mg | 0.38mg | 3% |
| Vitamin B2 | 0.23mg | 0.195mg | 3% |
| Choline | 27.2mg | 17.5mg | 2% |
| Carbs | 5.52g | 3.04g | 1% |
| Vitamin D | 0 IU | 10 IU | 1% |
| Potassium | 132mg | 105mg | 1% |
| Vitamin D | 0µg | 0.2µg | 1% |
| Vitamin B1 | 0.023mg | 0.013mg | 1% |
| Vitamin B6 | 0.056mg | 0.043mg | 1% |
| Vitamin K | 2.1µg | 1.1µg | 1% |
| Folate | 9µg | 12µg | 1% |
| Protein per 100 calories | 1.7571428571428571g | 6.471264367816092g | N/A |
| Calories per 10 g protein | 569.1056910569106kcal | 154.52930728241563kcal | N/A |
| Net carbs | 5.52g | 3.04g | N/A |
| Magnesium | 9mg | 11mg | 0% |
| Sugar | 3.76g | 0.27g | N/A |
| Copper | 0.018mg | 0.021mg | 0% |
| Starch | 0.35g | 0% | |
| Manganese | 0.011mg | 0.006mg | 0% |
| Vitamin B3 | 0.091mg | 0.104mg | 0% |
| Tryptophan | 0.069mg | 0.125mg | 0% |
| Threonine | 0.233mg | 0.517mg | 0% |
| Isoleucine | 0.324mg | 0.589mg | 0% |
| Leucine | 0.657mg | 1.221mg | 0% |
| Lysine | 0.567mg | 1.338mg | 0% |
| Methionine | 0.191mg | 0.281mg | 0% |
| Phenylalanine | 0.291mg | 0.556mg | 0% |
| Valine | 0.395mg | 0.692mg | 0% |
| Histidine | 0.175mg | 0.459mg | 0% |
| Omega-3 - EPA | 0.01g | 0g | N/A |
| Omega-3 - ALA | 0.125g | N/A | |
| Omega-3 - DPA | 0.02g | 0g | N/A |
| Omega-3 - Eicosatrienoic acid | 0.002g | N/A | |
| Omega-6 - Gamma-linoleic acid | 0.002g | N/A | |
| Omega-6 - Dihomo-gamma-linoleic acid | 0.036g | N/A | |
| Omega-6 - Eicosadienoic acid | 0.007g | N/A | |
| Omega-6 - Linoleic acid | 0.807g | N/A |
People also compare
References
All the values for which the sources are not specified explicitly are taken from FDA’s Food Central. The exact link to the food presented on this page can be found below.
- Cream cheese - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/173418/nutrients
- Ricotta - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/170851/nutrients
All the Daily Values are presented for males aged 31-50, for 2000-calorie diets.