Chestnut vs Water chestnut - In-Depth Nutrition Comparison


Summary
Chestnuts have more minerals, Vitamin C, fats, calories and contain lower sugar than water chestnuts.
Water chestnuts are lower in sodium, glycemic index, and saturated fats have more fiber and Vitamin B-family.
Introduction
At first, it may seem that chestnuts and water chestnuts are the same food, but they are not. We will discover the nutritional value, differences, and similarities between chestnuts and water chestnuts.
What's The Actual Difference?
Water chestnuts and chestnuts are nothing like each other. The only thing they share is the name, and here their similarities end. Water chestnuts, also known as Chinese water chestnuts, are aquatic vegetables that grow in marshes, ponds, and lakes. On the other hand, chestnuts are tree nuts that have eight or nine species of trees and shrubs.
Nutrition
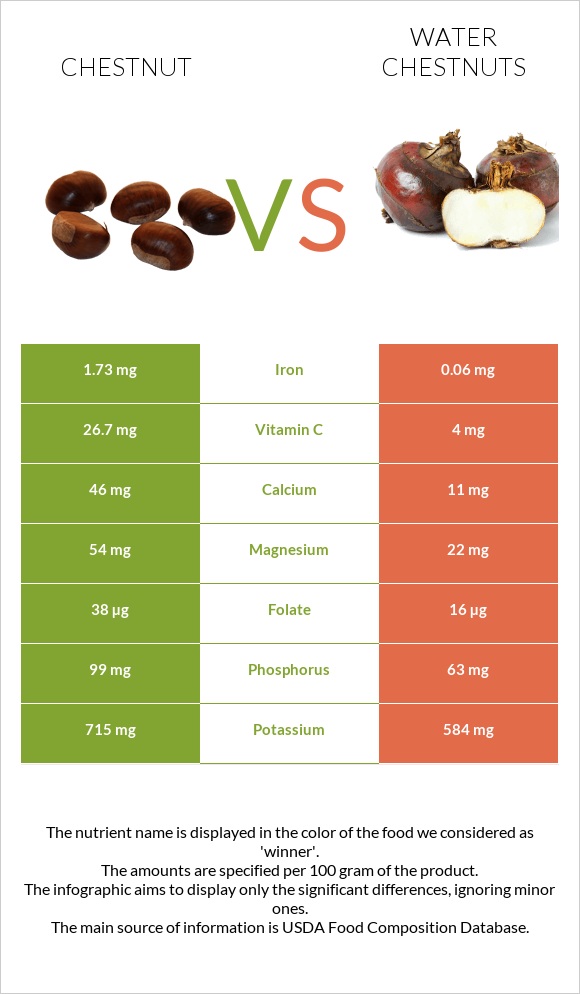
You can find nutritional infographics at the bottom of this page that visually show the differences between chestnut and water chestnut.
The food varieties used in this article are raw Chinese water chestnut and boiled and streamed European chestnut.
Fats
Both water chestnuts and chestnuts have a tiny amount of fat. However, the fat content of chestnuts is higher in comparison with water chestnuts.
It has 1.38g overall fat per 100g, whereas water chestnuts have 0.1g per 100g. As you can see, this number differs a bit.
Both have no trans fats, which make them suitable in the case of diets.
Calories
The number of calories in chestnuts is higher than in water chestnuts. But here again, the difference is very little.
Chestnuts have 131 kcal per 100g, whereas water chestnuts contain 97 kcal per 100g. Both are suitable for low-calorie diets.
Carbs
Chestnut contains more carbs than water chestnuts. It has 26.76 g carbs in 100g, while water chestnuts have 23.94g.
The total carbs number of these two foods is almost the same, but they differ by the number of net carbs.
All carbs in chestnuts are net carbs, whereas water chestnuts have 20.94 g net carbs and 3g dietary fiber per 100g.
Cholesterol
Chestnuts and water chestnuts have no cholesterol.
Minerals
When it comes to the minerals content, chestnuts have a relatively high number.
In particular, chestnuts have iron, calcium, magnesium, potassium, phosphorus, and copper than water chestnuts. Moreover, it contains four times more calcium. Important notes, chestnuts fall in the range of 8% of foods as a source of potassium. These nuts can cover your daily potassium intake by 20%.
On the other hand, water chestnuts contain more zinc and less sodium than chestnuts.
Mineral Comparison
Contains
more
MagnesiumMagnesium
+145.5%
Contains
more
CalciumCalcium
+318.2%
Contains
more
PotassiumPotassium
+22.4%
Contains
more
IronIron
+2783.3%
Contains
more
CopperCopper
+44.8%
Contains
more
PhosphorusPhosphorus
+57.1%
Contains
more
ManganeseManganese
+158%
Contains
more
ZincZinc
+100%
Contains
less
SodiumSodium
-48.1%
Vitamins
Both water chestnuts and chestnuts have a moderate amount of vitamins.
For instance, water chestnuts have a higher number of Vitamin B2, Vitamin B3, Vitamin B5, and Vitamin B6.
On the other hand, chestnuts are higher in Vitamin C, Vitamin A, and folate.
Chestnuts have almost seven times more Vitamin C, covering your daily need 25% more than water chestnuts.
Both lack Vitamin B12 and Vitamin D.
Vitamin Comparison
Contains
more
Vitamin CVitamin C
+567.5%
Contains
more
Vitamin AVitamin A
+∞%
Contains
more
FolateFolate
+137.5%
Contains
more
Vitamin B2Vitamin B2
+92.3%
Contains
more
Vitamin B3Vitamin B3
+36.8%
Contains
more
Vitamin B5Vitamin B5
+51.6%
Contains
more
Vitamin B6Vitamin B6
+40.8%
Weight Loss
Since both chestnuts and water chestnuts are low in calories, fats, and carbs, they may be suitable for low-calorie, low-fat, and low-carb diets. They also may be added to your list of recommended foods in the case of DASH, Atkins, Mediterranean, and Paleo diets.
Health Benefits
This section of the article will discover the health impact of water chestnuts and chestnuts, the benefits, and the downsides of their consumption.
Phenolics
Both chestnuts and water chestnuts have a high total phenolic content, including free and bound phenolics.
Tidal phenols in chestnuts include anthocyanins, flavonoids, proanthocyanidins, and isoflavones. These substances have potent antioxidant properties [1].
Water chestnuts' main phenolic compounds are gallocatechin gallate, epicatechin gallate, and catechin gallate. They also have trace amounts of anthocyanins, proanthocyanidins, and isoflavones [2].
Cardiovascular Health
Both water chestnuts and chestnuts contain antioxidants that may help reduce the risk of cardiovascular problems. According to research, the flavonoids found in these foods may help protect the heart from oxidative stress linked to strokes and heart disease [1]. Because of their high mineral and chemical content, water chestnuts have been used to treat risk factors such as high blood pressure.
Gallic acid and ellagic acid, both found in water chestnuts, have been shown in studies to help protect the heart against oxidative stress linked to heart disease [2].
Moreover, chestnuts are high in potassium, which aids in the maintenance of the heart by allowing electricity to flow freely throughout the body. One study found that eating a potassium-rich diet can reduce the risk of heart disease by 27% and strokes by 24% [4].
Cancer
Water chestnuts and chestnuts are high in flavonoids and phenolic compounds, with antioxidant properties.
Water chestnuts, in particular, are high in gallocatechin gallate, epicatechin gallate, and catechin gallate. These compounds possess potent antioxidant properties and have been shown to protect against free radical-related diseases such as cancer. They also contain anthocyanins and isoflavones, which may aid in the prevention of oxidative stress-related diseases. A malignant tumor is the world's second leading cause of death. The mechanisms of the anti-tumor effect are linked to the direct killing of cancer cells or the stimulation of the immune system to fight the tumor. According to the study, water chestnut extract has therapeutic potential for breast, colon, pancreatic, prostate, oral, and kidney cancers [1] [5].
On the other hand, chestnuts have anti-cancer properties as well. According to research, chestnuts may be able to cure stomach cancer. Furthermore, these nuts contain a lot of Vitamin C, which has anti-cancer properties. Chestnuts may be beneficial in treating stomach cancer and epistaxis, according to one study [6].
Boost Immune System
Chestnuts are an excellent immune system booster due to their high concentration of Vitamin C and other antioxidant compounds and trace minerals like copper. According to research, Vitamin C may aid in the recovery of people suffering from the common cold.
Vitamin C increases the production of white blood cells and acts as an antioxidant, lowering the risk of free radical formation and neutralizing them before they mutate healthy cells or cause oxidative stress near vital organs. This can help the immune system focus its pathogens and disease prevention efforts [6].
Anti-inflammatory effects
Water chestnuts contain " puchiin " compound with potent anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties. Puchiin has been known for a long time and is considered the second plant-derived antibacterial substance after penicillin. Puchiins' antibacterial properties and functions are similar to penicillin in boosting immune function [5].
Other Health Benefits
Chestnuts are rich in magnesium. They are found in approximately 21% of foods as a source of magnesium. Research suggests that migraine sufferers may have low magnesium levels. Several studies have shown magnesium supplements to help prevent and treat migraine headaches [7].
Downsides and Risks
Allergy
The allergen responsible for the reaction in cases of chestnut allergy is most likely one of the lipid transfer proteins. Thirty percent of chestnut-allergic patients experience severe anaphylactic reactions when exposed to the allergen. Chesnut allergy may include wheezing, throat swelling, and difficulty breathing [8].
Because water chestnut is not a nut, there have been no reports of allergic people to water chestnuts. Consult your doctor if you experience food allergy symptoms such as itching or swelling around your mouth after eating water, chestnuts, or other food.
Taste and Culinary
Rather than another type of nut, chestnuts have a slightly sweet flavor similar to sweet potato. You can use chestnuts in desserts, baking, chocolate truffles, salads, and stuffing with cranberries or apples.
Water chestnuts are typically sweet, nutty, and tart all at the same time. You can eat water chestnuts raw, boiled, fried, grilled, pickled, or candied.
References
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/33532353/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31906347/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3133749/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/23674806/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/27603811/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/25307916/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31691193/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7811165/
Infographic
All nutrients comparison - raw data values
| Nutrient |  |
 |
DV% diff. |
| Vitamin C | 26.7mg | 4mg | 25% |
| Manganese | 0.854mg | 0.331mg | 23% |
| Iron | 1.73mg | 0.06mg | 21% |
| Copper | 0.472mg | 0.326mg | 16% |
| Fiber | 3g | 12% | |
| Magnesium | 54mg | 22mg | 8% |
| Vitamin E | 1.2mg | 8% | |
| Vitamin B2 | 0.104mg | 0.2mg | 7% |
| Vitamin B6 | 0.233mg | 0.328mg | 7% |
| Choline | 36.2mg | 7% | |
| Folate | 38µg | 16µg | 6% |
| Phosphorus | 99mg | 63mg | 5% |
| Calcium | 46mg | 11mg | 4% |
| Potassium | 715mg | 584mg | 4% |
| Vitamin B5 | 0.316mg | 0.479mg | 3% |
| Polyunsaturated fat | 0.545g | 0.043g | 3% |
| Calories | 131kcal | 97kcal | 2% |
| Fats | 1.38g | 0.1g | 2% |
| Zinc | 0.25mg | 0.5mg | 2% |
| Vitamin B3 | 0.731mg | 1mg | 2% |
| Protein | 2g | 1.4g | 1% |
| Carbs | 27.76g | 23.94g | 1% |
| Sodium | 27mg | 14mg | 1% |
| Selenium | 0.7µg | 1% | |
| Vitamin B1 | 0.148mg | 0.14mg | 1% |
| Saturated fat | 0.26g | 0.026g | 1% |
| Monounsaturated fat | 0.476g | 0.002g | 1% |
| Net carbs | 27.76g | 20.94g | N/A |
| Sugar | 4.8g | N/A | |
| Vitamin A | 1µg | 0µg | 0% |
| Vitamin K | 0.3µg | 0% | |
| Tryptophan | 0.022mg | 0% | |
| Threonine | 0.071mg | 0% | |
| Isoleucine | 0.079mg | 0% | |
| Leucine | 0.118mg | 0% | |
| Lysine | 0.118mg | 0% | |
| Methionine | 0.047mg | 0% | |
| Phenylalanine | 0.084mg | 0% | |
| Valine | 0.112mg | 0% | |
| Histidine | 0.055mg | 0% |
Macronutrient Comparison
| Contains more ProteinProtein | +42.9% |
| Contains more FatsFats | +1280% |
| Contains more CarbsCarbs | +16% |
| Contains more OtherOther | +54.9% |
Fat Type Comparison
| Contains more Mono. FatMonounsaturated fat | +23700% |
| Contains more Poly. FatPolyunsaturated fat | +1167.4% |
| Contains less Sat. FatSaturated fat | -90% |
People also compare
References
All the values for which the sources are not specified explicitly are taken from FDA’s Food Central. The exact link to the food presented on this page can be found below.
- Chestnut - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/170168/nutrients
- Water chestnuts - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/170066/nutrients
All the Daily Values are presented for males aged 31-50, for 2000-calorie diets.




